Mounting Stroke Crisis in India: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 38681344
- PMCID: PMC11052531
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.57058
Mounting Stroke Crisis in India: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Stroke, a neurological disorder, has emerged as a formidable health challenge in India, with its incidence on the rise. Increased risk factors, which also correlate with economic prosperity, are linked to this rise, including hypertension, diabetes, obesity, sedentary lifestyle, and alcohol intake. Particularly worrisome is the impact on young adults, a pivotal segment of India's workforce. Stroke encompasses various clinical subtypes and cerebrovascular disorders (CVDs), contributing to its multifaceted nature. Globally, stroke's escalating burden is concerning, affecting developing nations. To combat this trend effectively and advance prevention and treatment strategies, comprehensive and robust data on stroke prevalence and impact are urgently required. In India, these encompass individuals with elevated BMIs, and those afflicted by hypertension, diabetes, or a familial history of stroke. Disparities in stroke incidence and prevalence manifest across India, with differences in urban and rural settings, gender-based variations, and regional disparities. Early detection, dietary changes, effective risk factor management, and equitable access to stroke care are required to address this issue. Government initiatives, like the National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases, and Stroke (NPCDCS) 2019, provide guidelines, but effective implementation and awareness campaigns are vital. Overcoming barriers to stroke care, especially in rural areas, calls for improved infrastructure, awareness campaigns, and support systems. Data standardization and comprehensive population studies are pivotal for informed public health policies.
Keywords: cerebrovascular disorders; disability-adjusted life years (dalys); india; low to middle income countries; stroke; stroke care challenges.
Copyright © 2024, Hedau et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
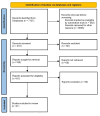
Figures

Similar articles
-
Analysis of the global burden of CKD-T2DM in young and middle-aged adults in 204 countries and territories from 2000 to 2019: A systematic study of the global burden of disease in 2019.Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2024 Nov;217:111884. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2024.111884. Epub 2024 Oct 9. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2024. PMID: 39389473
-
Beyond the black stump: rapid reviews of health research issues affecting regional, rural and remote Australia.Med J Aust. 2020 Dec;213 Suppl 11:S3-S32.e1. doi: 10.5694/mja2.50881. Med J Aust. 2020. PMID: 33314144
-
Cardiovascular Diseases Among Indian Older Adults: A Comprehensive Review.Cardiovasc Ther. 2024 Jun 25;2024:6894693. doi: 10.1155/2024/6894693. eCollection 2024. Cardiovasc Ther. 2024. PMID: 39742010 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Changes in blood pressure among users of lay health worker or volunteer operated community-based blood pressure programs over time: a systematic review protocol.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015 Oct;13(10):30-40. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2015-1927. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015. PMID: 26571280
-
The 2023 Latin America report of the Lancet Countdown on health and climate change: the imperative for health-centred climate-resilient development.Lancet Reg Health Am. 2024 Apr 23;33:100746. doi: 10.1016/j.lana.2024.100746. eCollection 2024 May. Lancet Reg Health Am. 2024. PMID: 38800647 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Gender-Based Differences in Stroke Types and Risk Factors Among Young Adults: A Comparative Retrospective Analysis.J Clin Med. 2025 Jan 21;14(3):663. doi: 10.3390/jcm14030663. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 39941335 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Incidence & prevalence of stroke in India: a systematic review. Kamalakannan S, Gudlavalleti AS, Gudlavalleti VS, Goenka S, Kuper H. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29265018/ Indian J Med Res. 2017;146:175–185. - PMC - PubMed
-
- The top 10 causes of death. [ Sep; 2023 ]. 2023. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-d... https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-d...
-
- Risk factors of stroke. [ Sep; 2023 ]. 2023. https://ncdirindia.org/all_reports/pbsrbook/resources/PBSR_Report_2021_C... https://ncdirindia.org/all_reports/pbsrbook/resources/PBSR_Report_2021_C...
-
- Role of diabetes, hypertension, and cigarette smoking on atherosclerosis. Mathur RK. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2945206/ J Cardiovasc Dis Res. 2010;1:64–68. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
