The effect of charge and albumin on cellular uptake of supramolecular polymer nanostructures
- PMID: 38682307
- PMCID: PMC11111113
- DOI: 10.1039/d3tb02631k
The effect of charge and albumin on cellular uptake of supramolecular polymer nanostructures
Abstract
Intracellular delivery of functional biomolecules by using supramolecular polymer nanostructures has gained significant interest. Here, various charged supramolecular ureido-pyrimidinone (UPy)-aggregates were designed and formulated via a simple "mix-and-match" method. The cellular internalization of these UPy-aggregates in the presence or absence of serum proteins by phagocytic and non-phagocytic cells, i.e., THP-1 derived macrophages and immortalized human kidney cells (HK-2 cells), was systematically investigated. In the presence of serum proteins the UPy-aggregates were taken up by both types of cells irrespective of the charge properties of the UPy-aggregates, and the UPy-aggregates co-localized with mitochondria of the cells. In the absence of serum proteins only cationic UPy-aggregates could be effectively internalized by THP-1 derived macrophages, and the internalized UPy-aggregates either co-localized with mitochondria or displayed as vesicular structures. While the cationic UPy-aggregates were hardly internalized by HK-2 cells and could only bind to the membrane of HK-2 cells. With adding and increasing the amount of serum albumin in the cell culture medium, the cationic UPy-aggregates were gradually taken up by HK-2 cells without anchoring on the cell membranes. It is proposed that the serum albumin regulates the cellular internalization of UPy-aggregates. These results provide fundamental insights for the fabrication of supramolecular polymer nanostructures for intracellular delivery of therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures

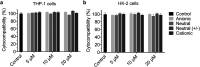




Similar articles
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
From natural to synthetic hydrogels: how much biochemical complexity is required for mechanotransduction?J Mater Chem B. 2025 Jan 2;13(2):610-621. doi: 10.1039/d4tb01774a. J Mater Chem B. 2025. PMID: 39601124
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
[Volume and health outcomes: evidence from systematic reviews and from evaluation of Italian hospital data].Epidemiol Prev. 2013 Mar-Jun;37(2-3 Suppl 2):1-100. Epidemiol Prev. 2013. PMID: 23851286 Italian.
-
Eliciting adverse effects data from participants in clinical trials.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jan 16;1(1):MR000039. doi: 10.1002/14651858.MR000039.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29372930 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pelaz B. Alexiou C. Alvarez-Puebla R. A. Alves F. Andrews A. M. Ashraf S. Balogh L. P. Ballerini L. Bestetti A. Brendel C. Bosi S. Carril M. Chan W. C. W. Chen C. Chen X. Chen X. Cheng Z. Cui D. Du J. Dullin C. Escudero A. Feliu N. Gao M. George M. Gogotsi Y. Grünweller A. Gu Z. Halas N. J. Hampp N. Hartmann R. K. Hersam M. C. Hunziker P. Jian J. Jiang X. Jungebluth P. Kadhiresan P. Kataoka K. Khademhosseini A. Kopeček J. Kotov N. A. Krug H. F. Lee D. S. Lehr C.-M. Leong K. W. Liang X.-J. Ling Lim M. Liz-Marzán L. M. Ma X. Macchiarini P. Meng H. Möhwald H. Mulvaney P. Nel A. E. Nie S. Nordlander P. Okano T. Oliveira J. Park T. H. Penner R. M. Prato M. Puntes V. Rotello V. M. Samarakoon A. Schaak R. E. Shen Y. Sjöqvist S. Skirtach A. G. Soliman M. G. Stevens M. M. Sung H.-W. Tang B. Z. Tietze R. Udugama B. N. VanEpps J. S. Weil T. Weiss P. S. Willner I. Wu Y. Yang L. Yue Z. Zhang Q. Zhang Q. Zhang X.-E. Zhao Y. Zhou X. Parak W. J. ACS Nano. 2017;11:2313–2381. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.6b06040. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Li Y. Li P. Li R. Xu Q. Adv. Ther. 2020;3:2000178. doi: 10.1002/adtp.202000178. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

