Pharmaceutical cost savings from the treatment of oncology patients in clinical trials
- PMID: 38679197
- PMCID: PMC12049827
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bj.2024.100742
Pharmaceutical cost savings from the treatment of oncology patients in clinical trials
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was twofold: to assess the annual pharmaceutical savings associated with the treatment of cancer patients at Marqués de Valdecilla University Hospital and to estimate the cost of innovative antineoplastic therapies that patients receive as experimental treatment, both during clinical trials throughout 2020.
Material and methods: An observational and financial analysis of the drug cost related to clinical trials was applied. Direct cost savings to the Regional Health System of Cantabria and the cost of innovative therapies used as an experimental treatment in clinical trials were quantified.
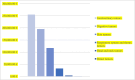
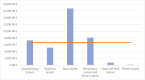
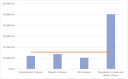
Results: This study includes 38 clinical trials with a sample of 101 patients. The clinical trials analyzed provide a total cost savings of €603,350.21 and an average cost saving of €6630.22 per patient. Furthermore, the total investment amounts to €789,892.67, with an average investment of €15,488.09 per patient.
Conclusions: Clinical trials are essential for the advancement of science. Furthermore, clinical trials can be a significant source of income for both hospitals and Regional Health Systems, contributing to their financial sustainability.
Keywords: Avoided cost; Cancer; Clinical trials; Cost saving; Drugs; Investigational medicinal product.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of Chang Gung University. This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Evaluation of drug cost savings related to clinical trials from the perspective of a university hospital.Eur J Hosp Pharm. 2024 Oct 25;31(6):520-525. doi: 10.1136/ejhpharm-2022-003671. Eur J Hosp Pharm. 2024. PMID: 37248032
-
Savings to the Colombian health system with the implementation of externally funded oncology clinical trials.Biomedica. 2025 Mar 28;45(1):51-63. doi: 10.7705/biomedica.7239. Biomedica. 2025. PMID: 40257946 Free PMC article. English, Spanish.
-
Free drugs in clinical trials and their potential cost saving impact on the National Health Service: a retrospective cost analysis in Italy.Lung Cancer. 2013 Aug;81(2):236-40. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2013.03.021. Epub 2013 May 4. Lung Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23648072
-
Interventional Pharmacoeconomics: A Novel Mechanism for Unlocking Value.Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2020 Sep;108(3):487-493. doi: 10.1002/cpt.1853. Epub 2020 May 12. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2020. PMID: 32298471 Review.
-
Financial relationships in economic analyses of targeted therapies in oncology.J Clin Oncol. 2012 Apr 20;30(12):1316-20. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2011.38.6078. Epub 2012 Mar 19. J Clin Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22430267 Review.
Cited by
-
Sacred codes: Preservation, permutation and expression.Biomed J. 2025 Apr;48(2):100852. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2025.100852. Epub 2025 Apr 4. Biomed J. 2025. PMID: 40188876 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cortegiani A, Absalom AR. Importance of proper conduct of clinical trials. Br J Anaesth. 2021;126(2):354–356. - PubMed
-
- Nasr MM, Nasr MM, Shehata LH. Clinical oncology research; Review on contemporary methodology standards. Curr Probl Cancer. 2021;45(5) - PubMed
-
- El Weber. valor del medicamento desde una perspectiva social 2021. Fundación Weber; Madrid: 2021.
-
- Sobrero A, Puccini A, Bregni G, Bruzzi P. The urgent need to improve the tools to assess clinical benefit and value of cancer treatment. Eur J Cancer. 2017;83:324–328. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

