Antioxidant and anti‑inflammatory effects of esculin and esculetin (Review)
- PMID: 38682114
- PMCID: PMC11046185
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2024.12536
Antioxidant and anti‑inflammatory effects of esculin and esculetin (Review)
Abstract
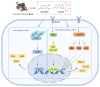
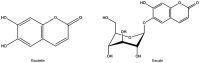
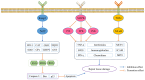
Fraxinus chinensis Roxb is a deciduous tree, which is distributed worldwide and has important medicinal value. In Asia, the bark of Fraxinus chinensis Roxb is a commonly used traditional Chinese medicine called Qinpi. Esculetin is a coumarin compound derived from the bark of Fraxinus chinensis Roxb and its glycoside form is called esculin. The aim of the present study was to systematically review relevant literature on the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of esculetin and esculin. Esculetin and esculin can promote the expression of various endogenous antioxidant proteins, such as superoxide dismutase, glutathione peroxidase and glutathione reductase. This is associated with the activation of the nuclear factor erythroid-derived factor 2-related factor 2 signaling pathway. The anti-inflammatory effects of esculetin and esculin are associated with the inhibition of the nuclear factor κ-B and mitogen-activated protein kinase inflammatory signaling pathways. In various inflammatory models, esculetin and esculin can reduce the expression levels of various proinflammatory factors such as tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-6, thereby inhibiting the development of inflammation. In summary, esculetin and esculin may be promising candidates for the treatment of numerous diseases associated with inflammation and oxidative stress, such as ulcerative colitis, acute lung and kidney injury, lung cancer, acute kidney injury.
Keywords: anti-inflammatory; antioxidant; esculetin; esculin.
Copyright: © 2024 Ju et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Esculetin and esculin (esculetin 6-O-glucoside) occur as inclusions and are differentially distributed in the vacuole of palisade cells in Fraxinus ornus leaves: a fluorescence microscopy analysis.J Photochem Photobiol B. 2014 Nov;140:28-35. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2014.06.012. Epub 2014 Jun 28. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2014. PMID: 25063983
-
Pharmacological activities of esculin and esculetin: A review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Oct 6;102(40):e35306. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000035306. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37800835 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-oxidative and photo-protective effects of coumarins isolated from Fraxinus chinensis.Arch Pharm Res. 2007 Oct;30(10):1293-301. doi: 10.1007/BF02980270. Arch Pharm Res. 2007. PMID: 18038908
-
Esculetin Protects Human Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells from Lipopolysaccharide-induced Inflammation and Cell Death.Curr Eye Res. 2018 Sep;43(9):1169-1176. doi: 10.1080/02713683.2018.1481517. Epub 2018 Jun 6. Curr Eye Res. 2018. PMID: 29806490
-
Esculetin: A review of its pharmacology and pharmacokinetics.Phytother Res. 2022 Jan;36(1):279-298. doi: 10.1002/ptr.7311. Epub 2021 Nov 22. Phytother Res. 2022. PMID: 34808701 Review.
Cited by
-
Ochratoxin A induces immunotoxicity by targeting Annexin A1 mediated neutrophil apoptosis in zebrafish.Front Immunol. 2025 Jan 24;16:1542964. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1542964. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39925799 Free PMC article.
-
4-Hydroxycoumarin Exhibits Antinociceptive and Anti-Inflammatory Effects Through Cytokine Modulation: An Integrated In Silico and In Vivo Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 19;26(6):2788. doi: 10.3390/ijms26062788. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40141429 Free PMC article.
-
Esculetin Attenuates the Migration and Invasion of Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells by Attenuating Matrix Metalloproteinase Activity and Strengthening Tight Junctions.J Cancer Prev. 2025 Jun 30;30(2):111-117. doi: 10.15430/JCP.25.014. J Cancer Prev. 2025. PMID: 40621158 Free PMC article.
-
Role of esculin antioxidant on remediation of lead toxicity on flax growth and yield components.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Jul 3;25(1):863. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06870-7. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 40610863 Free PMC article.
-
Mortality of Musca domestica (Diptera: Muscidae) in response to exposure to a fungal entomopathogen in combination with eicosanoid biosynthesis inhibitors.J Insect Sci. 2025 May 9;25(3):16. doi: 10.1093/jisesa/ieaf060. J Insect Sci. 2025. PMID: 40459990 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fernández-Sánchez A, Madrigal-Santillán E, Bautista M, Esquivel-Soto J, Morales-González A, Esquivel-Chirino C, Durante-Montiel I, Sánchez-Rivera G, Valadez-Vega C, Morales-González JA. Inflammation, oxidative stress, and obesity. Int J Mol Sci. 2011;12:3117–3132. doi: 10.3390/ijms12053117. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yang J, Xiang D, Xiang D, He W, Liu Y, Lan L, Li G, Jiang C, Ren X, Liu D, Zhang C. Baicalin protects against 17α-ethinylestradiol-induced cholestasis via the sirtuin 1/hepatic nuclear receptor-1α/farnesoid X receptor pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2020;10(1685) doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01685. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
