Comparison of Siglec-1 protein networks and expression patterns in sperm and male reproductive tracts of mice, rats, and humans
- PMID: 38680147
- PMCID: PMC11045525
- DOI: 10.14202/vetworld.2024.645-657
Comparison of Siglec-1 protein networks and expression patterns in sperm and male reproductive tracts of mice, rats, and humans
Abstract
Background: Sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectin 1 (Siglec-1) is a transmembrane glycoprotein involved in the sialic acid (Sia)-dependent regulation of the immune system. Siglec-1 expression has recently been identified in the male reproductive tract (MRT) of several species, including humans, cattle, horses, and sheep, and may play a role in modulating fertility in a Sia-dependent manner.
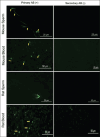
Materials and methods: In this study, protein-protein interaction (PPI) analysis of Siglec-1 was conducted to identify associated network protein conservation, and the expression of Siglec-1 in the MRT of mice and rats, including their accessory sex glands and spermatozoa was determined by immunostaining.
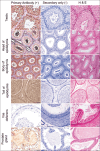
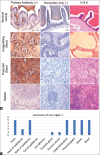
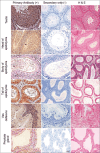
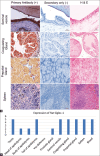
Results: Network analysis of proteins with Siglec-1 in mice and rats demonstrated significant similarity to human Siglec-1 networks, suggesting a similar conservation of network proteins between these species and, hence, a potential conservation role in immune modulation and function. Specific immunostaining patterns of mouse and rat testes, epididymis, ductus deferens, accessory sex gland tissues, and sperm were detected using human Siglec-1. These results confirmed that the human Siglec-1 antibody could cross-react with mouse and rat Siglec-1, suggesting that the specific expression patterns of Siglec-1 in the MRT and sperm of both mice and rats are similar to those observed in other species.
Conclusions: The conservation of Siglec-1 expression patterns in sperm and within the MRT and the similarity of protein networks for Siglec-1 across species suggest that Siglec-1 may function in a similar manner across species. These results also suggest that rodents may serve as a valuable model system for exploring the function of Siglecs in the reproductive system across species and their potential role in modulating fertility in a Sia-dependent manner.
Keywords: female reproductive tract; male reproductive tract; protein–protein interaction; sialic acid; sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectin-1.
Copyright: © Almhanna, et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Warren L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J. Biol. Chem. 1959;234(8):1971–1975. - PubMed
-
- Schröter S, Osterhoff C, McArdle W, Ivell R. The glycocalyx of the sperm surface. Hum. Reprod. Update. 1999;5(4):302–313. - PubMed
-
- Varki A, Schauer R. Essentials of Glycobiology. 2nd ed. United States: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 2009. Sialic Acids. - PubMed
-
- Crocker P.R, Paulson J.C, Varki A. Siglecs and their roles in the immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007;7(4):255–266. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

