GDF11 inhibits the malignant progression of hepatocellular carcinoma via regulation of the mTORC1‑autophagy axis
- PMID: 38682112
- PMCID: PMC11046183
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2024.12540
GDF11 inhibits the malignant progression of hepatocellular carcinoma via regulation of the mTORC1‑autophagy axis
Abstract
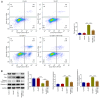
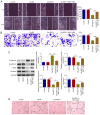
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a common malignant tumor, which is associated with a poor prognosis and high mortality rate. It is well known that growth differentiation factor 11 (GDF11) acts as a tumor suppressor in various types of cancer, including HCC. The present study aimed to determine the tumor-suppressive properties of GDF11 in HCC and to assess the intrinsic mechanisms. In the present study, the human hepatoma cell line Huh-7 was transfected with the GDF11 overexpression plasmid (Oe-GDF11) for gain-of-function experiments to investigate the effects of GDF11 on the biological behaviors of HCC cells, including proliferation, colony formation, apoptosis, cell cycle arrest, migration, invasion, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and angiogenesis. The proliferation, colony formation, apoptosis, cell cycle, migration, invasion and angiogenesis of HCC cells were assessed by CCK-8, EdU staining, colony formation, flow cytometry, wound healing, Transwell and tube formation assays, respectively. Apoptosis-, cell cycle-, EMT-related key factors were also determined by western blot assay. Furthermore, Oe-GDF11-transfected Huh-7 cells were treated with the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) activator MHY1485 for rescue experiments to explore whether GDF11 could exert antitumor effects against HCC via mediating the mTOR complex 1 (mTORC1)-autophagy axis. In the present study, GDF11 was verified to be lowly expressed in HCC cells. Overexpression of GDF11 inhibited the proliferation, colony formation, migration, invasion, EMT and angiogenesis of HCC cells, and facilitated the apoptosis and cell cycle arrest of HCC cells. Additionally, it was verified that overexpression of GDF11 inactivated the mTORC1 signaling pathway to enhance autophagy in HCC cells. Treatment with the mTOR activator MHY1485 partially reversed the tumor-suppressive effects of GDF11 overexpression on HCC. In conclusion, GDF11 may exert tumor-suppressive properties in HCC cells through inactivating the mTORC1 signaling pathway to strengthen autophagy.
Keywords: growth differentiation factor 11; hepatocellular carcinoma; mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1-autophagy axis.
Copyright: © 2024 Wu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Emodin inhibits invasion and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via regulating autophagy-mediated degradation of snail and β-catenin.BMC Cancer. 2022 Jun 18;22(1):671. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09684-0. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35715752 Free PMC article.
-
Dramatic antitumor effects of the dual mTORC1 and mTORC2 inhibitor AZD2014 in hepatocellular carcinoma.Am J Cancer Res. 2014 Dec 15;5(1):125-39. eCollection 2015. Am J Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 25628925 Free PMC article.
-
SOX18 Affects Cell Viability, Migration, Invasiveness, and Apoptosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) Cells by Participating in Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) Progression and Adenosine Monophosphate Activated Protein Kinase (AMPK)/Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR).Med Sci Monit. 2019 Aug 20;25:6244-6254. doi: 10.12659/MSM.915729. Med Sci Monit. 2019. PMID: 31427562 Free PMC article.
-
Dampened VEPH1 activates mTORC1 signaling by weakening the TSC1/TSC2 association in hepatocellular carcinoma.J Hepatol. 2020 Dec;73(6):1446-1459. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.06.027. Epub 2020 Jun 28. J Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 32610114
-
GDF11 exhibits tumor suppressive properties in hepatocellular carcinoma cells by restricting clonal expansion and invasion.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2019 Jun 1;1865(6):1540-1554. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2019.03.003. Epub 2019 Mar 16. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2019. PMID: 30890427
Cited by
-
NR4A3 suppresses bladder cancer progression by modulating autophagy via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway.Eur J Histochem. 2025 Jun 17;69(3):4221. doi: 10.4081/ejh.2025.4221. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Eur J Histochem. 2025. PMID: 40586548 Free PMC article.
-
SPDL1 overexpression was associated with poor prognosis and immune status in HCC through in vitro experiment and bioinformatics analysis.Discov Oncol. 2025 Jul 11;16(1):1310. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-03089-8. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40643715 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting cell death mechanisms: the potential of autophagy and ferroptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma therapy.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 9;15:1450487. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1450487. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39315094 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cao M, Ren Y, Li Y, Deng J, Su X, Tang Y, Yuan F, Deng H, Yang G, He Z, et al. Lnc-ZEB2-19 inhibits the progression and lenvatinib resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma by attenuating the NF-κB signaling pathway through the TRA2A/RSPH14 axis. Int J Biol Sci. 2023;19:3678–3693. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.85270. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Liu Y, Yao Y, Liao B, Zhang H, Yang Z, Xia P, Jiang X, Ma W, Wu X, Mei C, et al. A positive feedback loop of CENPU/E2F6/E2F1 facilitates proliferation and metastasis via ubiquitination of E2F6 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Biol Sci. 2022;18:4071–4087. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.69495. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
