A Scoping Review of Assertiveness Therapy for Reducing Bullying Behavior and Its Impacts Among Adolescents
- PMID: 38680879
- PMCID: PMC11048288
- DOI: 10.2147/JMDH.S460343
A Scoping Review of Assertiveness Therapy for Reducing Bullying Behavior and Its Impacts Among Adolescents
Abstract
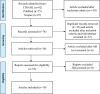
Bullying is a global problem in adolescents which has increased every year. One of the factors in the occurrence of bullying is the ability of interpersonal skills. This ability can build good relationships with assertive between adolescents and can prevent bullying. The purpose of this study is to describe assertiveness therapy for reducing bullying behavior and its impacts among adolescents. The method used in this study is scoping review. The search strategy used is PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews through three databases namely PubMed, CINAHL, and Scopus. The authors used inclusion criteria and exclusion criteria in the selection of articles. The major keywords used in the article search were bullying, assertiveness therapy, and adolescents. Data analysis used descriptive qualitative. The results showed that there were 10 articles that discussed assertive therapy. All articles show that assertiveness therapy can reduce bullying behavior and its impact significantly, such as reducing the impact of anxiety and increasing self-esteem. Assertiveness therapy methods carried out in the form of education, games, and role play. Education is carried out online and offline. Educational media is provided directly and through media such as educational videos which can be accessed at any time. Gender and cultural approaches are important aspects in the implementation of assertive therapy. Assertive therapy can improve interpersonal skills, social skills, empathy and assertiveness so that it can reduce bullying behavior and its impacts in adolescents. Then, this data becomes the basis for nurses to carry out assertive therapy as an effort to prevent and reduce bullying behavior in adolescents.
Keywords: adolescents; assertiveness; bullying; impacts.
© 2024 Yosep et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in this study.
Similar articles
-
KiVa anti-bullying program: preventing bullying and reducing Bulling Behavior among students - a scoping review.BMC Public Health. 2024 Oct 22;24(1):2923. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-20086-8. BMC Public Health. 2024. Retraction in: BMC Public Health. 2025 Mar 19;25(1):1071. doi: 10.1186/s12889-025-22342-x. PMID: 39438845 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
A Scoping Review of the Online Interventions by Nurses for Reducing Negative Impact of Bullying on Students.J Multidiscip Healthc. 2023 Mar 24;16:773-783. doi: 10.2147/JMDH.S406050. eCollection 2023. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2023. PMID: 36998991 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring nursing interventions in family-based approaches for preventing bullying among children and adolescents: a scoping review.BMC Nurs. 2025 May 27;24(1):601. doi: 10.1186/s12912-025-03221-7. BMC Nurs. 2025. PMID: 40426113 Free PMC article.
-
Empathy's Crucial Role: Unraveling Impact on Students Bullying Behavior - A Scoping Review.J Multidiscip Healthc. 2024 Jul 17;17:3483-3495. doi: 10.2147/JMDH.S469921. eCollection 2024. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2024. PMID: 39056092 Free PMC article.
-
A Scoping Review of Anti-Bullying Interventions: Reducing Traumatic Effect of Bullying Among Adolescents.J Multidiscip Healthc. 2024 Jan 20;17:289-304. doi: 10.2147/JMDH.S443841. eCollection 2024. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2024. PMID: 38268849 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Experiences of bullying among nursing students during clinical practice: a scoping review of qualitative studies.BMC Nurs. 2024 Nov 14;23(1):832. doi: 10.1186/s12912-024-02439-1. BMC Nurs. 2024. PMID: 39543548 Free PMC article.
-
KiVa anti-bullying program: preventing bullying and reducing Bulling Behavior among students - a scoping review.BMC Public Health. 2024 Oct 22;24(1):2923. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-20086-8. BMC Public Health. 2024. Retraction in: BMC Public Health. 2025 Mar 19;25(1):1071. doi: 10.1186/s12889-025-22342-x. PMID: 39438845 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Beyond the trauma: a scoping review of nursing interventions for improving psychological well-being in adolescents bullying victims.BMC Nurs. 2025 Jul 25;24(1):973. doi: 10.1186/s12912-025-03642-4. BMC Nurs. 2025. PMID: 40713664 Free PMC article.
-
The Perception and Roles of School Mental Health Professionals Regarding School Bullying (Suluk Audwani) in Oman: A Qualitative Study in an Urban Setting.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2024 Jul 28;21(8):991. doi: 10.3390/ijerph21080991. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39200602 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yadav BS, Kaur H. A review on the problem of adolescent due to the excessive use of technology: cyberbully. Int J Sci Technol Res. 2020;9(3):3537–3541.
-
- Hinduja S, Patchin JW. Bullying and cyberbullying offending among us youth: The influence of six parenting dimensions. J Child Fam Stud. 2022;31(5):1454–1473.
-
- Lee J, Hong JS, Resko SM, Tripodi SJ. Face-to-face bullying, cyberbullying, and multiple forms of substance use among school-age adolescents in the USA. School Ment Health. 2018;10:12–25. doi:10.1007/s12310-017-9231-6 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources