Selection, characterization, and biosensing applications of DNA aptamers targeting cyanotoxin BMAA
- PMID: 38681844
- PMCID: PMC11046380
- DOI: 10.1039/d4ra02384f
Selection, characterization, and biosensing applications of DNA aptamers targeting cyanotoxin BMAA
Abstract
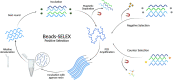
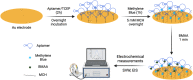
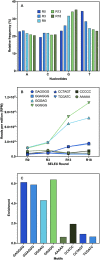
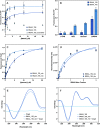
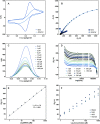
Scientists have established a connection between environmental exposure to toxins like β-N-methylamino-l-alanine (BMAA) and a heightened risk of neurodegenerative disorders. BMAA is a byproduct from certain strains of cyanobacteria that are present in ecosystems worldwide and is renowned for its bioaccumulation and biomagnification in seafood. The sensitivity, selectivity, and reproducibility of the current analytical techniques are insufficient to support efforts regarding food safety and environment monitoring adequately. This work outlines the in vitro selection of BMAA-specific DNA aptamers via the systematic evolution of ligands through exponential enrichment (SELEX). Screening and characterization of the full-length aptamers was achieved using the SYBR Green (SG) fluorescence displacement assay. Aptamers BMAA_159 and BMAA_165 showed the highest binding affinities, with dissociation constants (Kd) of 2.2 ± 0.1 μM and 0.32 ± 0.02 μM, respectively. After truncation, the binding affinity was confirmed using a BMAA-conjugated fluorescence assay. The Kd values for BMAA_159_min and BMAA_165_min were 6 ± 1 μM and 0.63 ± 0.02 μM, respectively. Alterations in the amino proton region studied using solution nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) provided further evidence of aptamer-target binding. Additionally, circular dichroism (CD) spectroscopy revealed that BMAA_165_min forms hybrid G-quadruplex (G4) structures. Finally, BMAA_165_min was used in the development of an electrochemical aptamer-based (EAB) sensor that accomplished sensitive and selective detection of BMAA with a limit of detection (LOD) of 1.13 ± 0.02 pM.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

