Underground communication: Long non-coding RNA signaling in the plant rhizosphere
- PMID: 38679911
- PMCID: PMC11287177
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xplc.2024.100927
Underground communication: Long non-coding RNA signaling in the plant rhizosphere
Abstract
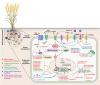
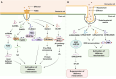
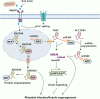
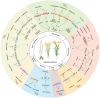
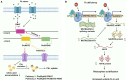
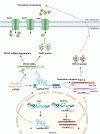
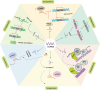
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have emerged as integral gene-expression regulators underlying plant growth, development, and adaptation. To adapt to the heterogeneous and dynamic rhizosphere, plants use interconnected regulatory mechanisms to optimally fine-tune gene-expression-governing interactions with soil biota, as well as nutrient acquisition and heavy metal tolerance. Recently, high-throughput sequencing has enabled the identification of plant lncRNAs responsive to rhizosphere biotic and abiotic cues. Here, we examine lncRNA biogenesis, classification, and mode of action, highlighting the functions of lncRNAs in mediating plant adaptation to diverse rhizosphere factors. We then discuss studies that reveal the significance and target genes of lncRNAs during developmental plasticity and stress responses at the rhizobium interface. A comprehensive understanding of specific lncRNAs, their regulatory targets, and the intricacies of their functional interaction networks will provide crucial insights into how these transcriptomic switches fine-tune responses to shifting rhizosphere signals. Looking ahead, we foresee that single-cell dissection of cell-type-specific lncRNA regulatory dynamics will enhance our understanding of the precise developmental modulation mechanisms that enable plant rhizosphere adaptation. Overcoming future challenges through multi-omics and genetic approaches will more fully reveal the integral roles of lncRNAs in governing plant adaptation to the belowground environment.
Keywords: biotic and abiotic cues; heavy metals; long non-coding RNAs; nutrients; phytoremediation; rhizosphere microbiome.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Long non-coding RNAs: emerging players regulating plant abiotic stress response and adaptation.BMC Plant Biol. 2020 Oct 12;20(1):466. doi: 10.1186/s12870-020-02595-x. BMC Plant Biol. 2020. PMID: 33046001 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Characters of Non-Coding RNAs and Their Biological Roles in Plant Development and Abiotic Stress Response.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 8;23(8):4124. doi: 10.3390/ijms23084124. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35456943 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Long Noncoding RNAs in Plant Stress Tolerance.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1631:41-68. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7136-7_3. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28735390
-
Exploring the emerging role of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in plant biology: Functions, mechanisms of action, and future directions.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2024 Jul;212:108797. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2024.108797. Epub 2024 Jun 4. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2024. PMID: 38850732 Review.
-
Long Noncoding RNAs in Response to Hyperosmolarity Stress, but Not Salt Stress, Were Mainly Enriched in the Rice Roots.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 5;25(11):6226. doi: 10.3390/ijms25116226. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38892412 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Transcriptomic Comparison of Rice lncRNAs in Response to Feeding by Brown Planthopper Populations with Different Virulence.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 8;26(8):3486. doi: 10.3390/ijms26083486. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40331941 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA gatekeepers: Orchestrating rhizospheric dynamics.J Integr Plant Biol. 2025 Mar;67(3):845-876. doi: 10.1111/jipb.13860. Epub 2025 Feb 21. J Integr Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 39981727 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

