Soluble expression of recombinant coagulation factor IX protein using Escherichia coli
- PMID: 38681671
- PMCID: PMC11052911
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2024.101714
Soluble expression of recombinant coagulation factor IX protein using Escherichia coli
Abstract
Hemophilia B is a congenital bleeding disorder caused by factor IX (FIX) deficiency. Generation of recombinant FIX (rFIX) is required for detecting a Hemophilia B indicator, anti-FIX antibody. In this study, we described a method for producing recombinant FIX (rFIX) using Escherichia coli. We constructed a FIX-expressing plasmid without a fusion tag protein-encoding gene and produced rFIX as a soluble form within five days. Dose-dependent curve was obtained from ELISA using anti-FIX antibody, indicating that the rFIX can be used as an antigen to detect anti-FIX antibody with high affinity and sensitivity.
Keywords: Escherichia coli; Factor IX; Hemophilia; Protein expression; Recombinant protein.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
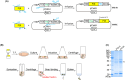
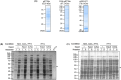
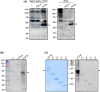
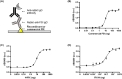
References
-
- Lin S.W., Dunn J.J., Studier F.W., Stafford D.W. Expression of human factor IX and its subfragments in Escherichia coli and generation of antibodies to the subfragments. Biochemistry. 1987;26:5267–5274. - PubMed
-
- Lee Y., Hur H., Kim M. Cloning and expression of human clotting factor 9 cDNA in Escherichia coli. Biomedical Science Letters. 1996;2:231–240.
-
- DiMichele D. Inhibitor development in haemophilia B: an orphan disease in need of attention. Br. J. Haematol. 2007;138:305–315. - PubMed
-
- Qing G., Ma L.C., Khorchid A., Swapna G.V., Mal T.K., Takayama M.M., Xia B., Phadtare S., Ke H., Acton T., Montelione G.T., Ikura M., Inouye M. Cold-shock induced high-yield protein production in Escherichia coli. Nat. Biotechnol. 2004;22:877–882. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

