Impact of Lipid Composition on Vesicle Protein Adsorption: A BSA Case Study
- PMID: 38680315
- PMCID: PMC11044229
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.3c09131
Impact of Lipid Composition on Vesicle Protein Adsorption: A BSA Case Study
Abstract
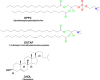
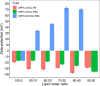
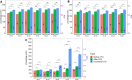
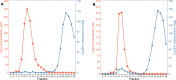
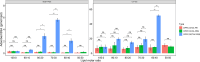
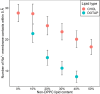
Investigating the interaction between liposomes and proteins is of paramount importance in the development of liposomal formulations with real potential for bench-to-bedside transfer. Upon entering the body, proteins are immediately adsorbed on the liposomal surface, changing the nanovehicles' biological identity, which has a significant impact on their biodistribution and pharmacokinetics and ultimately on their therapeutic effect. Albumin is the most abundant plasma protein and thus usually adsorbs immediately on the liposomal surface. We herein report a comprehensive investigation on the adsorption of model protein bovine serum albumin (BSA) onto liposomal vesicles containing the zwitterionic lipid 1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (DPPC), in combination with either cholesterol (CHOL) or the cationic lipid 1,2-dioleoyl-3-trimethylammoniumpropane (DOTAP). While many studies regarding protein adsorption on the surface of liposomes with different compositions have been performed, to the best of our knowledge, the differential responses of CHOL and DOTAP upon albumin adsorption on vesicles have not yet been investigated. UV-vis spectroscopy and sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) revealed a strong influence of the phospholipid membrane composition on protein adsorption. Hence, it was found that DOTAP-containing vesicles adsorb proteins more robustly but also aggregate in the presence of BSA, as confirmed by DLS and TEM. Separation of liposome-protein complexes from unadsorbed proteins performed by means of centrifugation and size exclusion chromatography (SEC) was also investigated. Our results show that neither method can be regarded as a golden experimental setup to study the protein corona of liposomes. Yet, SEC proved to be more successful in the separation of unbound proteins, although the amount of lipid loss upon liposome elution was higher than expected. In addition, coarse-grained molecular dynamics simulations were employed to ascertain key membrane parameters, such as the membrane thickness and area per lipid. Overall, this study highlights the importance of surface charge and membrane fluidity in influencing the extent of protein adsorption. We hope that our investigation will be a valuable contribution to better understanding protein-vesicle interactions for improved nanocarrier design.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
