Dynasore Alleviates LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury by Inhibiting NLRP3 Inflammasome-Mediated Pyroptosis
- PMID: 38681210
- PMCID: PMC11055558
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S444408
Dynasore Alleviates LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury by Inhibiting NLRP3 Inflammasome-Mediated Pyroptosis
Abstract
Background: Acute lung injury (ALI) and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) are clinically severe respiratory disorders without available pharmacological therapies. Dynasore is a cell-permeable molecule that inhibits GTPase activity and exerts protective effects in several disease models. However, whether dynasore can alleviate lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced ALI is unknown. This study investigated the effect of dynasore on macrophage activation and explored its potential mechanisms in LPS-induced ALI in vitro and in vivo.
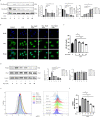
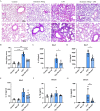
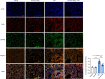
Methods: Bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) were activated classically with LPS or subjected to NLRP3 inflammasome activation with LPS+ATP. A mouse ALI model was established by the intratracheal instillation (i.t.) of LPS. The expression of PYD domains-containing protein 3 (NLRP3), caspase-1, and gasdermin D (GSDMD) protein was detected by Western blots. Inflammatory mediators were analyzed in the cell supernatant, in serum and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays. Morphological changes in lung tissues were evaluated by hematoxylin and eosin staining. F4/80, Caspase-1 and GSDMD distribution in lung tissue was detected by immunofluorescence.
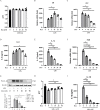
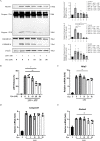
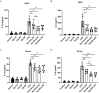
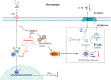
Results: Dynasore downregulated nuclear factor (NF)-κB signaling and reduced proinflammatory cytokine production in vitro and inhibited the production and release of interleukin (IL)-1β, NLRP3 inflammasome activation, and macrophage pyroptosis through the Drp1/ROS/NLRP3 axis. Dynasore significantly reduced lung injury scores and proinflammatory cytokine levels in both BALF and serum in vivo, including IL-1β and IL-6. Dynasore also downregulated the co-expression of F4/80, caspase-1 and GSDMD in lung tissue.
Conclusion: Collectively, these findings demonstrated that dynasore could alleviate LPS-induced ALI by regulating macrophage pyroptosis, which might provide a new therapeutic strategy for ALI/ARDS.
Keywords: NLRP3 inflammasome; acute lung injury; acute respiratory distress syndrome; dynasore; inflammation; pyroptosis.
© 2024 Shan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Alpha-linolenic acid pretreatment alleviates NETs-induced alveolar macrophage pyroptosis by inhibiting pyrin inflammasome activation in a mouse model of sepsis-induced ALI/ARDS.Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 27;14:1146612. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1146612. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37051243 Free PMC article.
-
Tangeretin attenuates acute lung injury in septic mice by inhibiting ROS-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation via regulating PLK1/AMPK/DRP1 signaling axis.Inflamm Res. 2024 Jan;73(1):47-63. doi: 10.1007/s00011-023-01819-8. Epub 2023 Dec 26. Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 38147126
-
Modulating the NLRP3 Inflammasome: Acitretin as a potential treatment for Sepsis-induced acute lung injury.Int Immunopharmacol. 2025 Apr 24;153:114504. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2025.114504. Epub 2025 Apr 3. Int Immunopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40187888
-
Pyroptosis and polarization of macrophages in septic acute lung injury induced by lipopolysaccharide in mice.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2024 Mar;12(3):e1197. doi: 10.1002/iid3.1197. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2024. PMID: 38501547 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NLRP3 Inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis in acute lung injury: Roles of main lung cell types and therapeutic perspectives.Int Immunopharmacol. 2025 May 8;154:114560. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2025.114560. Epub 2025 Apr 5. Int Immunopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40184810 Review.
Cited by
-
Bibliometric analysis of pyroptosis in pathogenesis and treatment of acute lung injury.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jan 22;11:1488796. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1488796. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 39911675 Free PMC article.
-
Main Ingredient of Yinhua Pinggan Granules Combined with Meropenem Alleviated Lung Injury Induced by Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae via Inhibiting NF-κB Pathway and NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025 May 15;35:e2412014. doi: 10.4014/jmb.2412.12014. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40374526 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

