Research advances in the influence of lipid metabolism on cognitive impairment
- PMID: 38682015
- PMCID: PMC11045198
- DOI: 10.1002/ibra.12018
Research advances in the influence of lipid metabolism on cognitive impairment
Abstract
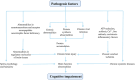
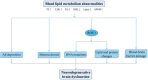
Cognitive impairment (CI) is a mental disorder related to cognition and understanding, which is mainly categorized into mild CI and senile dementia. This disease is associated with multiple factors, such as chronic brain injury, aging, chronic systemic disease, mental state, and psychological factors. However, the pathological mechanism of CI remains unclear; it is usually associated with such underlying diseases as diabetes and hyperlipidemia. It has been demonstrated that abundant lipid metabolism indexes in the human body are closely related to CI, including total cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, triglycerides, apolipoprotein, and so forth. As a crucial risk factor for CI, hyperlipidemia is of great significance in the occurrence and development of CI. However, the specific correlation between dyslipidemia and CI is still not fully elucidated. Besides, the efficacy of lipid-lowering drugs in the prophylaxis and treatment of CI has not been clarified. In this study, relevant advances in the influence of lipid metabolism disorders in CI will be reviewed, in an attempt to explore the effect of mediating blood lipid levels on the prophylaxis and treatment of CI, thus providing a reference for its clinical management.
Keywords: cognitive dysfunction; hyperlipidemia; lipid metabolism.
© 2022 The Authors. Ibrain published by Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University (AHZMU) and Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Apolipoprotein E ε4 Allele-Dependent Relationship Between Serum Lipid Levels and Cognitive Function: A Population-Based Cross-sectional Study.Front Aging Neurosci. 2020 Mar 13;12:44. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2020.00044. eCollection 2020. Front Aging Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32231559 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of dietary cholesterol and fat, blood lipids, and risk for dementia in older women vary by APOE genotype.Alzheimers Dement. 2023 Dec;19(12):5742-5754. doi: 10.1002/alz.13358. Epub 2023 Jul 12. Alzheimers Dement. 2023. PMID: 37438877 Free PMC article.
-
Serum lipoprotein levels, statin use, and cognitive function in older women.Arch Neurol. 2002 Mar;59(3):378-84. doi: 10.1001/archneur.59.3.378. Arch Neurol. 2002. PMID: 11890840 Clinical Trial.
-
Overall and Sex-Specific Effect of Berberine for the Treatment of Dyslipidemia in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trials.Drugs. 2023 Apr;83(5):403-427. doi: 10.1007/s40265-023-01841-4. Epub 2023 Mar 21. Drugs. 2023. PMID: 36941490
-
Intensive LDL-cholesterol lowering therapy and neurocognitive function.Pharmacol Ther. 2017 Feb;170:181-191. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2016.11.001. Epub 2016 Nov 16. Pharmacol Ther. 2017. PMID: 27865998 Review.
Cited by
-
Causal association of obesity with epigenetic aging and telomere length: a bidirectional mendelian randomization study.Lipids Health Dis. 2024 Mar 12;23(1):78. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02042-y. Lipids Health Dis. 2024. PMID: 38475782 Free PMC article.
-
Association of birth weight with type 2 diabetes mellitus and the mediating role of fatty acids traits: a two-step mendelian randomization study.Lipids Health Dis. 2024 Apr 2;23(1):97. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02087-z. Lipids Health Dis. 2024. PMID: 38566047 Free PMC article.
-
Cognitive dysfunction in diabetes - the 'forgotten' diabetes complication: a narrative review.Scand J Prim Health Care. 2025 Jun;43(2):448-454. doi: 10.1080/02813432.2025.2455136. Epub 2025 Jan 28. Scand J Prim Health Care. 2025. PMID: 39876043 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of diagnosis biomarkers based on the delirium-related genes.Int J Surg. 2024 Feb 1;110(2):1291-1293. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000000874. Int J Surg. 2024. PMID: 37939102 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Investigation of the shared biological mechanisms and common biomarker APTAF1 of sleep deprivation and mild cognitive impairment using integrated bioinformatics analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Apr 17;15:1387569. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1387569. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38694919 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
