Two randomized controlled trials of nudges to encourage referrals to centralized pharmacy services for evidence-based statin initiation in high-risk patients: Rationale and design of the SUPER LIPID program
- PMID: 38679189
- PMCID: PMC11795838
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ahj.2024.04.013
Two randomized controlled trials of nudges to encourage referrals to centralized pharmacy services for evidence-based statin initiation in high-risk patients: Rationale and design of the SUPER LIPID program
Abstract
Background: In patients with or at risk for atherosclerotic vascular disease, statins reduce the incidence of major adverse cardiovascular events, but the majority of US adults with an indication for statin therapy are not prescribed statins at guideline-recommended intensity. Clinicians' limited time to address preventative care issues is cited as one factor contributing to gaps in statin prescribing. Centralized pharmacy services can fulfill a strategic role for population health management through outreach, education, and statin prescribing for patients at elevated ASCVD risk, but best practices for optimizing referrals of appropriate patients are unknown.
Study design and objectives: SUPER LIPID (NCT05537064) is a program consisting of two pragmatic clinical trials testing the effect of nudges in increasing referrals of appropriate patients to a centralized pharmacy service for lipid management, conducted within 11 primary care practices in a large community health system. In both trials, patients were eligible for inclusion if they had an assigned primary care provider (PCP) in a participating practice and were not prescribed a high- or moderate-intensity statin despite an indication, identified via an electronic health record (EHR) algorithm. Trial #1 was a stepped wedge trial, conducted at a single practice with randomization at the PCP level, of an interruptive EHR message that appeared during eligible patients' visits and facilitated referral to the pharmacy service. For the first 3 months, no PCPs received the message; for the second 3 months, half were randomly selected to receive the message; and for the last 3 months, all PCPs received the message. Trial #2 was a cluster-randomized trial conducted at 10 practices, with randomization at the practice level. Practices were randomized to usual care or to have eligible patients automatically referred to centralized pharmacy services via a referral order placed in PCPs EHR inboxes for co-signature. In both trials, when a patient was referred to centralized pharmacy services, a pharmacist reviewed the patient's chart, contacted the patient, and initiated statin therapy if the patient agreed. The primary endpoint of both trials was the proportion of patients prescribed a statin; secondary endpoints include the proportion of patients prescribed a statin at guideline-recommended intensity, the proportion of patients filling a statin prescription, and serum low-density lipoprotein level.
Conclusions: SUPER LIPID is a pair of pragmatic clinical trials assessing the effectiveness of two strategies to encourage referral of appropriate patients to a centralized pharmacy service for lipid management. The trial results will develop the evidence base for simple, scalable, EHR-based strategies to integrate clinical pharmacists into population health management and increase appropriate statin prescribing.
Clinical trial registration: clinicaltrials.gov; NCT05537064.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest Dr. Fanaroff reports a career development grant from the American Heart Association. Dr. Adusumalli is an employee of CVS Health. Dr. Volpp is a co-owner of a behavioral economics consulting firm, VAL Health and receives unrelated research funding from Independence Blue Cross and the American Heart Association. All other authors report no relevant conflicts of interest.
Figures
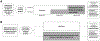
Similar articles
-
A systematic review and economic evaluation of statins for the prevention of coronary events.Health Technol Assess. 2007 Apr;11(14):1-160, iii-iv. doi: 10.3310/hta11140. Health Technol Assess. 2007. PMID: 17408535
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
Population-based interventions for reducing sexually transmitted infections, including HIV infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004;(2):CD001220. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001220.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Mar 16;(3):CD001220. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001220.pub3. PMID: 15106156 Updated.
-
Drugs for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults after general anaesthesia: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 19;10(10):CD012859. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012859.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33075160 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions for preventing and reducing the use of physical restraints of older people in general hospital settings.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Aug 25;8(8):CD012476. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012476.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36004796 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Encouraging Pharmacist Referrals for Evidence-Based Statin Initiation: Two Cluster Randomized Clinical Trials.JAMA Cardiol. 2025 May 1;10(5):473-481. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2025.0244. JAMA Cardiol. 2025. PMID: 40136263 Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Grundy SM, Stone NJ, Bailey AL, Beam C, Birtcher KK, Blumenthal RS, Braun LT, de Ferranti S, Faiella-Tommasino J, Forman DE, Goldberg R, Heidenreich PA, Hlatky MA, Jones DW, Lloyd-Jones D, Lopez-Pajares N, Ndumele CE, Orringer CE, Peralta CA, Saseen JJ, Smith SC, Sperling L, Virani SS, Yeboah J. 2018 AHA/ACC/AACVPR/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/ADA/AGS/APhA/ASPC/NLA/PCNA Guideline on the Management of Blood Cholesterol. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 2018;25709.
-
- Lowenstern A, Li S, Navar AM, Virani S, Lee LV, Louie MJ, Peterson ED, Wang TY. Does clinician-reported lipid guideline adoption translate to guideline-adherent care? An evaluation of the Patient and Provider Assessment of Lipid Management (PALM) registry. Am Heart J. 2018;200:118–124. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

