Percutaneous Closure of Bilateral Pulmonary Artery Aneurysms in Behcet's Disease
- PMID: 38680129
- PMCID: PMC11047295
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaccas.2024.102341
Percutaneous Closure of Bilateral Pulmonary Artery Aneurysms in Behcet's Disease
Abstract
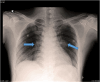
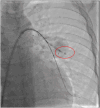
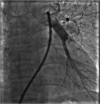
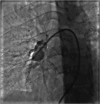
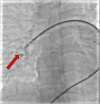
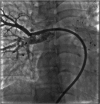
Behcet's disease is a multisystemic vasculitis. It can affect the pulmonary artery in 2% to 5% cases. We discuss a case of a young male diagnosed with Behcet's disease on immunosuppressive therapy who presented with bilateral pulmonary artery aneurysms which were closed with covered stent and other devices.
Keywords: autoimmune; imaging; occluder; pulmonary circulation; stents; vascular disease.
© 2024 Published by Elsevier on behalf of the American College of Cardiology Foundation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have reported that they have no relationships relevant to the contents of this paper to disclose.
Figures





References
-
- Modaghegh M.H.S., Kazemzadeh G.H., Jokar M.H. A case of Behçet disease with pulmonary artery pseudoaneurysm: long term follow-up. East Mediterr Heal J. 2010;16(3):346–349. - PubMed
-
- Yuan S.M. Aneurismas de artérias pulmonares na doença de Behçet. J Vasc Bras. 2014;13(3):217–228.
-
- Hamuryudan V., Er T., Seyahi E., et al. Pulmonary artery aneurysms in Behçet syndrome. Am J Med. 2004;117(11):867–870. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

