Anti-biofilm activity of marine algae-derived bioactive compounds
- PMID: 38680918
- PMCID: PMC11055458
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1270174
Anti-biofilm activity of marine algae-derived bioactive compounds
Abstract
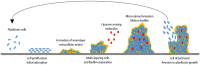
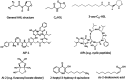
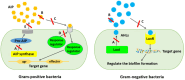
A large number of microbial species tend to communicate and produce biofilm which causes numerous microbial infections, antibiotic resistance, and economic problems across different industries. Therefore, advanced anti-biofilms are required with novel attributes and targets, such as quorum sensing communication system. Meanwhile, quorum sensing inhibitors as promising anti-biofilm molecules result in the inhibition of particular phenotype expression blocking of cell-to-cell communication, which would be more acceptable than conventional strategies. Many natural products are identified as anti-biofilm agents from different plants, microorganisms, and marine extracts. Marine algae are promising sources of broadly novel compounds with anti-biofilm activity. Algae extracts and their metabolites such as sulfated polysaccharides (fucoidan), carotenoids (zeaxanthin and lutein), lipid and fatty acids (γ-linolenic acid and linoleic acid), and phlorotannins can inhibit the cell attachment, reduce the cell growth, interfere in quorum sensing pathway by blocking related enzymes, and disrupt extracellular polymeric substances. In this review, the mechanisms of biofilm formation, quorum sensing pathway, and recently identified marine algae natural products as anti-biofilm agents will be discussed.
Keywords: algae extracts; anti-biofilm activity; biofilm; marine natural products; quorum quenching; quorum sensing; quorum sensing inhibition.
Copyright © 2024 Behzadnia, Moosavi-Nasab and Oliyaei.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Alreshidi M., Badraoui R., Adnan M., Patel M., Alotaibi A., Saeed M., et al. (2023). Phytochemical profiling, antibacterial, and antibiofilm activities of Sargassum sp.(brown algae) from the Red Sea: ADMET prediction and molecular docking analysis. Algal Res. 69:102912. doi: 10.1016/j.algal.2022.102912 - DOI
-
- Al-TmimiG S., Al-Rrubaai G., Zaki N. H. (2018). Antibiofilm activity of intracellular extracts of Westiellopsis prolifica isolated from local environment in Baghdad. JGPT 10, 281–288.
-
- Ashrafudoulla M., Kim H. J., Her E., Shaila S., Park S. H., Ha S. D. (2023). Characterization of Salmonella Thompson-specific bacteriophages and their preventive application against Salmonella Thompson biofilm on eggshell as a promising antimicrobial agent in the food industry. Food Control 154:110008. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2023.110008 - DOI
-
- Ashrafudoulla M., Mevo S. I. U., Song M., Chowdhury M. A. H., Shaila S., Kim D. H., et al. (2023). Antibiofilm mechanism of peppermint essential oil to avert biofilm developed by foodborne and food spoilage pathogens on food contact surfaces. J. Food Sci. 88, 3935–3955. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.16712, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

