Patients' Satisfaction After Breast Reconstruction Surgery Using Autologous versus Implants: A Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 38679979
- PMCID: PMC11162712
- DOI: 10.31557/APJCP.2024.25.4.1205
Patients' Satisfaction After Breast Reconstruction Surgery Using Autologous versus Implants: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Introduction: Breast cancer is a common disease that affects women globally and causes physical and emotional challenges. Breast reconstructive surgery aims to restore the shape of the breast after a mastectomy. Two common approaches used today are tissue-based or autologous and implant-based reconstruction. Autologous breast reconstruction has the advantage of being more affordable, but the resulting shape is less attractive. At the same time, the implant technique produces a more pleasing shape at a more expensive cost.
Objective: To compare the level of patients' satisfaction after breast reconstruction using the implant technique with the autologous technique using the Breast-Q questionnaire.
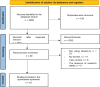
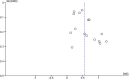
Methods: This research was a meta-analytic study to compare patients' satisfaction levels with breast reconstruction using the autologous technique compared with the implant technique. We searched several research articles from PubMed, EMBASE, and the Cochrane Library from 2014 to 2023. Then, we conducted an analysis using Revman 5.4. The results of the study were presented in a forest plot diagram.
Results: From the search results, there were 3980 studies. Then, exclusion and inclusion were carried out, and the results obtained were 16 research articles. Of the 16 studies, analysis was then carried out, and the results obtained were satisfaction in breast patients with a sample size of 7284. The standard result of the mean difference was 0.55 (95% CI 0.41-0.68) p < 0.00001. Satisfaction with the reconstruction results with a sample size of 2935. The standard result of the mean difference was 0.48 (95% CI 0.28-0.69) p < 0.00001. Patients' sexual satisfaction with a sample size of 7149. The standard result of the mean difference was 0.27 (95% CI 0.17-0.37) p < 0.00001. Patients' satisfaction with nipple shapes with a sample of 426. The standard result of the mean difference was 0.22 (95% CI -0.00-0.44) p = 0.06. Patients' satisfaction with plastic surgeons with a sample size of 272. The standard result of the mean difference was 0.52 (95% CI 0.25-0.80) p= 0.0002.
Conclusion: The autologous breast reconstruction technique is better than the implant-based reconstruction technique in terms of patient satisfaction with the breast, reconstruction outcome, sexual satisfaction, nipple shapes, and plastic surgeons based on the Breast-Q questionnaire. The findings of this comprehensive study indicate that breast cancer survivors who choose autologous reconstruction have higher levels of satisfaction across multiple domains than those who decide implant-based reconstruction.
Keywords: Autologous; Questionnaire; breast reconstruction; implant-based; patients' satisfaction.
Figures




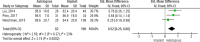
References
-
- Yarso K, Suyatmi S, Syah F, Manuaba I, Hakimi H, Astuti I, et al. Association of sdf-1 with metastasis in breast cancer patient at sanglah hospital, bali. Bali Med J. 2016;5:134.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

