Angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers for preventing the progression of diabetic kidney disease
- PMID: 38682786
- PMCID: PMC11057222
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD006257.pub2
Angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers for preventing the progression of diabetic kidney disease
Abstract
Background: Guidelines suggest that adults with diabetes and kidney disease receive treatment with angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitors (ACEi) or angiotensin receptor blockers (ARB). This is an update of a Cochrane review published in 2006.
Objectives: We compared the efficacy and safety of ACEi and ARB therapy (either as monotherapy or in combination) on cardiovascular and kidney outcomes in adults with diabetes and kidney disease.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Kidney and Transplants Register of Studies to 17 March 2024 through contact with the Information Specialist using search terms relevant to this review. Studies in the Register are identified through searches of CENTRAL, MEDLINE, and EMBASE, conference proceedings, the International Clinical Trials Registry Platform (ICTRP) Search Portal, and ClinicalTrials.gov.
Selection criteria: We included studies evaluating ACEi or ARB alone or in combination, compared to each other, placebo or no treatment in people with diabetes and kidney disease.
Data collection and analysis: Two authors independently assessed the risk of bias and extracted data. Summary estimates of effect were obtained using a random-effects model, and results were expressed as risk ratios (RR) and their 95% confidence intervals (CI) for dichotomous outcomes and mean difference (MD) or standardised mean difference (SMD) and 95% CI for continuous outcomes. Confidence in the evidence was assessed using the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) approach.
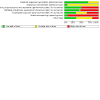
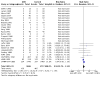
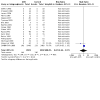
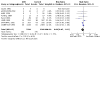
Main results: One hundred and nine studies (28,341 randomised participants) were eligible for inclusion. Overall, the risk of bias was high. Compared to placebo or no treatment, ACEi may make little or no difference to all-cause death (24 studies, 7413 participants: RR 0.91, 95% CI 0.73 to 1.15; I2 = 23%; low certainty) and with similar withdrawals from treatment (7 studies, 5306 participants: RR 1.03, 95% CI 0.90 to 1.19; I2 = 0%; low certainty). ACEi may prevent kidney failure (8 studies, 6643 participants: RR 0.61, 95% CI 0.39 to 0.94; I2 = 0%; low certainty). Compared to placebo or no treatment, ARB may make little or no difference to all-cause death (11 studies, 4260 participants: RR 0.99, 95% CI 0.85 to 1.16; I2 = 0%; low certainty). ARB have uncertain effects on withdrawal from treatment (3 studies, 721 participants: RR 0.85, 95% CI 0.58 to 1.26; I2 = 2%; low certainty) and cardiovascular death (6 studies, 878 participants: RR 3.36, 95% CI 0.93 to 12.07; low certainty). ARB may prevent kidney failure (3 studies, 3227 participants: RR 0.82, 95% CI 0.72 to 0.94; I2 = 0%; low certainty), doubling of serum creatinine (SCr) (4 studies, 3280 participants: RR 0.84, 95% CI 0.72 to 0.97; I2 = 32%; low certainty), and the progression from microalbuminuria to macroalbuminuria (5 studies, 815 participants: RR 0.44, 95% CI 0.23 to 0.85; I2 = 74%; low certainty). Compared to ACEi, ARB had uncertain effects on all-cause death (15 studies, 1739 participants: RR 1.13, 95% CI 0.68 to 1.88; I2 = 0%; low certainty), withdrawal from treatment (6 studies, 612 participants: RR 0.91, 95% CI 0.65 to 1.28; I2 = 0%; low certainty), cardiovascular death (13 studies, 1606 participants: RR 1.15, 95% CI 0.45 to 2.98; I2 = 0%; low certainty), kidney failure (3 studies, 837 participants: RR 0.56, 95% CI 0.29 to 1.07; I2 = 0%; low certainty), and doubling of SCr (2 studies, 767 participants: RR 0.88, 95% CI 0.52 to 1.48; I2 = 0%; low certainty). Compared to ACEi plus ARB, ACEi alone has uncertain effects on all-cause death (6 studies, 1166 participants: RR 1.08, 95% CI 0.49 to 2.40; I2 = 20%; low certainty), withdrawal from treatment (2 studies, 172 participants: RR 0.78, 95% CI 0.33 to 1.86; I2 = 0%; low certainty), cardiovascular death (4 studies, 994 participants: RR 3.02, 95% CI 0.61 to 14.85; low certainty), kidney failure (3 studies, 880 participants: RR 1.36, 95% CI 0.79 to 2.32; I2 = 0%; low certainty), and doubling of SCr (2 studies, 813 participants: RR 1.14, 95% CI 0.70 to 1.85; I2 = 0%; low certainty). Compared to ACEi plus ARB, ARB alone has uncertain effects on all-cause death (7 studies, 2607 participants: RR 1.02, 95% CI 0.76 to 1.37; I2 = 0%; low certainty), withdrawn from treatment (3 studies, 1615 participants: RR 0.81, 95% CI 0.53 to 1.24; I2 = 0%; low certainty), cardiovascular death (4 studies, 992 participants: RR 3.03, 95% CI 0.62 to 14.93; low certainty), kidney failure (4 studies, 2321 participants: RR 1.15, 95% CI 0.67 to 1.95; I2 = 29%; low certainty), and doubling of SCr (3 studies, 2252 participants: RR 1.18, 95% CI 0.85 to 1.64; I2 = 0%; low certainty). Comparative effects of different ACEi or ARB and low-dose versus high-dose ARB were rarely evaluated. No study compared different doses of ACEi. Adverse events of ACEi and ARB were rarely reported.
Authors' conclusions: ACEi or ARB may make little or no difference to all-cause and cardiovascular death compared to placebo or no treatment in people with diabetes and kidney disease but may prevent kidney failure. ARB may prevent the doubling of SCr and the progression from microalbuminuria to macroalbuminuria compared with a placebo or no treatment. Despite the international guidelines suggesting not combining ACEi and ARB treatment, the effects of ACEi or ARB monotherapy compared to dual therapy have not been adequately assessed. The limited data availability and the low quality of the included studies prevented the assessment of the benefits and harms of ACEi or ARB in people with diabetes and kidney disease. Low and very low certainty evidence indicates that it is possible that further studies might provide different results.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00168857 NCT00274118 NCT00241085 NCT02620306 NCT00317915 NCT00381134 NCT00141453 NCT00308347 NCT00494715 NCT00242346 NCT00000516 NCT00419835 NCT00153101 NCT00555217 NCT00340678 NCT00252694 NCT00252720 NCT00252733 NCT00095654 NCT00171600 NCT00208221 NCT04238702 NCT05189015 NCT05593575 NCT00240422 NCT00905528 NCT05753696.
Copyright © 2024 The Cochrane Collaboration. Published by John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Patrizia Natale: No relevant interests were disclosed
Suetonia Palmer: No relevant interests were disclosed
Sakar Navaneethan: Baylor College of Medicine (Employment), AstraZeneca (Independent Contractor ‐ Data And Safety Monitoring), Vifor Pharma (Independent Contractor ‐ Consultant), Eli Lilly and Company (Independent Contractor ‐ Consultant), Boehringer Ingelheim (Independent Contractor ‐ Consultant), Keryx Biopharmaceuticals, Inc. (Money paid to institution: Grant / Contract), Bayer (Independent Contractor ‐ End Point Review Committee), U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (Employment)
Jonathan Craig: No relevant interests were disclosed
Giovanni Strippoli: No relevant interests were disclosed
Figures







































































Update of
-
Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor antagonists for preventing the progression of diabetic kidney disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006 Oct 18;2006(4):CD006257. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006257. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Apr 29;4:CD006257. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006257.pub2. PMID: 17054288 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
ABCD 1996 {published data only}
-
- Estacio RO, Jeffers B, Biggerstaff S, Schrier RW. Effects of a calcium channel antagonist versus an ACE inhibitor on diabetic nephropathy [abstract no: S1064]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1998;9(Program & Abstracts):114A. [CENTRAL: CN-00445260]
-
- Estacio RO, Jeffers BW, Gifford N, Schrier RW. Effect of blood pressure control on diabetic microvascular complications in patients with hypertension and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2000;23 Suppl 2:B54-64. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Estacio RO, Jeffers BW, Hiatt WR, Biggerstaff SL, Gifford N, Schrier RW. The effect of nisoldipine as compared with enalapril on cardiovascular outcomes in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes and hypertension. New England Journal of Medicine 1998;338(10):645-52. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Estacio RO, Mehler P, Esler A, Schrier RW. Aggressive lowering of blood pressure in normotensive type 2 diabetic patients: beneficial effects on stroke, progression of retinopathy and nephropathy [abstract no: A0763]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2001;12(Program & Abstracts):146A. [CENTRAL: CN-00445261]
-
- Estacio RO, Savage S, Nagel NJ, Schrier RW. Baseline characteristics of participants in the Appropriate Blood pressure Control in Diabetes trial. Controlled Clinical Trials 1996;17(3):242-57. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
ABCD‐2V 2006 {published data only}
-
- Estacio RO, Coll JR, Tran ZV, Schrier RW. Effect of intensive blood pressure control with valsartan on urinary albumin excretion in normotensive patients with type 2 diabetes. American Journal of Hypertension 2006;19(12):1241-8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Estacio RO, Esler A, Lundgren R, Schrier RW. Aggressive blood pressure control with valsartan in normotensive type 2 diabetic patients results in regression of albuminuria [abstract no: SU-PO165]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2004;15(Oct):568A. [CENTRAL: CN-00644364]
Abe 2007a {published data only}
-
- Abe H, Minatoguchi S, Ohashi H, Murata I, Minagawa T, Okuma T, et al. Renoprotective effect of the addition of losartan to ongoing treatment with an angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor in type-2 diabetic patients with nephropathy. Hypertension Research - Clinical & Experimental 2007;30(10):929-35. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Ahmad 1997 {published data only}
-
- Ahmad J, Siddiqui MA, Ahmad H. Effective postponement of diabetic nephropathy with enalapril in normotensive type 2 diabetic patients with microalbuminuria. Diabetes Care 1997;20(10):1576-81. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Ahmad 2003 {published data only}
-
- Ahmad J, Shafique S, Abidi SM, Parwez I. Effect of 5-year enalapril therapy on progression of microalbuminuria and glomerular structural changes in type 1 diabetic subjects. Diabetes Research & Clinical Practice 2003;60(2):131-8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
AIPRI 1996 {published data only}
-
- Apperloo AJ, Rensma PL. Effect of benazepril in chronic renal insufficiency. New England Journal of Medicine 1996;335(8):596-7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Curren CG. Effect of benazepril in chronic renal insufficiency. New England Journal of Medicine 1996;335(8):597. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Hogan TJ, Elliott WJ, Seto AH, Bakris GL. Antihypertensive treatment with and without benazepril in patients with chronic renal insufficiency: a US economic evaluation. Pharmacoeconomics 2002;20(1):37-47. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Locatelli F, Carbarns IR, Maschio G, Mann JF, Ponticelli C, Ritz E, et al. Long-term progression of chronic renal insufficiency in the AIPRI Extension Study. The Angiotensin-Converting-Enzyme Inhibition in Progressive Renal Insufficiency Study Group. Kidney International - Supplement 1997;63:S63-6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Locatelli F, Del Vecchio L, Andrulli S, Marai P, Tentori F. The role of underlying nephropathy in the progression of renal disease. Kidney International - Supplement 2000;75:S49-55. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
AMADEO 2008 {published data only}
-
- AMADEO: A trial to compare telmisartan 40mg titrated to 80mg versus losartan 100mg in hypertensive type-2 diabetic patients with overt nephropathy. The Protection Trial Programme - Micardis Protection 2005. [CENTRAL: CN-00583661]
-
- Bakris G, Burgess E, Weir M, Davidai G, Koval S. Telmisartan is more effective than losartan in reducing proteinuria in patients with diabetic nephropathy. Kidney International 2008;74(3):364-9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Bakris G, Burgess E, Weir M, Koval S. Influence of glycaemic control on proteinuria in patients with type 2 diabetes and overt nephropathy and hypertension: results of the AMADEO trial [abstract no: 0601-P]. Diabetes 2007;56(Suppl 1):A159. [CENTRAL: CN-00765394]
-
- Moranne O, Bakris G, Fafin C, Favre G, Pradier C, Esnault VL. Determinants and changes associated with aldosterone breakthrough after angiotensin II receptor blockade in patients with type 2 diabetes with overt nephropathy. Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology: CJASN 2013;8(10):1694-701. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
-
- Moranne OP, Bakris GL, Esnault VL. Predictors of aldosterone breakthrough with ARB treatment in diabetic nephropathy [abstract no: F-FC315]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2009;20(Abstract Suppl):73A.
Arai 2008 {published data only}
-
- Arai T, Ohashi H. Angiotensin receptor blockers and microalbuminuria in hypertensive patients with early (microalbuminuric) stage diabetic nephropathy. Molecular Medicine Reports 2008;1(3):391-3. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Arpitha 2020 {published data only}
-
- Arpitha KS, Lakshminarayana K. A comparative study of efficacy of enalapril versus telmisartan in patients with diabetic nephropathy. National Journal of Physiology, Pharmacy & Pharmacology 2020;10(10):894‐9. [EMBASE: 2005173747]
ATLANTIS 2000 {published data only}
-
- O'Hare P, Bilbous R, Mitchell T, O'Callaghan CJ, Viberti GC. Low-dose ramipril reduces microalbuminuria in type 1 diabetic patients without hypertension: results of a randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Care 2000;23(12):1823-9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Atmaca 2006 {published data only}
-
- Atmaca A, Gedik O. Effects of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blockers, and their combination on microalbuminuria in normotensive patients with type 2 diabetes. Advances in Therapy 2006;23(4):615-22. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Bakris 1994 {published data only}
-
- Bakris GL, Slataper R, Vicknair N, Sadler R. ACE inhibitor mediated reductions in renal size and microalbuminuria in normotensive, diabetic subjects. Journal of Diabetes & its Complications 1994;8(1):2-6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Bansal 2004 {published data only}
-
- Bansal R, Agarwal SK, Tiwari SC. Short term effects of maximum tolerable doses of ACE-inhibitor (lisinopril), angiotensin receptor blocker (losartan) and add-on losartan on proteinuria and glomerular filtration rate [abstract]. Indian Journal of Nephrology 2004;14(3):110-1. [CENTRAL: CN-01658567]
-
- Bansal R, Agarwal SK. Study of maximum tolerable doses of ACE-I (lisinopril), ARB (losartan) and add-on ARB on proteinuria and progression of renal disease in patients of type 2 diabetes with early nephropathy: results of one year follow up [abstract no: CNO-9]. In: 36th Annual Conference of the Indian Society of Nephrology (ISNCON 2005); 2005 Dec 1-3; Cochin, India. 2005:34. [CENTRAL: CN-01658566]
Bauer 1992 {published data only}
-
- Bauer JH, Reams GP, Hewett J, Klachko D, Lau A, Messina C, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial to evaluate the effect of enalapril in patients with clinical diabetic nephropathy. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 1992;20(5):443-57. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Bilo 1993 {published data only}
-
- Bilo H, Kluitman E, Ballegooie E, Potter van Loon BJ, Bakker K, Michels B, et al. Long term use of captopril or nifedipine in normotensive microalbuminuric patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Research 1993;23(3):115-22. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Bilo HJ, Ballegooie E, Potter van Loon BJ, Gans RO, Donker AJ. Captopril or nifedipine in normotensive microalbuminuric IDDM patients [abstract no: 85P]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1992;3(3):331. [CENTRAL: CN-00583442]
Bojestig 2001 {published data only}
-
- Bojestig M, Karlberg BE, Lindstrom T, Nystrom FH. Reduction of ACE activity is insufficient to decrease microalbuminuria in normotensive patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2001;24(5):919-24. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
CALM 2000 {published data only}
-
- Cooper ME, Mogensen CE, CALM Study Group. Role of candesartan, lisinopril and their combination on blood pressure and albuminuria in hypertensive microalbuminuric diabetic subjects [abstract no: 84]. Nephrology 2000;5(3):A87. [CENTRAL: CN-00509141]
-
- Mogensen CE, Neldam S, Tikkanen I, Oren S, Viskoper R, Watts RW, et al. Randomised controlled trial of dual blockade of renin-angiotensin system in patients with hypertension, microalbuminuria, and non-insulin dependent diabetes: the candesartan and lisinopril microalbuminuria (CALM) study. BMJ 2000;321(7274):1440-4. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
CALM II 2003 {published data only}
-
- Andersen NH, Knudsen ST, Poulsen PL, Poulsen SH, Helleberg K, Eiskjaer H, et al. Dual blockade with candesartan cilexetil and lisinopril in hypertensive patients with diabetes mellitus: rationale and design. Journal of the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System 2003;4(2):96-9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Andersen NH, Poulsen PL, Knudsen ST, Poulsen SH, Eiskjaer H, Hansen KW, et al. Long-term dual blockade with candesartan and lisinopril in hypertensive patients with diabetes: the CALM II study. Diabetes Care 2005;28(2):273-7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Knudsen ST, Andersen NH, Poulsen SH, Eiskjaer H, Hansen KW, Helleberg K, et al. Pulse pressure lowering effect of dual blockade with candesartan and lisinopril vs. high-dose ACE inhibition in hypertensive type 2 diabetic subjects: a CALM II study post-hoc analysis. American Journal of Hypertension 2008;21(2):172-6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Capek 1994 {published data only}
-
- Capek M, Schnack C, Ludvik B, Kautzky-Willer A, Banyai M, Prager R. Effects of captopril treatment versus placebo on renal function in type 2 diabetic patients with microalbuminuria: a long-term study. Clinical Investigator 1994;72(12):961-6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
CAPTOPRIL 1992 {published data only}
-
- Bain R, Rohde R, Hunsicker LG, McGill J, Kobrin S, Lewis EJ. A controlled clinical trial of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition in type I diabetic nephropathy: study design and patient characteristics. The Collaborative Study Group. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1992;3(4 Suppl):S97-103. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Breyer J, McGill J, Nahman S, Lewis E, Bain R, Cooper M, et al. Predictors of the rate of progression of renal insufficiency in patients with insulin-dependent diabetes and overt diabetic nephropathy [abstract no: 38P]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1993;4(Program & Abstracts):301. [CENTRAL: CN-00483327]
-
- Breyer JA, Bain RP, Evans JK, Nahman NS Jr, Lewis EJ, Cooper M, et al. Predictors of the progression of renal insufficiency in patients with insulin-dependent diabetes and overt diabetic nephropathy. The Collaborative Study Group. Kidney International 1996;50(5):1651-8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Breyer JA, Hunsicker LG, Bain RP, Lewis EJ. Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition in diabetic nephropathy. The Collaborative Study Group. Kidney International - Supplement 1994;45:S156-60. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Hebert LA, Bain RP, Verme D, Cattran D, Whittier FC, Tolchin N, et al. Remission of nephrotic range proteinuria in type I diabetes. Collaborative Study Group. Kidney International 1994;46(6):1688-93. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Carella 1999 {published data only}
-
- Carella MJ, Gossain VV, Jones J. The effects of a low-dose regimen of fosinopril on elevated urinary albumin excretion in normotensive type 1 diabetic patients. Journal of Medicine 1999;30(5-6):305-20. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Castelao 1999 {published data only}
-
- Castelao AM, Ramos R, Sanchez-Zamorano MA, Alsina J. Comparison of losartan vs enalapril in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with diabetic nephropathy [abstract no: A0652]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1999;10(Program & Abstracts):127A. [CENTRAL: CN-00550750]
CAT 2008 {published data only}
-
- Nakao N, Fujimori A, Hasegawa A, Matsushima H. A combination treatment of an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor and angiotensin-receptor blocker can inhibit plasma renin-angiotensin system more completely and persistently as compared with high or moderate dose angiotensin-receptor blocker treatments in type 2 diabetic nephropathy: nested cohort study of candesartan-trandolapril trial in diabetic CKD (CAT Trial) [abstract no: MP156]. NDT Plus 2008;1(Suppl 1):ii285.
Chase 1993 {published data only}
-
- Chase HP, Garg SK, Harris S, Hoops S, Jackson WE, Holmes DL. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor treatment for young normotensive diabetic subjects: a two-year trial. Annals of Ophthalmology 1993;25(8):284-9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Chen 2018b {published data only}
-
- Chen Y, Liu P, Chen X, Li Y, Zhang F, Wang Y. Effects of different doses of irbesartan combined with spironolactone on urinary albumin excretion rate in elderly patients with early type 2 diabetic nephropathy. American Journal of the Medical Sciences 2018;355(5):418-24. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Cheng 1990 {published data only}
-
- Cheng IK, Ma JT, Yeh GR, Chan MK. Comparison of captopril and enalapril in the treatment of hypertension in patients with non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus and nephropathy. International Urology & Nephrology 1990;22(3):295-303. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Cocchi 1989 {published data only}
-
- Cocchi R, Degli EE, et al. Does captopril reduce proteinuria in normotensive, non-azotaemic diabetic patients? [abstract]. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 1989;4(5):433. [CENTRAL: CN-00260423]
Cordonnier 1999 {published data only}
-
- Cordonnier DJ, Pinel N, Barro C, Maynard M, Zaoui P, Halimi S, et al. Expansion of cortical interstitium is limited by converting enzyme inhibition in type 2 diabetic patients with glomerulosclerosis. The Diabiopsies Group. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1999;10(6):1253-63. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Cordonnier DJ, Pinel N, Barro C, Zaoui P. Renal interstital expansion is modified by perindopril in true diabetic glomerulosclerosis (DG) in type 2 (NIDDM) diabetic patients. a 2 years sequential biopsy study [abstract no: A0522]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1997;8(Program & Abstracts):110A. [CENTRAL: CN-00444912]
-
- Cordonnier DJ, Pinel N. Renal interstitial expansion is modified by perindopril in true diabetic glomerulosclerosis (DG) in type 2 (NIDDM) diabetic patients. A 2 years sequential biopsy study [abstract]. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 1997;12(9):A89. [CENTRAL: CN-00261382]
-
- Langham R, Gow RM, Zhang Y, Kelly DJ, Cordonnier D, Pinel N, et al. Blockade of the renin-angiotensin system attenuates renal TGF-b gene expression and activity in human diabetic nephropathy [abstract no: M-PO20058]. Nephrology 2005;10(Suppl):A30.
-
- Langham RG, Kelly DJ, Cox AJ, Thomson NM, Holthofer H, Zaoui P, et al. Proteinuria and the expression of the podocyte slit diaphragm protein, nephrin, in diabetic nephropathy: effects of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition [abstract no: F-PO529]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2002;13(September, Program & Abstracts):167A. - PubMed
Crepaldi 1998 {published data only}
-
- Crepaldi G, Carta Q, Deferrari G, Mangili R, Navalesi R, Santeusanio F, et al. Effects of lisinopril and nifedipine on the progression to overt albuminuria in IDDM patients with incipient nephropathy and normal blood pressure. The Italian Microalbuminuria Study Group in IDDM. Diabetes Care 1998;21(1):104-10. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
DETAIL 2002 {published data only}
-
- Barnett A. Preventing renal complications in type 2 diabetes: results of the diabetics exposed to telmisartan and enalapril trial. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2006;17(4 Suppl 2):S132-5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Barnett AH, Bain SC, Bouter P, Karlberg B, Madsbad S, Jervell J, et al. Angiotensin-receptor blockade versus converting-enzyme inhibition in type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. New England Journal of Medicine 2004;351(19):1952-61. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- DETAIL: Diabetics exposed to telmisartan and enalapril [brochure]. The Protection Trial Programme - Micardis Protection 2005:20.
-
- Rippin J, Bain SC, Barnett AH, DETAIL S. Rationale and design of diabetics exposed to telmisartan and enalapril (DETAIL) study [Erratum in: N Engl J Med. 2005 Apr 21;352(16)1731]. Journal of Diabetes & its Complications 2002;16(3):195-200. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Deyneli 2006 {published data only}
-
- Deyneli O, Yavuz D, Velioglu A, Cacina H, Aksoy N, Haklar G, et al. Effects of ACE inhibition and angiotension II receptor blockade on glomerular basement membrane protein excretion and change selectivity in type 2 diabetic patients. JRAAS - Journal of the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System 2006;7(2):98-103. [EMBASE: 44383504] - PubMed
DIABHYCAR 1996 {published data only}
-
- Azizi M, Menard J, Peyrard S, Lievre M, Marre M, Chatellier G. Assessment of patients' and physicians' compliance to an ACE inhibitor treatment based on urinary N-acetyl Ser-Asp-Lys-Pro determination in the Noninsulin-Dependent Diabetes, Hypertension, Microalbuminuria, Proteinuria, Cardiovascular Events, and Ramipril (DIABHYCAR) study. Diabetes Care 2006;29(6):1331-6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Lievre M, Marre M, Chatellier G, Plouin P, Reglier J, Richardson L, et al. The non-insulin-dependent diabetes, hypertension, microalbuminuria or proteinuria, cardiovascular events, and ramipril (DIABHYCAR) study: design, organization, and patient recruitment. DIABHYCAR Study Group. Controlled Clinical Trials 2000;21(4):383-96. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Marre M, Lievre M, Chatellier G, Mann J, Passa P, Menard J. Effects of low dose ramipril on cardiovascular and renal outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and raised excretion of urinary albumin: randomised, double blind, placebo controlled trial (the DIABHYCAR study). BMJ 2004;328(7438):495-9. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
-
- Marre M, Lievre M, Chatellier G, Vasmant D, Mann J, Passa P, et al. Low-dose ramipril (1.25 mg/day) does not decrease cardiovascular events in type 2 diabetes patients with microalbuminuria/proteinuria: the DIABHYCAR (type 2 DIABetes, HYpertension, CArdiovascular events and Ramipril) study [abstract no: 185]. In: 38th Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD); 2002 Sept 1-5; Budapest, Hungary. 2002.
-
- Marre M, Lievre M, Vasmant D, Gallois Y, Hadjadj S, Reglier JC, et al. Determinants of elevated urinary albumin in the 4,937 type 2 diabetic subjects recruited for the DIABHYCAR Study in Western Europe and North Africa. Diabetes Care 2000;23 Suppl 2:B40-8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Dragovic 2003 {published data only}
-
- Dragovic T, Hrvacevic R, Ajdinovic B, Vujanic S. Efficacy of valsartan in the treatment of persistent microalbuminuria in normotensive patients with type 1 diabetes [Efikasnost valsartana u terapiji perzistentne mikroalbuminurije kod normotenzivnih bolesnika sa tipom 1 secerne bolesti]. Vojnosanitetski Pregled 2003;60(5):555-64. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Dragovic T, Mijuskovic Z, Karajovic J, Andelkovic Z. Effect of AT1 receptor blockers on plasma lipid profiles in type 1 diabetic patients with incipient diabetic nephropathy [Efekat primene blokatora AT1 receptora na lipidni profil kod bolesnika sa secernom bolesti tip 1 I pocetnom dijabetesnom nefropatijom]. Jugoslovenska Medicinska Biohemija 2005;24(1):21-6. [EMBASE: 40188044]
DROP 2006 {published data only}
-
- Hollenberg NK, Parving H, Viberti G, Remuzzi G. The Diovan Reduction Of Proteinutria (DROP) study: albuminuria response to high-doses of valsartan in type 2 diabetes mellitus [abstract no: TH-PO244]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2006;17(Abstracts):158A. [CENTRAL: CN-00602042]
-
- Hollenberg NK, Parving HH, Viberti G, Remuzzi G, Ritter S, Zelenkofske S, et al. Albuminuria response to very high-dose valsartan in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Journal of Hypertension 2007;25(9):1921-6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Weir MR, Hollenberg NK, Remuzzi G, Zappe DH, Meng X, Parving HH. Varying patterns of the antihypertensive and antialbuminuric response to higher doses of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system blockade in albuminuric hypertensive type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Journal of Hypertension 2011;29(10):2031-7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Weir MR, Hollenberg NK, Zappe DH, Meng X, Parving HH, Viberti G, et al. Antihypertensive effects of double the maximum dose of valsartan in African-American patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and albuminuria. Journal of Hypertension 2010;28(1):186-93. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Durruty 1990 {published data only}
-
- Durruty P, Krause P, Perez F, Garcia de los RM, Lopez G, Durruty G. Microalbuminuria in insulin-dependent diabetics: the prevention of diabetic nephropathy [Microalbuminuria en diabeticos insulinodependientes: prevencion de la nefropatia diabetica]. Revista Medica de Chile 1990;118(12):1319-25. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Durruty 1996 {published data only}
-
- Durruty P, Tapia JC, Ugarte C, Perez E, Krause P, Soto N, et al. Urinary albumin excretion in non-insulin-dependent diabetic patients. Effects of an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor [Excrecion urinaria de albumina en diabeticos no insulino-dependientes. Efecto de un inhibidor de la enzima convertidora de angiotensina]. Revista Medica de Chile 1996;124(9):1036-44. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
ESPRIT 1992 {published data only}
-
- Effect of 3 years of antihypertensive therapy on renal structure in type 1 diabetic patients with albuminuria: the European Study for the Prevention of Renal Disease in Type 1 Diabetes (ESPRIT). Diabetes 2001;50(4):843-50. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Viberti GC, Bilous RW, El Nahas AM, Hersh A, Remuzzi G. A pilot, multicentre, randomized, double-blind, parallel study evaluating the efficacy and tolerability of enalapril, nifedipine retard and placebo on the evolution of diabetic nephropathy in normotensive, insulin-dependent diabetic patients with increased urinary albumin excretion. Journal of Nephrology 1992;5:99-109.
-
- White KE, Bilous RW, Marshall SM, El Nahas M, Remuzzi G, Piras G, et al. Podocyte number in normotensive type 1 diabetic patients with albuminuria. Diabetes 2002;51(10):3083-9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
EUCLID 1997 {published data only}
-
- Chaturvedi N, Sjolie AK, Stephenson JM, Abrahamian H, Keipes M, Castellarin A, et al. Effect of lisinopril on progression of retinopathy in normotensive people with type 1 diabetes. The EUCLID Study Group. EURODIAB Controlled Trial of Lisinopril in Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus. Lancet 1998;351(9095):28-31. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Fuller JH, EUCLID Study Group, Anzalone D. Renal effect of lisinopril in insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM) without hypertension [abstract no: A0560]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1996;7(9):1357. [CENTRAL: CN-00583621]
-
- Penno G, Chaturvedi N, Talmud PJ, Cotroneo P, Manto A, Nannipieri M, et al. Effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) gene polymorphism on progression of renal disease and the influence of ACE inhibition in IDDM patients: findings from the EUCLID randomized controlled trial. EURODIAB Controlled Trial of Lisinopril in IDDM. Diabetes 1998;47(9):1507-11. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Randomised placebo-controlled trial of lisinopril in normotensive patients with insulin-dependent diabetes and normoalbuminuria or microalbuminuria. The EUCLID Study Group. Lancet 1997;349(9068):1787-92. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Schalkwijk CG, Chaturvedi N, Twaafhoven H, Hinsbergh VW, Stehouwer CD. Amadori-albumin correlates with microvascular complications and precedes nephropathy in type 1 diabetic patients. European Journal of Clinical Investigation 2002;32(7):500-6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
FANTASTIC 2017 {published data only}
-
- Yoo TH, Hong SJ, Kim S, Shin S, Kim DK, Lee JP, et al. The FimAsartaN proTeinuriA SusTaIned reduCtion in comparison with losartan in diabetic chronic kidney disease (FANTASTIC) trial. Hypertension Research - Clinical & Experimental 2022;45(12):2008‐17. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Fogari 2013a {published data only}
-
- Fogari R, Mugellini A, Zoppi A, Gualtierotti R, Lazzari P, Derosa G, et al. Effect of imidapril versus ramipril on urinary albumin excretion in hypertensive patients with type 2 diabetes and microalbuminuria. Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy 2013;14(18):2463-73. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Garg 1998 {published data only}
-
- Garg SK, Chase HP, Jackson WE, Harris S, Carmain JA, Hansen MH, et al. Renal and retinal changes after treatment with ramipril and pentoxifyline in subjects with IDDM. Annals of Ophthalmology - Glaucoma 1998;30(1):33-7. [EMBASE: 28128821]
Hansen 1994 {published data only}
-
- Captopril reduces the risk of nephropathy in IDDM patients with microalbuminuria. The Microalbuminuria Captopril Study Group. Diabetologia 1996;39(5):587-93. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Hansen KW, Klein F, Christensen PD, Sorensen K, Andersen PH, Moller J, et al. Effects of captopril on ambulatory blood pressure, renal and cardiac function in microalbuminuric type 1 diabetic patients. Diabete et Metabolisme 1994;20(5):485-93. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Mogensen CE, Cooper M, European Microalbuminuria Captopril Study Group. Captopril (C) delays progression to overt renal disease in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM) patients with microalbuminuria [abstract]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1992;3(3):336. [CENTRAL: CN-00461342]
-
- Viberti G, Mogensen CE, Groop LC, Pauls JF. Effect of captopril on progression to clinical proteinuria in patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus and microalbuminuria. European Microalbuminuria Captopril Study Group. JAMA 1994;271(4):275-9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Viberti G, European Microalbuminuria Captopril Study Group (EMCSG). The effect of captopril on the progression of microalbuminuria in insulin-dependent diabetes [abstract]. In: 12th International Congress of Nephrology; 1993 Jun 13-18; Jerusalem, Israel. 1993:424. [CENTRAL: CN-00740489]
Hommel 1995 {published data only}
-
- Hommel E, Jensen B, Parving H. Long-term effect of captopril on kidney function in normotensive insulin dependent diabetic patients (IDDM) with diabetic nephropathy [abstract no: 444]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1995;6(3):450. [CENTRAL: CN-00484393]
HOPE 1996 {published data only}
-
- Effects of ramipril on cardiovascular and microvascular outcomes in people with diabetes mellitus: results of the HOPE study and MICRO-HOPE substudy. Heart Outcomes Prevention Evaluation Study Investigators [Erratum appears in Lancet 2000 Sep 2;356(9232):860]. Lancet 2000;355(9200):253-9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Gerstein HC, Bosch J, Pogue J, Taylor DW, Zinman B, Yusuf S. Rationale and design of a large study to evaluate the renal and cardiovascular effects of an ACE inhibitor and vitamin E in high-risk patients with diabetes. The MICRO-HOPE Study. Microalbuminuria, cardiovascular, and renal outcomes. Heart Outcomes Prevention Evaluation. Diabetes Care 1996;19(11):1225-8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Gerstein HC, Pogue J, Mann JF, Lonn E, Dagenais GR, McQueen M, et al. The relationship between dysglycaemia and cardiovascular and renal risk in diabetic and non-diabetic participants in the HOPE study: a prospective epidemiological analysis. Diabetologia 2005;48(9):1749-55. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Gerstein HC. Diabetes and the HOPE study: implications for macrovascular and microvascular disease. International Journal of Clinical Practice. Supplement 2001;(117):8-12. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Hoogwerf BJ, Young JB. The HOPE study. Ramipril lowered cardiovascular risk, but vitamin E did not. Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine 2000;67(4):287-93. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
IDNT 2001 {published data only}
-
- Aguilar D, Goldhaber SZ, Gans DJ, Levey AS, Porush JG, Lewis JB, et al. Clinically unrecognized Q-wave myocardial infarction in patients with diabetes mellitus, systemic hypertension, and nephropathy. American Journal of Cardiology 2004;94(3):337-9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Atkins RC, Briganti EM, Lewis JB, Hunsicker LG, Braden G, Champion de Crespigny PJ, et al. Proteinuria reduction and progression to renal failure in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and overt nephropathy. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 2005;45(2):281-7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Atkins RC, Briganti EM, Wiegmann TB. Effect of baseline proteinuria and change in proteinuria with treatment on the risk of renal endpoints in the Irbesartan Diabetic Nephropathy Trial (IDNT) [abstract no: F-FC033]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2002;13(September, Program & Abstracts):7A. [CENTRAL: CN-00444265]
-
- Atkins RC, Jerums G, Gilbert RE, Lewis EJ, Hunsicker LG. A clinical trial in patients with overt type 2 diabetic nephropathy [abstract no: 11]. Nephrology 2002;7(Suppl 3):A3. [CENTRAL: CN-00790194]
-
- Berl T, Hunsicker LG, Lewis JB, Pfeffer MA, Porush JG, Rouleau JL, et al. Cardiovascular outcomes in the Irbesartan Diabetic Nephropathy Trial of patients with type 2 diabetes and overt nephropathy. Annals of Internal Medicine 2003;138(7):542-9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
INNOVATION 2005 {published data only}
-
- INNOVATION: Incipient to overt: angiotensin II receptor blocker, telmisartan, investigation on type II diabetic nephropathy. The Protection Trial Programme - Micardis Protection 2005.
-
- Makino H, Haneda M, Babazono T, Moriya T, Ito S, Iawamoto Y, et al. Incipient to overt: angiotensin II blocker, telmisartan, investigation on type 2 diabetic nephropathy (INNOVATION) study [abstract no: TH-PO243]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2006;17(Abstracts):158A. [CENTRAL: CN-00601997]
-
- Makino H, Haneda M, Babazono T, Moriya T, Ito S, Iwamoto Y, et al. Microalbuminuria reduction with telmisartan in normotensive and hypertensive Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes: a post-hoc analysis of the Incipient to Overt: Angiotensin II Blocker, Telmisartan, Investigation on Type 2 Diabetic Nephropathy (INNOVATION) study. Hypertension Research - Clinical & Experimental 2008;31(4):657-64. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Makino H, Haneda M, Babazono T, Moriya T, Ito S, Iwamoto Y, et al. Prevention of transition from incipient to overt nephropathy with telmisartan in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2007;30(6):1577-8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Makino H, Haneda M, Babazono T, Moriya T, Ito S, Iwamoto Y, et al. The telmisartan renoprotective study from incipient nephropathy to overt nephropathy--rationale, study design, treatment plan and baseline characteristics of the incipient to overt: angiotensin II receptor blocker, telmisartan, Investigation on Type 2 Diabetic Nephropathy (INNOVATION) Study. Journal of International Medical Research 2005;33(6):677-86. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
IRMA‐2 2001 {published data only}
-
- Andersen S, Brochner-Mortensen J, Parving HH. Kidney function during and after withdrawal of long-term irbesartan treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes and microalbuminuria [abstract no: F-FC025]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2003;14(Nov):6A. - PubMed
-
- Andersen S, Brochner-Mortensen J, Parving HH. Kidney function during and after withdrawal of long-term irbesartan treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes and microalbuminuria. Diabetes Care 2003;26(12):3296-302. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Broedbaek K, Henriksen T, Weimann A, Petersen M, Andersen JT, Afzal S, et al. Long-term effects of Irbesartan treatment and smoking on nucleic acid oxidation in patients with type 2 diabetes and microalbuminuria: an Irbesartan in patients with type 2 diabetes and Microalbuminuria (IRMA 2) substudy. Diabetes Care 2011;34(5):1192-8. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
-
- Coyle D, Rodby R, Soroka S, Levin A, Muirhead N, Cotret PR, et al. Cost-effectiveness of irbesartan 300 mg given early versus late in patients with hypertension and a history of type 2 diabetes and renal disease: a Canadian perspective. Clinical Therapeutics 2007;29(7):1508-23. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
JAPAN‐IDDM 2002 {published data only}
-
- Katayama S, Kikkawa R, Isogai S, Sasaki N, Matsuura N, Tajima N, et al. Effect of captopril or imidapril on the progression of diabetic nephropathy in Japanese with type 1 diabetes mellitus: a randomized controlled study (JAPAN-IDDM). Diabetes Research & Clinical Practice 2002;55(2):113-21. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Jerums 2001 {published data only}
-
- Jerums G, Allen TJ, Campbell DJ, Cooper ME, Gilbert RE, Hammond JJ, et al. Long-term comparison between perindopril and nifedipine in normotensive patients with type 1 diabetes and microalbuminuria. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 2001;37(5):890-9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Thomas MC, Jerums G, Tsalamandris C, Macisaac R, Panagiotopoulos S, Cooper ME, et al. Increased tubular organic ion clearance following chronic ACE inhibition in patients with type 1 diabetes. Kidney International 2005;67(6):2494-9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Jerums 2004 {published data only}
-
- Jerums G, Allen TJ, Campbell DJ, Cooper ME, Gilbert RE, Hammond JJ, et al. Long-term renoprotection by perindopril or nifedipine in non-hypertensive patients with type 2 diabetes and microalbuminuria. Diabetic Medicine 2004;21(11):1192-9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kavgaci 2002 {published data only}
-
- Kavgaci H, Sahin A, Onder Ersoz H, Erem C, Ozdemir F. The effects of losartan and fosinopril in hypertensive type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Research & Clinical Practice 2002;58(1):19-25. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kitamura 2020 {published data only}
Ko 2005 {published data only}
-
- Ko GT, Tsang CC, Chan HC. Stabilization and regression of albuminuria in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes: a one-year randomized study of valsartan versus enalapril. Advances in Therapy 2005;22(2):155-62. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Krairittichai 2009 {published data only}
-
- Krairittichai U, Chaisuvannarat V. Effects of dual blockade of renin-angiotensin system in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with diabetic nephropathy. Journal of the Medical Association of Thailand 2009;92(5):611-7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Lacourciere 2000 {published data only}
-
- Lacourciere Y, Belanger A, Godin C, Halle JP, Ross S, Wright N, et al. Long-term comparison of losartan and enalapril on kidney function in hypertensive type 2 diabetics with early nephropathy. Kidney International 2000;58(2):762-9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Laffel 1995 {published data only}
-
- Captopril reduces the risk of nephropathy in IDDM patients with microalbuminuria. The Microalbuminuria Captopril Study Group. Diabetologia 1996;39(5):587-93. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Laffel L, Gans DJ, McGill JB, Captopril Nephropathy Study Group. Captopril decreases the rate of progression of renal disease in normotensive, insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM) patients with microalbuminuria [abstract]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1993;4(Program & Abstracts):304. [CENTRAL: CN-00484730]
-
- Laffel LM, McGill JB, Gans DJ. The beneficial effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition with captopril on diabetic nephropathy in normotensive IDDM patients with microalbuminuria. North American Microalbuminuria Study Group. American Journal of Medicine 1995;99(5):497-504. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Larsen 1990 {published data only}
-
- Larsen M, Hommel E, Parving HH, Lund-Andersen H. Protective effect of captopril on the blood-retina barrier in normotensive insulin-dependent diabetic patients with nephropathy and background retinopathy. Graefes Archive for Clinical & Experimental Ophthalmology 1990;228(6):505-9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Lebovitz 1994 {published data only}
-
- Lebovitz H, Cnaan A, Wiegmann T, Broadstone V, Schwartz S, Sica D, et al. Enalapril slows the progressioin of renal disease in non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM): results of a 3-yr multicenter, randomized, prospective, double-blind study [abstract]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1992;3(3):335. [CENTRAL: CN-0046114]
-
- Lebovitz HE, Wiegmann TB, Cnaan A, Shahinfar S, Sica DA, Broadstone V, et al. Renal protective effects of enalapril in hypertensive NIDDM: role of baseline albuminuria. Kidney International - Supplement 1994;45:S150-5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Lee 1990 {published data only}
-
- Lee S, Kim TY, Lim JS, Kim HK, Lee JW. Prospective study of effect of converting enzyme inhibitor, captopril, on renal function and proteinuria in diabetic nephropathy [abstract]. In: 11th International Congress of Nephrology. 1990:160A.
Lewis 1995 {published data only}
-
- Lewis EJ, Rohde R, Raymond B, Collaborative Study Group. A follow-up study of the course of nephropathy in type I diabetes mellitus [abstract no: P1222]. Nephrology 1997;3(Suppl 1):S379. [CENTRAL: CN-00461163]
-
- Lewis JB, Berl T, Bain RP, Rohde RD, Lewis EJ. Effect of intensive blood pressure control on the course of type 1 diabetic nephropathy. Collaborative Study Group. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 1999;34(5):809-17. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Rodby R, Rohde R, Evans J, Bain R, Mulcahy W, Lewis E. Design and baseline characteristics of the study of the effect of intensity of blood pressure (BP) management on the progression of type 1 diabetic nephropathy [abstract]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1994;5(3):382. [CENTRAL: CN-00644275] - PubMed
-
- Rodby RA, Rohde R, Evans J, Bain RP, Mulcahy WS, Lewis EJ. The study of the effect of intensity of blood pressure management on the progression of type 1 diabetic nephropathy: study design and baseline patient characteristics. Collaborative Study Group. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1995;5(10):1775-81. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Lin 1995 {published data only}
-
- Lin M, Yang Y, Chiang H, Lee D, Wang S, Chang M, et al. Beneficial effects of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors on cardiovascular and renal functions in patients with hypertension and diabetes. Acta Cardiologica Sinica 1995;11(1):30-8. [EMBASE: 25120726]
LIRICO 2007 {published data only}
-
- Maione A, Nicolucci A, Craig JC, Tognoni G, Moschetta A, Palasciano G, et al. Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers and combined therapy in microalbuminuric patients with one or more cardiovascular risk factors. Protocol of the Long-term Impact of RAS Inhibition on Cardiorenal Outcomes randomized trial (LIRICO) [ACE-inibizione, antagonismo recettoriale e terapia combinata in soggetti microalbuminurici con fattori di rischio cardiovascolare. Protocollo dello studio randomizzato multicentrico ''Long-term impact of RAS inhibition on cardiorenal outcomes-LIRICO]. Giornale Italiano di Nefrologia 2007;24(5):446-56. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Maione A, Nicolucci A, Craig JC, Tognoni G, Moschetta A, Palasciano G, et al. Protocol of the long-term impact of RAS inhibition on cardiorenal outcomes (LIRICO) randomized trial. Journal of Nephrology 2007;20(6):646-55. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Saglimbene V, Palmer SC, Ruospo M, Natale P, Maione A, Nicolucci A, et al. The Long-Term Impact of Renin-Angiotensin System (RAS) Inhibition on Cardiorenal Outcomes (LIRICO): a randomized, controlled trial. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2018;29(12):2890-99. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
-
- Strippoli GF, Palmer S, Saglimbene VM, Ruospo M, Hegbrant JB, Craig JC. ACE inhibitor, ARB, or combined therapy in patients with diabetes and microalbuminuria: the long-term impact of RAS inhibition on cardiorenal outcomes (LIRICO) randomized clinical trial [abstract no: SA-OR115]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2017;28(Abstract Suppl):103. [EMBASE: 633700766]
Marre 1987 {published data only}
-
- Marre M. Microalbuminuria and ACE inhibition in non-hypertensive diabetics. Journal of Diabetic Complications 1990;4(2):84-5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Marre M. Recent advance in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy: angiotensin I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors. Journal of Diabetic Complications 1991;5(2-3):91. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
MDNSG 1993 {published data only}
-
- Gilbert RE, Jerums G, Allen TJ, Hammond J, Cooper ME, Melbourne Diabetic Nephropathy Study Group. Effect of different antihypertensive agents in normotensive microalbuminuric patients with IDDM and NIDDM [abstract no: 16P]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1994;5(3):377.
-
- Melbourne Diabetic Nephropathy Study Group, Allen T, Cooper ME, Jerums G, De Luise M, Alford F, et al. Effects of different antihypertensive agents in normotensive microalbuminuric type I and type II diabetic patients [abstract]. Kidney International 1994;45:1270.
-
- Melbourne Diabetic Nephropathy Study Group, Cooper ME, Allen T, Jerums G, DeLuise M, Alford F, et al. Effects of different antihypertensive agents in normotensive microalbuminuric type I and type II diabetic patients [abstract]. In: 12th International Congress of Nephrology. 1993:424.
Mehdi 2009 {published data only}
-
- Mehdi UF, Adams-Huet B, Raskin P, Vega GL, Toto RD. Effect of an angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB) or a mineralocorticoid antagonist (MRA) added-on to maximally-dosed angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor (ACEi) regimen in diabetic nephropathy (DN) [abstract no: TH-FC128]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2008;19(Abstracts Issue):28A. [CENTRAL: CN-00756304]
-
- Mehdi UF, Adams-Huet B, Toto RD. Mechanism of hyperkalemia during combined renin angiotensin aldosterone system (RAAS) blockade in diabetic nephropathy [abstract no: SA-PO2246]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2009;20(Abstract Suppl):623A.
-
- Mulder S, Lambers Heerspink HJ, Perco P, Toto RD, Pena M. Validation of a systems biology derived urinary metabolite panel for prediction of albuminuria response to spironolactone therapy in type 2 diabetes [abstract no: FR-PO461]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2018;29(Abstract Suppl):539-40. [EMBASE: 633734135]
-
- Srivastava A, Adams-Huet B, Vega GL, Toto RD. Effect of losartan and spironolactone on lipoprotein metabolism in diabetic nephropathy [abstract no: 266]. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 2012;59(4):A81. [EMBASE: 71074879]
Muirhead 1999 {published data only}
-
- Cheung R, Lewanczuk RZ, Rodger NW, Huff MW, Oddou-Stock P, Botteri F, et al. The effect of valsartan and captopril on lipid parameters in patients with type II diabetes mellitus and nephropathy. International Journal of Clinical Practice 1999;53(8):584-92. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Muirhead N, Feagan BF, Mahon J, Lewanczuk RZ, Rodger NW, Botteri F, et al. The effects of valsartan and captopril on reducing microalbuminuria in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a placebo-controlled trial. Current Therapeutic Research, Clinical & Experimental 1999;60(12):650-60. [EMBASE: 30036150]
Nakamura 2002a {published data only}
-
- Nakamura T, Ushiyama C, Osada S, Takahashi Y, Shimada N, Ebihara I, et al. Combination therapy of trandolapril and candesartan cilexetil reduces microalbuminuria and urinary endothelin-1 excretion in patients with type 2 diabetes. Clinical & Experimental Nephrology 2002;6(3):135-9. [PMID: ] - PubMed
-
- Nakamura T, Ushiyama C, Suzuki S, Shimada N, Sekizuka K, Ebihara I, et al. Comparison between the angiotensin II receptor antagonist candesartan cilexetil and the angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor trandolapril in microalbuminuria of patients with early diabetic nephropathy. Nephron 2000;86(2):247. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Nakamura 2010c {published data only}
-
- Nakamura T, Fujiwara N, Sato E, Ueda Y, Sugaya T, Koide H. Renoprotective effects of various angiotensin II receptor blockers in patients with early-stage diabetic nephropathy. Kidney & Blood Pressure Research 2010;33(3):213-20. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Nankervis 1998 {published data only}
-
- Nankervis A, Nicholls K, Kilmartin G, Allen P, Ratnaike S, Martin FI. Effects of perindopril on renal histomorphometry in diabetic subjects with microalbuminuria: a 3-year placebo-controlled biopsy study. Metabolism: Clinical & Experimental 1998;47(12 Suppl 1):12-5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Niu 2008 {published data only}
-
- Niu W, Zhao S. The effect of benazepril in treatment of the patients with early diabetic nephropathy with normotensive and microalbuminuria. China Tropical Medicine 2008;8(2):229-30. [CENTRAL: CN-00796267]
O'Donnell 1993 {published data only}
-
- O'Donnell MJ, Rowe BR, Lawson N, Horton A, Gyde OH, Barnett AH. Placebo-controlled trial of lisinopril in normotensive diabetic patients with incipient nephropathy. Journal of Human Hypertension 1993;7(4):327-32. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Ogawa 2007 {published data only}
-
- Ogawa S, Takeuchi K, Mori T, Nako K, Tsubono Y, Ito S. Effects of monotherapy of temocapril or candesartan with dose increments or combination therapy with both drugs on the suppression of diabetic nephropathy. Hypertension Research - Clinical & Experimental 2007;30(4):325-34. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
ONTARGET 2004 {published data only}
-
- Anderson C, Teo K, Gao P, Arima H, Dans A, Unger T, et al. Renin-angiotensin system blockade and cognitive function in patients at high risk of cardiovascular disease: analysis of data from the ONTARGET and TRANSCEND studies. Lancet Neurology 2011;10(1):43-53. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Barzilay JI, Gao P, O'Donnell M, Mann JF, Anderson C, Fagard R, et al. Albuminuria and decline in cognitive function: The ONTARGET/TRANSCEND studies. Archives of Internal Medicine 2011;171(2):142-50. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Bohm M, Baumhakel M, Teo K, Sleight P, Probstfield J, Gao P, et al. Erectile dysfunction predicts cardiovascular events in high-risk patients receiving telmisartan, ramipril, or both: The ONgoing Telmisartan Alone and in combination with Ramipril Global Endpoint Trial/Telmisartan Randomized AssessmeNt Study in ACE iNtolerant subjects with cardiovascular Disease (ONTARGET/TRANSCEND) Trials. Circulation 2010;121(12):1439-46. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
ORIENT 2006 {published data only}
-
- Imai E, Chan J, Ito S, Haneda M, Makino H. Impact of olmesartan with or without ace inhibitor on renal and cardiovascular protection in type 2 diabetes with overt proteinuria [abstract no: Su322]. NDT Plus 2010;3(Suppl 3):iii416-7. [EMBASE: 70484542]
-
- Imai E, Chan J, Ito S, Haneda M, Makino H. Olmesartan reduces incidence of end stage diabetic nephropathy trial: ORIENT study [abstract no: F-FC313]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2009;20(Abstract Suppl):72A.
-
- Imai E, Chan JCN, Ito S, Haneda M, Mankino H. Effects of olmesartan on renal and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetic patients with overt nephropathy [abstract no: SA764]. In: World Congress of Nephrology; 2009 May 22-26; Milan, Italy. 2009.
-
- Imai E, Haneda M, Chan JC, Yamasaki T, Kobayashi F, Ito S, et al. Reduction and residual proteinuria are therapeutic targets in type 2 diabetes with overt nephropathy: a post hoc analysis (ORIENT-proteinuria). Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2013;28(10):2526-34. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Parving 1989 {published data only}
-
- Parving HH, Hommel E, Jensen BR, Hansen HP. Long-term beneficial effect of ACE inhibition on diabetic nephropathy in normotensive type 1 diabetic patients. Kidney International 2001;60(1):228-34. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Phillips 1993 {published data only}
-
- Phillips PJ, Phillipou G, Bowen KM, Lowe J, Yue DK, Wischusen J, et al. Diabetic microalbuminuria and cilazapril. American Journal of Medicine 1993;94(4A):58-60S. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Poulsen 2001 {published data only}
-
- Poulsen PL, Ebbehoj E, Mogensen CE. Lisinopril reduces albuminuria during exercise in low grade microalbuminuric type 1 diabetic patients: a double blind randomized study. Journal of Internal Medicine 2001;249(5):433-40. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Poulsen PL, Ebbehoj E, Nosadini R, Fioretto P, Deferrari G, Crepaldi G, et al. Early ACE-i intervention in microalbuminuric patients with type 1 diabetes: effects on albumin excretion, 24 h ambulatory blood pressure, and renal function. Diabetes & Metabolism 2001;27(2 Pt 1):123-8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
PREVEND IT 2000 {published data only}
-
- Asselbergs FW, Diercks GF, Hillege HL, Boven AJ, Janssen WM, Voors AA, et al. Effects of fosinopril and pravastatin on cardiovascular events in subjects with microalbuminuria. Circulation 2004;110(18):2809-16. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Asselbergs FW, Roon AM, Hillege HL, Jong PE, Gans RO, Smit AJ, et al. Effects of fosinopril and pravastatin on carotid intima-media thickness in subjects with increased albuminuria. Stroke 2005;36(3):649-53. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Asselbergs FW, van der Harst P, Roon AM, Hillege HL, Jong PE, Gans RO, et al. Long-term effects of pravastatin and fosinopril on peripheral endothelial function in albuminuric subjects. Atherosclerosis 2008;196(1):349-55. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Atthobari J, Asselbergs FW, Boersma C, Vries R, Hillege HL, Gilst WH, et al. Cost-effectiveness of screening for albuminuria and subsequent treatment with an ACE-inhibitor; a pharmaco-economic analysis [abstract no: TH-FC169]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2005;16:36A. [CENTRAL: CN-00583782]
-
- Atthobari J, Asselbergs FW, Boersma C, Vries R, Hillege HL, Gilst WH, et al. Cost-effectiveness of screening for albuminuria with subsequent fosinopril treatment to prevent cardiovascular events: A pharmacoeconomic analysis linked to the prevention of renal and vascular endstage disease (PREVEND) study and the prevention of renal and vascular endstage disease intervention trial (PREVEND IT). Clinical Therapeutics 2006;28(3):432-44. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
PRONEDI 2013 {published data only}
-
- Fernandez Juarez G, Luno J, Barrio V, Vinuesa SG, Praga M, Goicoechea M, et al. Effect of dual blockade of the renin-angiotensin system on the progression of type 2 diabetic nephropathy: a randomized trial. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 2013;61(2):211-8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Fernandez-Juarez G, Luno J, Barrio V, Vinuesa SG, Praga M, Goicoechea M, et al. 25 (OH) vitamin D levels and renal disease progression in patients with type 2 diabetic nephropathy and blockade of the renin-angiotensin system. Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology: CJASN 2013;8(11):1870-6. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fernandez-Juarez G, Villacorta PJ, Luno Fernandez JL, Martinez-Martinez E, Cachofeiro V, Barrio Lucia V, et al. High levels of circulating TNFR1 increase the risk of all-cause mortality and progression of renal disease in type 2 diabetic nephropathy. Nephrology 2017;22(5):354-60. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Fernandez-Juarez GM, Perez JV, Martinez EM, Cachofeiro V, Tato A, Ocana J, et al. Circulating TNF receptor levels and renal disease progression in patients with type 2 diabetic nephropathy and blockade of the renin angiotensin system [abstract no: SP300]. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2015;30(Suppl 3):iii478-9. [EMBASE: 72207626]
-
- Luno J, Gerna Maria F, Vinuesa SG, Goicoechea M, Dominguez JO, Losada LC, et al. Vitamin D levels and renal progression in type 2 diabetic patients with blockade of the renin angiotensin system [abstract no: TH-PO438]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2013;24(Abstract Suppl):201A.
Raj 2021 {published data only}
-
- Raj A, Verma N, Pal A, Chattopadhyay R. Comparative study of the renal effect of telmisartan and ramipril in patients with hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Journal of Cardiovascular Disease Research 2021;12(6):1056‐62. [EMBASE: 2017637667]
Ravid 1993 {published data only}
-
- Ravid M, Clutter WE. Long-term effect of enalapril on normotensive type II diabetes mellitus. Annals of Internal Medicine 1993;119(Suppl 1):6. [EMBASE: 23289262]
-
- Ravid M, Lang R, Rachmani R, Lishner M. Long-term renoprotective effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. A 7-year follow-up study. Archives of Internal Medicine 1996;156(3):286-9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Ravid M, Neumann L, Lishner M. Plasma lipids and the progression of nephropathy in diabetes mellitus type II: effect of ACE inhibitors. Kidney International 1995;47(3):907-10. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Ravid M, Savin H, Jutrin I, Bental T, Katz B, Lishner M. Long-term stabilizing effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition on plasma creatinine and on proteinuria in normotensive type II diabetic patients. Annals of Internal Medicine 1993;118(8):577-81. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Ravid M, Savin H, Jutrin I, Bental T, Lang R, Lishner M. Long-term effect of ACE inhibition on development of nephropathy in diabetes mellitus type II. Kidney International - Supplement 1994;45:S161-4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
RENAAL 2001 {published data only}
-
- Appel GB, Radhakrishnan J, Avram MM, DeFronzo RA, Escobar-Jimenez F, Campos MM, et al. Analysis of metabolic parameters as predictors of risk in the RENAAL study. Diabetes Care 2003;26(5):1402-7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Bakris GL, Weir MR, Shanifar S, Zhang Z, Douglas J, Dijk DJ, et al. Effects of blood pressure level on progression of diabetic nephropathy: results from the RENAAL study. Archives of Internal Medicine 2003;163(13):1555-65. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Boner G, Cooper ME, McCarroll K, Brenner BM, Zeeuw D, Kowey PR, et al. Adverse effects of left ventricular hypertrophy in the reduction of endpoints in NIDDM with the angiotensin II antagonist losartan (RENAAL) study. Diabetologia 2005;48(10):1980-7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Brenner BM, Cooper ME, Zeeuw D, Grunfeld JP, Keane WF, Kurokawa K, et al. The losartan renal protection study--rationale, study design and baseline characteristics of RENAAL (Reduction of Endpoints in NIDDM with the Angiotensin II Antagonist Losartan). Journal of the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System 2000;1(4):328-35. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Brenner BM, Cooper ME, Zeeuw D, Keane WF, Mitch WE, Parving HH, et al. Effects of losartan on renal and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. New England Journal of Medicine 2001;345(12):861-9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Rizzoni 2005 {published data only}
-
- Rizzoni D, Porteri E, De Ciuceis C, Sleiman I, Rodella L, Rezzani R, et al. Effect of treatment with candesartan or enalapril on subcutaneous small artery structure in hypertensive patients with noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Hypertension 2005;45(4):659-65. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Romero 1993 {published data only}
-
- Romero R, Salinas I, Lucas A, Abad E, Reverter JL, Johnston S, et al. Renal function changes in microalbuminuric normotensive type II diabetic patients treated with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. Diabetes Care 1993;16(4):597-600. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Ruggenenti 2019 {published data only}
-
- Ruggenenti P, Cortinovis M, Parvanova A, Trillini M, Iliev IP, Bossi AC, et al. Preventing microalbuminuria with benazepril, valsartan, and benazepril-valsartan combination therapy in diabetic patients with high-normal albuminuria: a prospective, randomized, open-label, blinded endpoint (PROBE) study. PLoS Medicine 2021;18(7):e1003691. [PMID: ] - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ruggenenti P, Trillini M, Barlovic DP, Cortinovis M, Pisani A, Parvanova A, et al. Effects of valsartan, benazepril and their combination in overt nephropathy of type 2 diabetes: A prospective, randomized, controlled trial. Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism 2019;21(5):1177-90. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Sano 1994 {published data only}
-
- Sano T, Hotta N, Kawamura T, Matsumae H, Chaya S, Sasaki H, et al. Effects of long-term enalapril treatment on persistent microalbuminuria in normotensive type 2 diabetic patients: results of a 4-year, prospective, randomized study. Diabetic Medicine 1996;13(2):120-4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Sano T, Kawamura T, Matsumae H, Sasaki H, Nakayama M, Hara T, et al. Effects of long-term enalapril treatment on persistent micro-albuminuria in well-controlled hypertensive and normotensive NIDDM patients. Diabetes Care 1994;17(5):420-4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Sato 2003 {published data only}
-
- Sato A, Tabata M, Hayashi K, Saruta T. Effects of the angiotensin II type 1 receptor antagonist candesartan, compared with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, on the urinary excretion of albumin and type IV collagen in patients with diabetic nephropathy. Clinical & Experimental Nephrology 2003;7(3):215-20. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Sawaki 2008 {published data only}
-
- Sawaki H, Terasaki J, Fujita A, Nakagawa S, Kanatsuna N, Sadahiro K, et al. A renoprotective effect of low dose losartan in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Research & Clinical Practice 2008;79(1):86-90. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Schram 2005 {published data only}
-
- Schram MT, Ittersum FJ, Spoelstra-de Man A, Dijk RA, Schalkwijk CG, Ijzerman RG, et al. Aggressive antihypertensive therapy based on hydrochlorothiazide, candesartan or lisinopril as initial choice in hypertensive type II diabetic individuals: effects on albumin excretion, endothelial function and inflammation in a double-blind, randomized clinical trial. Journal of Human Hypertension 2005;19(6):429-37. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Sengul 2006 {published data only}
-
- Sengul AM, Altuntas Y, Kurklu A, Aydin L. Beneficial effect of lisinopril plus telmisartan in patients with type 2 diabetes, microalbuminuria and hypertension. Diabetes Research & Clinical Practice 2006;71(2):210-9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
SMART 2009 {published data only}
-
- Burgess ED, Muirhead N, Cotret PR. A double-blind randomized controlled trial of high dose candesartan cilexetil in proteinuric renal disease - results from SMART (Supra Maximal Atacand Renal Trial) [abstract no: SA-FC104]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2007;18(Abstracts):57A.
-
- Muirhead N, Burgess E, Rene de Cotret P, SMART Investigators. A randomised controlled trial of high dose candesartan in the treatment of proteinuric renal disease: design and baseline characteristics [abstract no: SA-PO261]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2004;15(Oct):357-8A. [CENTRAL: CN-00550711]
SOLVD (Treatment) 1990 {published data only}
-
- Al-Ahmad A, Levey A, Rand W, Majunath G, Salem D, Gregory D, et al. Anemia and renal insufficiency as risk factors for mortality in patients with left ventricular dysfunction [abstract no: A0739]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2000;11(Sept):137A. [CENTRAL: CN-00550523]
-
- Al-Ahmad AM, Sarnak MJ, Rand W, Gregory D, Konstam MA, Salem DN, et al. Level of renal function as an independent predictor of mortality in patients with left ventricular dysfunction [abstract no: A0783]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1999;10(Program & Abstracts):152A. [CENTRAL: CN-00550524]
-
- Alsheikh-Ali AA, Trikalinos TA, Ruthazer R, Terrin N, Wong JB, Sarnak MJ, et al. Risk of arrhythmic and nonarrhythmic death in patients with heart failure and chronic kidney disease. American Heart Journal 2011;161(1):204-9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Bansal N, Tighiouart H, Weiner D, Griffith J, Vlagopoulos P, Salem D, et al. Anemia as a risk factor for kidney function decline in heart failure [abstract no: TH-PO928]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2005;16:322A. [CENTRAL: CN-01658120]
-
- Bansal N, Tighiouart H, Weiner D, Griffith J, Vlagopoulos P, Salem D, et al. Anemia as a risk factor for kidney function decline in individuals with heart failure. American Journal of Cardiology 2007;99(8):1137-42. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Stornello 1988 {published data only}
-
- Stornello M, Valvo EV, Puglia N, Scapellato L. Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition with a low dose of enalapril in normotensive diabetics with persistent proteinuria. Journal of Hypertension - Supplement 1988;6(4):S464-6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Stornello 1989 {published data only}
-
- Stornello M, Valvo EV, Scapellato L. Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition in normotensive type II diabetics with persistent mild proteinuria. Journal of Hypertension - Supplement 1989;7(6):S314-5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Tan 2002 {published data only}
-
- Tan KC, Chow WS, Ai VH, Lam KS. Effects of angiotensin II receptor antagonist on endothelial vasomotor function and urinary albumin excretion in type 2 diabetic patients with microalbuminuria. Diabetes/Metabolism Research Reviews 2002;18(1):71-6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Titan 2011 {published data only}
-
- Tavares G, Venturini G, Padilha K, Zatz R, Pereira AC, Thadhani RI, et al. 1,5-Anhydroglucitol predicts CKD progression in macroalbuminuric diabetic kidney disease: results from non-targeted metabolomics. Metabolomics 2018;14(4):39. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Titan S, Vieira JM Jr, Barros R, Zatz R. Urinary biomarkers and prediction of proteinuria progression in diabetic nephropathy [abstract no: M327]. In: World Congress of Nephrology; 2009 May 22-26; Milan, Italy. 2009.
-
- Titan SM, Vieira JM Jr, Barros RT, Zatz R. The effect of enalapril and losartan association therapy on proteinuria progression in advanced diabetic nephropathy: a double-blind randomized clinical trial [abstract no: TH-FC129]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2008;19(Abstracts Issue):28A.
-
- Titan SM, Vieira JM Jr, Dominguez WV, Barros RT, Zatz R. ACEI and ARB combination therapy in patients with macroalbuminuric diabetic nephropathy and low socioeconomic level: a double-blind randomized clinical trial. Clinical Nephrology 2011;76(4):273-83. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Titan SM, Vieira JM Jr, Dominguez WV, Moreira SR, Pereira AB, Barros RT, et al. Urinary MCP-1 and RBP: independent predictors of renal outcome in macroalbuminuric diabetic nephropathy. Journal of Diabetes & its Complications 2012;26(6):546-53. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Tong 2006 {published data only}
-
- Tong PC, Ko GT, Chan WB, Ma RC, So WY, Lo MK, et al. The efficacy and tolerability of fosinopril in Chinese type 2 diabetic patients with moderate renal insufficiency. Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism 2006;8(3):342-7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
TRANSCEND 2009 {published data only}
-
- Anderson C, Teo K, Gao P, Arima H, Dans A, Unger T, et al. Renin-angiotensin system blockade and cognitive function in patients at high risk of cardiovascular disease: analysis of data from the ONTARGET and TRANSCEND studies. Lancet Neurology 2011;10(1):43-53. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Barzilay JI, Gao P, O'Donnell M, Mann JF, Anderson C, Fagard R, et al. Albuminuria and decline in cognitive function: The ONTARGET/TRANSCEND studies. Archives of Internal Medicine 2011;171(2):142-50. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Bohm M, Baumhakel M, Teo K, Sleight P, Probstfield J, Gao P, et al. Erectile dysfunction predicts cardiovascular events in high-risk patients receiving telmisartan, ramipril, or both: The ONgoing Telmisartan Alone and in combination with Ramipril Global Endpoint Trial/Telmisartan Randomized AssessmeNt Study in ACE iNtolerant subjects with cardiovascular Disease (ONTARGET/TRANSCEND) Trials. Circulation 2010;121(12):1439-46. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Trevisan 1995 {published data only}
-
- Trevisan R, Tiengo A. Effect of low-dose ramipril on microalbuminuria in normotensive or mild hypertensive non-insulin-dependent diabetic patients. North-East Italy Microalbuminuria Study Group. American Journal of Hypertension 1995;8(9):876-83. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Tutuncu 2001 {published data only}
-
- Tutuncu NB, Gurlek A, Gedik O. Efficacy of ACE inhibitors and ATII receptor blockers in patients with microalbuminuria: a prospective study. Acta Diabetologica 2001;38(4):157-61. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
VA NEPHRON‐D 2009 {published data only}
-
- Fried LF, Duckworth W, Zhang JH, O'Connor T, Brophy M, Emanuele N, et al. Design of combination angiotensin receptor blocker and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor for treatment of diabetic nephropathy (VA NEPHRON-D). Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology: CJASN 2009;4(2):361-8. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fried LF, Emanuele N, Zhang JH, Brophy M, Conner T, Duckworth W, et al. Combined angiotensin inhibition for treatment of diabetic nephropathy: VA nephron D [abstract no: HI-OR03]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2013;24(Abstract Suppl):1B.
-
- Fried LF, Emanuele N, Zhang JH, Brophy M, Conner TA, Duckworth W, et al. Combined angiotensin inhibition for the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. New England Journal of Medicine 2013;369(20):1892-903. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Fried LF, Huang Y, Zhang JH, Palevsky PM, Johnson GR, Seliger SL, et al. ESRD and mortality after VA NEPHRON-D [abstract no: TH-PO717]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2017;28(Abstract Suppl):284. [EMBASE: 633704957]
-
- Huang Y, Johnson G, Kyriakides T, Zhang J. Ascertaining study participant safety using centralized electronic medical records in a clinical trial setting - lessons learned from the veteran affairs NEPHRON-D trial [abstract no: P27]. Trials 2017;18(Suppl 1):11. [EMBASE: 620925249]
Viberti 1994 {published data only}
-
- Viberti GC, Laffel L, Gans DJ, Microalbuminuria Captopril Study Group. Secondary prevention of diabetic nephropathy by captopril in patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM) and microalbuminuria [abstract no: 119P]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1994;5(3):385.
-
- Viverti GC, Microalbuminuria Captopril Study Group. Treatment of normotensive microalbuminuric IDDM patients [abstract]. In: 13th International Congress of Nephrology; 1995 Jul 2-6; Madrid, Spain. 1995:66. [CENTRAL: CN-00550656]
VIVALDI 2005 {published data only}
-
- Boger RH, Schwedhelm E, Maas R, Quispe-Bravo S, Skamira C. ADMA and oxidative stress may relate to the progression of renal disease: rationale and design of the VIVALDI study. Vascular Medicine 2005;10 Suppl 1:S97-102. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Galle J, Schwedhelm E, Pinnetti S, Boger RH, Wanner C. Antiproteinuric effects of angiotensin receptor blockers: telmisartan versus valsartan in hypertensive patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and overt nephropathy. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2008;23(10):3174-83. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- VIVALDI: A trial to investigate the efficacy of telmisartan 80mg versus valsartan 160mg in hypertensive type-2 diabetic patients with overt nephropathy. The Protection Trial Programme - Micardis Protection 2005.
Weil 2012 {published data only}
White 2001 {published data only}
-
- White KE, Pinel N, Bilous RW. Interstitial volume changes, but not glomerulopathy, are limited by angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition after 2 years of therapy in type 2 diabetic patients with nephropathy [abstract no: A0668]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2000;11(Sept):124A.
-
- White KE, Pinel N, Cordonnier DJ, Bilous RW. Does ACE inhibition slow progression of glomerulopathy in patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus? Diabetic Medicine 2001;18(11):933-6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Xia 1996 {published data only}
-
- Xia H, He R, Chen J. Protective effect of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor on renal function in normotensive non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus patients with early diabetic nephropathy and microalbuminuria. Chung-Hua Nei Ko Tsa Chih [Chinese Journal of Internal Medicine] 1996;35(8):533-6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Yao 2001a {published data only}
-
- Yao B, Hu G, Li Y, Liao Z, Zhang Y. The effect of perindopril in treatment of early diabetic nephropathy with normal blood pressure and microalbuminuria. Chung-Hua Nei Ko Tsa Chih [Chinese Journal of Internal Medicine] 2001;40(12):826-8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Yoldi 1995 {published data only}
-
- Yoldi A, Llorente I, Monreal M, Diez J, Salvador J. Is the suppression of growth hormone involved in the kidney-protecting effects of captopril in patients with diabetic nephropathy? [abstract]. In: ISN XIII International Congress of Nephrology; 1995 Jul 2-6; Madrid, Spain. 1995:198. [CENTRAL: CN-00509572]
Yoneda 2007 {published data only}
-
- Yoneda T, Takeda Y, Usukura M, Oda N, Takata H, Yamamoto Y, et al. Aldosterone breakthrough during angiotensin II receptor blockade in hypertensive patients with diabetes mellitus. American Journal of Hypertension 2007;20(12):1329-33. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Acbay 2001 {published data only}
-
- Acbay O. Effects of low-dose losartan treatment on persistent microalbuminuria in normotensive type 1 diabetic subjects. Journal of Endocrinological Investigation 2001;24(8):608-11. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Agarwal 2001 {published data only}
-
- Agarwal R, Siva S, Dunn SR, Sharma K. Add-on angiotensin II receptor blockade lowers urinary transforming growth factor-beta levels. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 2002;39(3):486-92. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Agarwal R. Add-on angiotensin receptor blockade with maximized ACE inhibition. Kidney International 2001;59(6):2282-9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Agarwal R. Proinflammatory effects of oxidative stress in chronic kidney disease: role of additional angiotensin II blockade. American Journal of Physiology - Renal Physiology 2003;284(4):F863-9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Alam 2001 {published data only}
-
- Alam SM, Abbas A, Vishnu R, Sharma BN. Study of ramipril, losartan and benazapril efficacy on microalbuminuria [abstract no: CNP 17]. Indian Journal of Nephrology 2001;11(3):118. [CENTRAL: CN-00460261]
Andersen 1999 {published data only}
-
- Andersen S, Parving H, Blouch K, Deckert M, Myers BD. Angiotensin II receptor blockade and barrier function in diabetic nephropathy [abstract no: A0642]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1999;10(Program & Abstracts):125A. [CENTRAL: CN-00550555]
Andersen 2000 {published data only}
-
- Andersen S, Tarnow L, Rossing P, Hansen BV, Parving HH. Renoprotective effects of angiotensin II receptor blockade in type 1 diabetic patients with diabetic nephropathy. Kidney International 2000;57(2):601-6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Parving HH, Andersen S, Rossing P, Hansen BV, Tarnow L. Renoprotective effects of angiotensin II receptor blockade in type 1 diabetic patients with diabetic nephropathy [abstract no: A0679]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1999;10(Program & Abstracts):132A. - PubMed
Bakris 2000 {published data only}
-
- Bakris GL, Siomos M, Bolton WK, Hebert l, Agerwall R, Catanzaro D, et al. Differential effects of valsartan (V) and lisinopril (L) on potassium [K+] homeostasis in hypertensive patients with nephropathy [abstract no: A0349]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1999;10(Program & Abstracts):68A. [CENTRAL: CN-00550414]
-
- Bakris GL, Siomos M, Richardson D, Janssen I, Bolton WK, Hebert L, et al. ACE inhibition or angiotensin receptor blockade: impact on potassium in renal failure. VAL-K Study Group. Kidney International 2000;58(5):2084-92. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Cetinkaya 2002 {published data only}
-
- Cetinkaya R, Odabas AR, Selcuk NY. Combination of enalapril and losartan therapy in diabetic nephropathy [abstract no: T129]. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2002;17(Suppl 12):225. [CENTRAL: CN-00509126]
Cetinkaya 2004 {published data only}
-
- Cetinkaya R, Odabas AR, Selcuk Y. Anti-proteinuric effects of combination therapy with enalapril and losartan in patients with nephropathy due to type 2 diabetes. International Journal of Clinical Practice 2004;58(5):432-5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Chan 1997 {published data only}
-
- Chan JC, Critchley JA, Tomlinson B, Chan TY, Cockram CS. Antihypertensive and anti-albuminuric effects of losartan potassium and felodipine in Chinese elderly hypertensive patients with or without non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. American Journal of Nephrology 1997;17(1):72-80. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Chonko 1993 {published data only}
-
- Chonko A, Donaldson D, Moore W, MacDougall M, Wiegmann T. Ramipril (R) has antiproteinuric effect and maintains renal function in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus (DM): a prospective double-blind dose finding trials (PRT) [abstract no: 39P]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1993;4(Program & Abstracts):302. [CENTRAL: CN-00483510]
Christensen 2001a {published data only}
-
- Christensen PK, Lund S, Parving H. Maintained autoregulation of glomerular filtration rate during candesartan treatment in hypertensive type 2 diabetic patients [abstract no: A4356]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2001;12(Program & Abstracts):832-3A. [CENTRAL: CN-00550725]
-
- Christensen PK, Lund S, Parving HH. Autoregulated glomerular filtration rate during candesartan treatment in hypertensive type 2 diabetic patients. Kidney International 2001;60(4):1435-42. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Daikuhara 2012 {published data only}
-
- Daikuhara H, Kikuchi F, Ishida T. The combination of OLmesartan and a CAlcium channel blocker (azelnidipine) or candesartan and a calcium channel blocker (amlodipine) in type 2 diabetic hypertensive patients: the OLCA study. Diabetes & Vascular Disease Research 2012;9(4):280-6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Dhillon 2003 {published data only}
-
- Dhillon KK, Mason E, Nanovic L, Laplace L, McCune TR. Combining ACE inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers to decrease proteinuria in patients with diabetic nephropathy [abstract no: SU-PO310]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2003;14(Nov):602A.
DIRECT Studies 2002 {published data only}
-
- Bilous R, Chaturvedi N, Sjolie AK, Fuller J, Klein R, Orchard T, et al. Effect of candesartan on microalbuminuria and albumin excretion rate in diabetes: three randomized trials. Annals of Internal Medicine 2009;151(1):11-20, W3-4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Bilous RW, Parving H, Nishi C. DIRECT-Renal: The effect of the angiotensive type 1 receptor blocker candesartan on the development of microalbuminuria in type 1 and type 2 diabetes [abstract no: LB-003]. In: American Society of Nephrology (ASN) Renal Week; 2008 Nov 4-9; Philadelphia, PA. 2008. [CENTRAL: CN-00724910]
-
- Bilous RW, Parving H, Orchard TJ, Klein R, Porta M, Fuller J, et al. Renin angiotensin system blockade is effective in preventing microalbuminuria in hypertensive but not normotensive people with type 2 diabetes; further analysis of the DIRECT Programme [abstract no: 223]. Diabetologia 2010;53(Suppl 1):S99. [EMBASE: 70262263]
-
- Chaturvedi N, Porta M, Klein R, Orchard T, Fuller J, Parving HH, et al. Effect of candesartan on prevention (DIRECT-Prevent 1) and progression (DIRECT-Protect 1) of retinopathy in type 1 diabetes: randomised, placebo-controlled trials. Lancet 2008;372(9647):1394-402. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Chaturvedi N, Sjoelie AK, Svensson A. The DIabetic Retinopathy Candesartan Trials (DIRECT) Programme, rationale and study design. Journal of the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System 2002;3(4):255-61. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
DREAM 2004 {published data only}
-
- Bangalore S, Messerli FH. Effect of ramipril on the incidence of diabetes. New England Journal of Medicine 2007;356(5):522-4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Bosch J, Yusuf S, Gerstein HC, Pogue J, Sheridan P, Dagenais G, et al. Effect of ramipril on the incidence of diabetes. New England Journal of Medicine 2006;355(15):1551-62. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Dagenais GR, Gerstein HC, Holman R, Budaj A, Escalante A, Hedner T, et al. Effects of ramipril and rosiglitazone on cardiovascular and renal outcomes in people with impaired glucose tolerance or impaired fasting glucose: results of the Diabetes REduction Assessment with ramipril and rosiglitazone Medication (DREAM) trial. Diabetes Care 2008;31(5):1007-14. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Epstein BJ, Cooper-DeHoff RM. Effect of ramipril on the incidence of diabetes. New England Journal of Medicine 2007;356(5):523-4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Gerstein HC, Yusuf S, Bosch J, Pogue J, Sheridan P, Dinccag N, et al. Effect of rosiglitazone on the frequency of diabetes in patients with impaired glucose tolerance or impaired fasting glucose: a randomised controlled trial [Erratum in: Lancet. 2006 Nov 18;368(9549):1770]. Lancet 2006;368(9541):1096-105. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Dreyling 1990 {published data only}
-
- Dreyling KW, Grotz W, Keller E, Schollmeyer P. Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) - inhibitors induce blood count changes in patients with diabetic nephropathy [abstract]. In: 11th International Congress of Nephrology. 1990:160A.
Drummond 1989 {published data only}
-
- Drummond K, Levy-Marchal C, Laborde K, Kindermans C, Wright C, Dechaux M, et al. Enalapril (E) in normotensive Type 1 diabetes (DM-1): a double blind cross-over study in patients with elevated glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and renal plasma flow (RPF) [abstract]. Kidney International 1988;33(1):189. [CENTRAL: CN-00583510]
-
- Drummond K, Levy-Marchal C, Laborde K, Kindermans C, Wright C, Dechaux M, et al. Enalapril does not alter renal function in normotensive, normoalbuminuric, hyperfiltering type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetic children. Diabetologia 1989;32(4):255-60. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Esnault 2005 {published data only}
-
- Ekhlas Eid A, Nguyen J, Delcroix C, Moutel M, Esnault VL. Effect of diuretics after dual blockade of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system on severe proteinuria [abstract no: TO22]. In: 41st Congress. European Renal Association. European Dialysis and Transplantation Association; 2004 May 15-18; Lisbon, Portugal. 2004:434-5. [CENTRAL: CN-00509172]
-
- Esnault VL, Ekhlas A, Delcroix C, Moutel MG, Nguyen JM. Diuretic and enhanced sodium restriction results in improved antiproteinuric response to RAS blocking agents. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2005;16(2):474-81. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Esnault VL, Ekhlas A, Nguyen JM, Delcroix C, Moutel MG. Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEI), angiotensin receptor blockers (ARB) and diuretics for refractory proteinuria [abstract no: SU-PO1030]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2003;14(Nov):762A. [CENTRAL: CN-00583888]
EUCTR2021‐001661‐21‐DK {published data only}
-
- EUCTR2021-001661-21-DK. Feasibility of aggressively lowering urine albumin in individuals with kidney biopsy-proven diabetic kidney disease - a pilot study. https://trialsearch.who.int/Trial2.aspx?TrialID=EUCTR2021-001661-21-DK (date accessed: 29 February 2024).
Fliser 2005 {published data only}
-
- Fliser D, Wagner K, Loos A, Tsikas D, Haller H. Chronic angiotensin II receptor blockade reduces intra(renal) vascular resistance in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus [abstract no: MP121]. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2005;20(Suppl 5):v240. [CENTRAL: CN-00740561] - PubMed
-
- Fliser D, Wagner KK, Loos A, Tsikas D, Haller H. Chronic angiotensin II receptor blockade reduces (intra)renal vascular resistance in patients with type 2 diabetes. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2005;16(4):1135-40. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Garg 2005 {published data only}
-
- Garg JP, Ellis R, Elliott WJ, Hasabou N, Chua D, Chertow GM, et al. Angiotensin receptor blockade and arterial compliance in chronic kidney disease: a pilot study. American Journal of Nephrology 2005;25(4):393-9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Haneda 2004 {published data only}
-
- Haneda M, Kikkawa R, Sakai H, Kawamori R. Antiproteinuric effect of candesartan cilexetil in Japanese subjects with type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. Diabetes Research & Clinical Practice 2004;66(1):87-95. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Hommel 1986 {published data only}
Hoque 2009 {published data only}
-
- Hoque R, Rahman MS, Iqbal M. Effect of enalapril and losartan on proteinuria in type 2 diabetic nephropathy patients. Bangladesh Medical Research Council Bulletin 2009;35(2):44-8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Hou 2017a {published data only}
Houlihan Losartan 2002 {published data only}
-
- Houlihan C, Allen T, Hovey A, Jenkins M, Cooper M, Jerums G. A low salt diet in patients with type II diabetes significantly amplifies the effects of angiotensin II receptor blockade with losartan [abstract no: 17]. Nephrology 2000;5(3):A71. [CENTRAL: CN-00509238]
-
- Houlihan CA, Akdeniz A, Tsalamandris C, Cooper ME, Jerums G, Gilbert RE. Urinary transforming growth factor-beta excretion in patients with hypertension, type 2 diabetes, and elevated albumin excretion rate: effects of angiotensin receptor blockade and sodium restriction. Diabetes Care 2002;25(6):1072-7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Houlihan CA, Allen T, Hovey A, Jenkins M, Cooper M, Jerums G. Comparison of regular versus low sodium diet on the effects of losartan in hypertensive subjects with type II diabetes [abstract no: A0624]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2000;11(Sept):116A. [CENTRAL: CN-00615874]
-
- Houlihan CA, Allen TJ, Baxter AL, Panangiotopoulos S, Casley DJ, Cooper ME, et al. A low-sodium diet potentiates the effects of losartan in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2002;25(4):663-71. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Igarashi 2006 {published data only}
-
- Igarashi M, Hirata A, Kadomoto Y, Tominaga M. Dual blockade of angiotensin II with enalapril and losartan reduces proteinuria in hypertensive patients with type 2 diabetes. Endocrine Journal 2006;53(4):493-501. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Inigo 2000 {published data only}
-
- Inigo PJ, Esmatjes E, Lario S, Flores L, Ruilope LM, Campistol JM. Losartan decreases TGF-b1 plasma levels and urinary albumin excretion in patients with diabetes type-II and microalbuminuria [abstract no: A0630]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2000;11(Sept):117A.
Insua 1988 {published data only}
-
- Insua A, Ribstein J, Mimran A. Comparative effect of captopril and nifedipine in normotensive patients with incipient diabetic nephropathy. Postgraduate Medical Journal 1988;64 Suppl 2:59-62. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Islam 2005 {published data only}
-
- Iqbal MM, Islam MN, Rahman MH, Banerjee SK, Hassan MS, Hossain RM, et al. Effect of renin angiotensin system inhibitors (ACEI) and blockers (ATRB) on proteinuria and blood pressure reduction in patients with diabetic nephropathy [abstract no: M-PO20059]. Nephrology 2005;10(Suppl):A30-1.
-
- Iqbal MM, Islam MN, Rahman MH, Banerjee SK, Hossain RM, Islam MS, et al. Tolerance of high dose enalapril and losartan for proteinuria and blood pressure reduction in patients with chronic kidney disease [abstract no: SO008]. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2006;21(Suppl 4):iv5.
-
- Islam MN, Mansur MA, Ahmed Z, Iqbal MM, Rahman MH, Ahmed T, et al. Alterations in serum K+ level at different doses of enalapril and losartan for treating type 2 diabetic CKD patients [abstract no: FP219]. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2007;22(Suppl 6):vi92. [CENTRAL: CN-00755274]
Jacobsen 2002 {published data only}
-
- Jacobsen P, Andersen S, Hansen BV, Parving HH. Dual blockade of the renin-angiotensin system in type 1 diabetic patients with diabetic nephropathy [abstract no: A0777]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2001;12(Program & Abstracts):148A. [CENTRAL: CN-01912811]
-
- Jacobsen P, Andersen S, Rossing K, Hansen BV, Parving HH. Dual blockade of the renin-angiotensin system in type 1 patients with diabetic nephropathy. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2002;17(6):1019-24. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Jacobsen PK, Rossing P, Parving HH. Impact of renin angiotensin system blockade on night to day blood pressure ratio in diabetic nephropathy. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2006;21(7):2030-1. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Jacobsen 2003 {published data only}
-
- Jacobsen P, Andersen S, Jensen BR, Parving HH. Additive effect of ACE inhibition and angiotensin II receptor blockade in type I diabetic patients with diabetic nephropathy. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2003;14(4):992-9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Jacobsen PK, Rossing P, Parving HH. Impact of renin angiotensin system blockade on night to day blood pressure ratio in diabetic nephropathy. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2006;21(7):2030-1. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Jacobsen 2003a {published data only}
-
- Jacobsen P, Andersen S, Rossing K, Jensen BR, Parving HH. Dual blockade of the renin-angiotensin system versus maximal recommended dose of ACE inhibition in diabetic nephropathy. Kidney International 2003;63(5):1874-80. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Jacobsen PK, Rossing P, Parving HH. Impact of renin angiotensin system blockade on night to day blood pressure ratio in diabetic nephropathy. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2006;21(7):2030-1. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Jiao 2022 {published data only}
-
- Jiao S, Dong Y, Chang X, Wu Y, Li H. Effects of alpha lipoic acid combined with olmesartan medoxomil on blood glucose and oxidation indicators in patients with diabetic nephropathy: a protocol for a parallel, randomized, double-blind, controlled clinical trial. Medicine 2022;101(17):e29080. [PMID: ] - PMC - PubMed
Keilani 1993 {published data only}
-
- Keilani T, Schlueter WA, Levin ML, Batlle DC. Improvement of lipid abnormalities associated with proteinuria using fosinopril, an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor. Annals of Internal Medicine 1993;118(4):246-54. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Schlueter W, Keilani T, Batlle DC. Metabolic effects of converting enzyme inhibitors: focus on the reduction of cholesterol and lipoprotein(a) by fosinopril. American Journal of Cardiology 1993;72(20):37-44H. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kincaid‐Smith 2002 {published data only}
-
- Kincaid-Smith P, Fairley K, Packham D. Comparison of the effect of 50% increase in angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor (ACEI) with a combination of candesartan and ACEI on proteinuria and blood pressure in chronic renal disease [abstract no: A0392]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2001;12(Program & Abstracts):75A. [CENTRAL: CN-00446096]
-
- Kincaid-Smith P, Fairley K, Packham D. Comparison of the effect of 50% increase in angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor (ACEI) with a combination of candesartan and ACEI on proteinuria and blood pressure in chronic renal disease [abstract no: P99]. Nephrology 2002;7(Suppl 3):A25. [CENTRAL: CN-00792336]
-
- Kincaid-Smith P, Fairley K, Packham D. Randomized controlled crossover study of the effect on proteinuria and blood pressure of adding an angiotensin II receptor antagonist to an angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor in normotensive patients with chronic renal disease and proteinuria. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2002;17(4):597-601. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Kincaid-Smith P, Fairley K. A fall in urine protein with combined angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor (ACEI) and aII receptor antagonist (AIIRA) treatment predicts a good outcome at three years in patients with chronic renal disease with continuing reduction in urine protein levels. Diabetic and obese patients with a poor response to combined ACEI and AIIRA treatment have a poor outcome [abstract no: M419]. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2003;18(Suppl 4):131. [CENTRAL: CN-00446094]
-
- Kincaid-Smith PS, Fairley KF, Packham D. Randomised controlled crossover study of the effect on proteinuria of adding an angiotensin 11-receptor antagonist (ARA) to an angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor (ACEI) [abstract no: A1825]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2000;11(Sept):349A. [CENTRAL: CN-00626048]
Lim 2007 {published data only}
-
- Lim SC, Koh AF, Goh SK, Chua CL, Heng BL, Subramaniam T, et al. Angiotensin receptor antagonist vs. angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor in Asian subjects with type 2 diabetes and albuminuria - a randomized crossover study. Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism 2007;9(4):477-82. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Lim SC, Liu JJ, Subramaniam T, Sum CF. Elevated circulating alpha-klotho by angiotensin II receptor blocker losartan is associated with reduction of albuminuria in type 2 diabetic patients. Journal of the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System 2014;15(4):487-90. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Mårup 2022 {published data only}
-
- Mårup FH, Peters CD, Christensen JH, Birn H. Can patiromer allow for intensified renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system blockade with losartan and spironolactone leading to decreased albuminuria in patients with chronic kidney disease, albuminuria and hyperkalaemia? An open-label randomised controlled trial: morphCKD. BMJ open 2022;12(2):e057503. [PMID: ] - PMC - PubMed
Masuda 2009 {published data only}
-
- Masuda S, Tamura K, Wakui H, Kanaoka T, Ohsawa M, Maeda A, et al. Effects of angiotensin II type 1 receptor blocker on ambulatory blood pressure variability in hypertensive patients with overt diabetic nephropathy. Hypertension Research - Clinical & Experimental 2009;32(11):950-5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Tamura K, Wakui H, Masuda SI, Kanaoka T, Ohsawa M, Maeda A, et al. Effects of angiotensin II type 1 receptor blocker on ambulatory blood pressure profile in hypertensive patients with overt diabetic nephropathy [abstract no: P295]. Hypertension 2009;54(4):e89. [EMBASE: 70024188] - PubMed
Mathiesen 1991 {published data only}
-
- Hansen PM, Mathiesen ER, Kofoed-Enevoldsen A, Deckert T. Possible effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition on glomerular charge selectivity. Journal of Diabetes & its Complications 1995;9(3):158-62. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Hansen PM, Mathiesen ER, Kofoed-Enevoldsen A. Possible effect of angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibition on glomerular charge selectivity [abstract]. In: 12th International Congress of Nephrology; 1993 Jun 13-18; Jerusalem, Israel. 1993:425. [CENTRAL: CN-00583297]
-
- Mathiesen ER, Hommel E, Hansen HP, Parving HH. Preservation of normal GFR with long term captopril treatment in normotensive IDDM patients with microalbuminuria [abstract no: A0546]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1997;8(Program & Abstracts):115A. [CENTRAL: CN-00446655]
Matos 2005 {published data only}
-
- Matos JP, Lourdes Rodrigues M, Ismerim VL, Boasquevisque EM, Genelhu V, Francischetti EA. Effects of dual blockade of the renin angiotensin system in hypertensive type 2 diabetic patients with nephropathy. Clinical Nephrology 2005;64(3):180-9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Matos JP, Lourdes Rodrigues M, Valenca D, Ismerim V, Boasquevisque E, Barroso S, et al. Dual blockade of the renin-angiotensin system reduces plasma aldosterone, proteinuria and urinary tgb-b1 in type 2 diabetic patients with nephropathy [abstract no: MP135]. In: 41st Congress. European Renal Association. European Dialysis and Transplantation Association; 2004 May 15-18; Lisbon, Portugal. 2004:275. [CENTRAL: CN-00636139]
Meier 2011 {published data only}
-
- Meier P, Maillard M, Meier R, Burnier M. Antiproteinuric effect of losartan: is a higher dose as effective as an association with an ACE inhibitor? Results of a randomised triple-crossover study in proteinuric patients [abstract no: F-PO1920]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2008;19(Abstracts Issue):543A.
-
- Meier P, Maillard M, Tremblay S, Meier R, Burnier M. Comparative 24h blood pressure effects of increasing doses of losartan and the association of losartan and an ACE inhibitor in proteinuric patients [abstract no: SA-PO2249]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2008;19(Abstracts Issue):617A.
-
- Meier P, Maillard MP, Meier JR, Tremblay S, Gauthier T, Burnier M. Combining blockers of the renin-angiotensin system or increasing the dose of an angiotensin II receptor antagonist in proteinuric patients: a randomized triple-crossover study. Journal of Hypertension 2011;29(6):1228-35. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Mimran 1988 {published data only}
-
- Mimran A, Insua A, Ribstein J, Monnier L, Bringer J, Mirouze J. Contrasting effects of captopril and nifedipine in normotensive patients with incipient diabetic nephropathy. Journal of Hypertension 1988;6(11):919-23. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
NCT00171600 {published data only}
-
- Antialbuminuric effects of valsartan and lisinopril [Comparative, open multicenter trial assessing the effect on albumin excretion rate of 320mg valsartan (with or without HCTZ) Vs 40mg lisinopril (with or without HCTZ) on hypertensive patients with diabetic and non-diabetic nephropathy and albuminuria]. www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct/show/NCT00171600 (first received 15 September 2005).
NCT00208221 {published data only}
-
- Higher dose of ramipril versus addition of telmisartan-ramipril in hypertension and diabetes [Comparison of a higher dose of ramipril to the addition of telmisartan 80 mg+ramipril 10 mg in patients with hypertension and diabetes]. www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00208221 (first received 21 September 2005).
NCT04238702 {published data only}
-
- Renohemodynamic Effects of Combined empagliflOzin and LosARtan (RECOLAR) [A randomized, comparator-controlled, cross-over intervention study to assess renal hemodynamics of mono- and combination therapy with SGLT-2 inhibitor empagliflozin and RAS-inhibitor losartan in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus]. www.clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT04238702 (first received 23 October 2021).
NCT05189015 {published data only}
-
- Effect of olmesartan on angiotensin(1-7) levels and vascular functions in diabetes and hypertension (Ang(1-7)) [Effect of olmesartan or amlodipine on serum angiotensin(1-7) levels and vascular functions in patients with type 2 diabetes and hypertension]. www.clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT05189015 (first received 12 January 2022).
NCT05593575 {published data only}
-
- Efficacy and safety of SPH3127 tablets on treating the diabetic kidney disease [A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, active-controlled, parallel, dose-finding phase 2 clinical study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of SPH3127 tablets in the treatment of diabetic kidney disease]. www.clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT05593575 (first received 25 October 2022).
New 1998 {published data only}
-
- New JP, Marshall SM, Bilous RW. Renal autoregulation is normal in newly diagnosed, normotensive, NIDDM patients. Diabetologia 1998;41(2):206-11. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Okura 2012 {published data only}
-
- Okura T, Kojima M, Machida H, Sugiyama M, Kato T, Komada T, et al. Effects of up-titration of candesartan versus candesartan plus amlodipine on kidney function in type 2 diabetic patients with albuminuria. Journal of Human Hypertension 2012;26(4):214-9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Parvanova 2001 {published data only}
-
- Parvanova P, Pisoni R, Dimitrov BD, Iliev I, Perna A, Ruggenenti P, et al. Relative renoprotective effect of ACE inhibitors (ACEi), angiotensin II antagonists (ATA), ACEi and ATA combination and dihydrophyridine calcium channel blockers (dCCBs) in overt nephropathy of type 2 diabetes [abstract]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2001;12(Program & Abstracts):153A. [CENTRAL: CN-00447108]
Pedersen 1992 {published data only}
-
- Pedersen MM, Hansen KW, Schmitz A, Sorensen K, Christensen CK, Mogensen CE. Effects of ACE inhibition supplementary to beta blockers and diuretics in early diabetic nephropathy. Kidney International 1992;41(4):883-90. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Pruijm 2013 {published data only}
-
- Pruijm M, Hofmann L, Zanchi A, Maillard M, Forni V, Muller ME, et al. Blockade of the renin-angiotensin system and renal tissue oxygenation as measured with BOLD-MRI in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Research & Clinical Practice 2013;99(2):136-44. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Rasi Hashemi 2012 {published data only}
-
- Rasi Hashemi S, Noshad H, Tabrizi A, Mobasseri M, Tayebi Khosroshahi H, Heydarnejad M, et al. Angiotensin receptor blocker and N-acetyl cysteine for reduction of proteinuria in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Iranian Journal of Kidney Diseases 2012;6(1):39-43. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Romanelli 1989 {published data only}
Rossing 2002 {published data only}
-
- Rossing K, Christensen PK, Jensen BR, Parving HH. Dual blockade of the renin-angiotensin system in diabetic nephropathy: a randomized double-blind crossover study. Diabetes Care 2002;25(1):95-100. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Rossing K, Christensen PK, Jensen BR, Parving HH. Dual blockade of the renin-angiotensin system in type 2 diabetic patients with diabetic nephropathy [abstract no: A0813]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2001;12(Program & Abstracts):155A. [CENTRAL: CN-00444816]
Rossing 2003 {published data only}
-
- Rossing K, Christensen PK, Hansen BV, Carstensen B, Parving HH. Optimal dose of candesartan for renoprotection in type 2 diabetic patients with nephropathy: a double-blind randomized cross-over study. Diabetes Care 2003;26(1):150-5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Rossing 2003a {published data only}
-
- Rossing K, Jacobsen P, Pietraszek L, Parving HH. Renoprotective effects of adding angiotensin II receptor blocker to maximal recommended doses of ACE inhibitor in diabetic nephropathy: a randomized double-blind crossover trial. Diabetes Care 2003;26(8):2268-74. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Rossing K, Jacobsen PK, Pietraszek L, Parving H. Renoprotective effects of adding angiotensin II receptor blocker to maximal recommended doses of ACE-inhibitor in diabetic nephropathy [abstract no: SU-PO307]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2003;14(Nov):601A. [CENTRAL: CN-00644353] - PubMed
Rossing 2005a {published data only}
-
- Rossing K, Mischak H, Parving HH, Christensen PK, Walden M, Hillmann M, et al. Impact of diabetic nephropathy and angiotensin II receptor blockade on urinary polypeptide patterns. Kidney International 2005;68(1):193-205. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Rossing 2005b {published data only}
-
- Nielsen SE, Rossing K, Hess G, Zdunek D, Jensen BR, Parving HH, et al. The effect of RAAS blockade on markers of renal tubular damage in diabetic nephropathy: u-NGAL, u-KIM1 and u-LFABP. Scandinavian Journal of Clinical & Laboratory Investigation 2012;72(2):137-42. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Nielsen SE, Rossing K, Jensen BR, Parving HH, Rossing P. Tubular damage in type 2 diabetic nephropathy: the effect of ultrahigh doses of irbesartan [abstract no: 1225]. Diabetologia 2010;53(Suppl 1):S484. [EMBASE: 70263264]
-
- Rabbani N, Adaikalakoteswari A, Rossing K, Rossing P, Tarnow L, Parving HH, et al. Effect of irbesartan treatment on plasma and urinary markers of protein damage in patients with type 2 diabetes and microalbuminuria. Amino Acids 2012;42(5):1627-39. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Rossing K, Schjoedt KJ, Jensen BR, Boomsma F, Parving HH. Enhanced renoprotective effects of ultrahigh doses of irbesartan in patients with type 2 diabetes and microalbuminuria. Kidney International 2005;68(3):1190-8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Rossing K, Schjoedt KJ, Parving H. Reduction of plasma N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide by angiotensin II receptor blockade in type 2 diabetic patients with microalbuminuria [abstract no: SA-PO043]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2006;17(Abstracts):585A.
Saka 2004 {published data only}
-
- Saka S, Yildiz N, Yildiz M, Orhon A, Isgüven P, Bakirci N, et al. Short-term comparison on antiproteinuric effects of losartan and enalapril in children with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus and nephropathy [abstract no: OPFC47]. Pediatric Nephrology 2004;19(9):C86.
Salem 2021 {published data only}
-
- Salem M, Sallam AM, Abdel-Aleem E, El-Mesallamy HO. Effect of lisinopril and verapamil on angiopoietin 2 and endostatin in hypertensive diabetic patients with nephropathy: a randomized trial. Hormone & Metabolic Research 2021;53(7):470‐7. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Sasso 2002 {published data only}
-
- Sasso FC, Carbonara O, Persico M, Iafusco D, Salvatore T, D'Ambrosio R, et al. Irbesartan reduces the albumin excretion rate in microalbuminuric type 2 diabetic patients independently of hypertension: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled crossover study. Diabetes Care 2002;25(11):1909-13. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Schjoedt 2005a {published data only}
-
- Schjoedt KJ, Jacobsen P, Rossing K, Boomsma F, Parving HH. Dual blockade of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in diabetic nephropathy: the role of aldosterone. Hormone & Metabolic Research 2005;37 Suppl 1:4-8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Schjoedt 2009a {published data only}
-
- Nielsen SE, Schjoedt KJ, Astrup AS, Tarnow L, Lajer M, Hansen PR, et al. Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin (NGAL) and Kidney Injury Molecule 1 (KIM1) in patients with diabetic nephropathy: a cross-sectional study and the effects of lisinopril. Diabetic Medicine 2010;27(10):1144-50. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Schjoedt KJ, Astrup AS, Persson F, Frandsen E, Boomsma F, Rossing K, et al. Optimal dose of lisinopril for renoprotection in type 1 diabetic patients with diabetic nephropathy: a randomised crossover trial. Diabetologia 2009;52(1):46-9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Schjoedt KJ, Astrup AS, Persson F, Parving H, Rossing P. Optimal dose of lisinopril for renoprotection in type 1 diabetic patients with diabetic nephropathy [abstract no: SA-PO1041]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2007;18(Abstracts):572A.
Schmieder 2005 {published data only}
-
- Fleischmann EH, Klingbeil AU, Schneider MP, Delles C, Schmieder RE. The effect of treatment with ultra high dose candesartan (64mg) on proteinuria: Interim results of a double-blind, randomized, multi-center study [abstract no: M427]. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2003;18(Suppl 4):133-4. [CENTRAL: CN-00445352]
-
- Schmieder RE, Klingbeil AU, Fleischmann EH, Delles C, Veelken R. Additive effect of ultra high dose (64 mg) candesartan on proteinuria: a double blind randomized study [abstract no: W-PO20003]. Nephrology 2005;10(Suppl 1):A244. [CENTRAL: CN-00602110]
-
- Schmieder RE, Klingbeil AU, Fleischmann EH, Delles C, Veelken R. Dose-response effect of angiotensin receptor blocker candesartan on proteinuria: a double blind, randomized study [abstract no: SP149]. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2005;20(Suppl 5):v69.
-
- Schmieder RE, Klingbeil AU, Fleischmann EH, Veelken R, Delles C. Additional antiproteinuric effect of ultra high dose (64mg) candesartan: a double blind, randomized study [abstract no: F-P0243]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2004;15(Oct):119A. [CENTRAL: CN-00602112] - PubMed
-
- Schmieder RE, Klingbeil AU, Fleischmann EH, Veelken R, Delles C. Additional antiproteinuric effect of ultrahigh dose candesartan: a double-blind, randomized, prospective study. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2005;16(10):3038-45. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Seher 2017 {published data only}
-
- Seher S, Iqbal A, Irum T. Comparing the effectiveness of lisinopril and losartan potassium in treatment of microalbuminurea in newly diagnosed type II diabetes mellitus. Medical Forum Monthly 2017;28(8):63-6. [EMBASE: 618953685]
Shand 2002 {published data only}
-
- Shand B. Comparative study of the effects of enalapril and losartan on glomerular size selectivity in patients with proteinuria with and without diabetes [abstract]. Australian & New Zealand Journal of Medicine 1999;29:596. [CENTRAL: CN-00319649]
-
- Shand BI, Lewis JG, Elder PA, Agarwal M. Antihypertensive treatment and glomerular size selectivity in hypertensive patients with renal parenchymal disease and proteinuria. Clinical Nephrology 2002;58(4):321-4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Shand BI, McGregor DO, Agarwal M, Lynn KL, Lewis J, Elder PA. Comparative study of the effects of enalapril and losartan on glomerular size selectivity in patients with proteinuria [abstract no: 22]. Nephrology 2000;5(1-2 Suppl):A8. [CENTRAL: CN-00319649]
SHIELD 2003 {published data only}
-
- Weir MR, Bakris MD, SHIELD (Study of Hypertension and the Efficacy of Lotrel in Diabetes). Benefits of BP control using ACE/CCB in type 2 diabetics [abstract no: 91]. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 2002;39(4):A33. [CENTRAL: CN-00403065]
Shu 1997 {published data only}
-
- Shu G, Yin D, et al. Clinical observation on benazepril treatment of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus patients with diabetic nephropathy [abstract no: P1220]. Nephrology 1997;3(Suppl 1):S378. [CENTRAL: CN-0191223]
Song 2003 {published data only}
-
- Kim M, Song JH, Lee SW, Lee SY, Park GH. Renoprotective effect of dual blockade of renin-angiotensin system by the combination of ACE inhibitor and ATII receptor antagonist in hypertensive IgA nephropathy [abstract no: SU-FC071]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2004;15(Oct):59A. [CENTRAL: CN-00626045]
-
- Song JH, Lee SW, Suh JH, Kim ES, Hong SB, Kim KA, et al. The effects of dual blockade of the renin-angiotensin system on urinary protein and transforming growth factor-beta excretion in 2 groups of patients with IgA and diabetic nephropathy. Clinical Nephrology 2003;60(5):318-26. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Song 2004a {published data only}
-
- Song JH, Lee SY, Park GH, Lee SW, Kim M. Effects of combination therapy of ACE inhibitor and ATII receptor blocker on proteinuria and renal TGF-b production in Type II overt diabetic nephropathy: a comparison with doubling dose of single therapies [abstract no: SU-PO154]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2004;15(Oct):566A.
Song 2006 {published data only}
-
- Song JH, Cha SH, Lee HJ, Lee SW, Park GH, Lee SW, et al. Effect of low-dose dual blockade of renin-angiotensin system on urinary TGF-beta in type 2 diabetic patients with advanced kidney disease. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2006;21(3):683-9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Song JH, Lee SW, Kim M, Park GH, Lee SW. Renoprotective benefits of low-dose combination of ACE inhibitor and ATII receptor blocker in advanced stage of overt diabetic nephropathy [abstract no: M-PO20056]. Nephrology 2005;10(Suppl):A30.
Suehiro 2021 {published data only}
-
- Suehiro T, Tsuruya K, Yoshida H, Tsujikawa H, Yamada S, Tanaka S, et al. Stronger effect of azilsartan on reduction of proteinuria compared to candesartan in patients with CKD: a randomized crossover trial. Kidney & Blood Pressure Research 2021;46(2):173‐84. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Suzuki 2011 {published data only}
Tan 2010 {published data only}
-
- Tan F, Mukherjee JJ, Lee KO, Lim P, Liew CF. Dual blockade of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system is safe and effective in reducing albuminuria in Asian type 2 diabetic patients with nephropathy. Singapore Medical Journal 2010;51(2):151-6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
TRENDY 2007 {published data only}
-
- Schmieder RE, Delles C, Mimran A, Fauvel JP, Ruilope L. Effects of telmisartan versus ramipril on endothelium function of the renal vasculature in Type 2 - diabetes [abstract no: M-PO20027]. Nephrology 2005;10(Suppl 1):A22-3. [CENTRAL: CN-00740460]
-
- Schmieder RE, Delles C, Mimran A, Fauvel JP, Ruilope LM. Impact of telmisartan versus ramipril on renal endothelial function in patients with hypertension and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2007;30(6):1351-6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Schmieder RE, Delles CC, Mimran A, Fauvel JP, Ruilope L. Effects of telmisartan versus ramipril on endothelium function of the renal vasculature in type 2 diabetes [abstract no: MP127]. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2005;20(Suppl 5):v242-3. [CENTRAL: CN-00740460]
-
- Schmieder RE, Schlaich MP, Mimran A, Fauvel JP, Ruilope L. Pathogenetic factors of atherosclerosis are disparately influenced by telmisartan and ramipril in Type 2 diabetes [abstract no: MO005]. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2006;21(Suppl 4):iv289. [CENTRAL: CN-00740458]
-
- Schmieder RE, Schlaich MP, Mimran A, Fauvel JP, Ruilope LM. Pathogenetic factors of atherosclerosis are disparately influenced by telmisartan and ramipril in type 2 diabetes [abstract no: TH-FC151]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2006;17(Abstracts):33A. [CENTRAL: CN-00740458]
Turab 2008 {published data only}
-
- Turab SM, Mashori GR, Naqvi A, Rabbi SF. Proteinuria a target for reno-protection in hypertensive patients with type 2 diabetic nephropathy. Medical Forum Monthly 2008;19(9):4-8. [EMBASE: 354488777]
van Nieuwenhoven 2004 {published data only}
-
- Nieuwenhoven FA, Rossing K, Andersen S, Oliver N, Goldschmeding R. Beneficial effect of dual blockade of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) on urinary connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) in Type 2 diabetic patients with nephropathy [abstract no: SU-PO180]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2004;15(Oct):571A. [CENTRAL: CN-00583815]
Vongterapak 1998 {published data only}
-
- Vongterapak S, Dahlan W, Nakasatien S, Anuntakulnatee T, Suppanich M, Kittipoom W, et al. Impediment of the progressions of microalbuminuria and hyperlipidemia in normotensive type 2 diabetes by low-dose ramipril. Journal of the Medical Association of Thailand 1998 Sep;81(9):671-81. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Wiegmann 1992 {published data only}
-
- Wiegmann TB, Herron KG, Chonko AM, MacDougall ML, Moore WV. Effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition on renal function and albuminuria in normotensive type I diabetic patients. Diabetes 1992;41(1):62-7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Wouda 2021 {published data only}
Zandbergen 2003 {published data only}
-
- Zandbergen AA, Baggen MG, Lamberts SW, Bootsma AH, Zeeuw D, Ouwendijk RJ. Effect of losartan on microalbuminuria in normotensive patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. A randomized clinical trial. Annals of Internal Medicine 2003;139(2):90-6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Zandbergen AA, Lamberts SW, Baggen MG, Janssen JA, Boersma E, Bootsma AH. The IGF-I system and the renal and haemodynamic effects of losartan in normotensive patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized clinical trial. Clinical Endocrinology 2006;64(2):203-8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Zhang 2019c {published data only}
-
- Zhang X, Yan Y, Shi J, Ma T, Hu C. Clinical observation of ACEI combined with ARB for treatment of diabetic nephropathy in elderly patients. International Journal of Clinical & Experimental Medicine 2019;12(6):7630-6. [EMBASE: 2002255351]
References to studies awaiting assessment
Andrysiak‐Mamos 1997 {published data only}
-
- Andrysiak-Mamos E, Majkowska L, Pynka S, Czekalski S. The reduction in 24 h blood pressure and diminution of microalbuminuria in incipient diabetic nephropathy treated with ACEI during 2 years [abstract]. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 1997;12(9):A90. [CENTRAL: CN-00509146]
Limonte 2024 {published data only}
-
- Limonte CP, Prince DK, Hoofnagle AN, Galecki A, Hirsch IB, Tian F, et al. Associations of biomarkers of tubular injury and inflammation with biopsy features in type 1 diabetes. Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology: CJASN 2024;19(1):44-55. [CENTRAL: CN-00509146] [DOI: 10.2215/CJN.0000000000000333] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Vijay 2000 {published data only}
-
- Vijay V, Jayaraman M, Snehalatha C, Shina K, Ramachandran A. Progression of persistent microalbuminuria in hypertensive versus normotensive type 2 diabetic patients: a follow-up study [abstract no: CNO18]. Indian Journal of Nephrology 2000;10:108.
Vineela 2023 {published data only}
-
- Vineela KN, Kodudula S, Sindu P, Srisangeetha G. A comparative study on the pleiotropic effects of Olmesartan and Telmisartan in hypertensive patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized, prospective, open labelled, hospital based study. Journal of Krishna Institute of Medical Sciences University 2023;12(3):113‐21. [EMBASE: 2026550529]
References to ongoing studies
CTRI/2023/05/052593 {published data only}
-
- Dual RAAS blockage in primary glomerular diseases. https://trialsearch.who.int/Trial2.aspx?TrialID=CTRI/2023/05/052593 (registration date: 12 May 2023).
NCT05753696 {published data only}
-
- Azilsartan in patients with diabetic kidney disease and hypertension [The effect of azilsartan in patients with diabetic kidney disease and hypertension]. https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT05753696 (date first posted: 3 March 2023).
TCTR20220426002 {published data only}
-
- Comparison of efficacy in renoprotection between Azilsartan medoxomil and Enalapril: a randomized, open-labeled controlled trial. https://trialsearch.who.int/Trial2.aspx?TrialID=TCTR20220426002 (registration date: 26 April 2022).
Additional references
Arendshorst 1999
-
- Arendshorst WJ, Brannstrom K, Ruan X. Actions of angiotensin II on the renal microvasculature. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology : JASN 1999;10 Suppl 11:S149-61. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Bonino 2019
Cheng 2014
-
- Cheng J, Zhang W, Zhang X, Han F, Li X, He X, et al. Effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin ii receptor blockers on all-cause mortality, cardiovascular deaths, and cardiovascular events in patients with diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis. JAMA Internal Medicine 2014;174(5):773-85. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Coleman 2019
-
- Coleman CI, Weeda ER, Kharat A, Bookhart B, Baker WL. Impact of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers on renal and mortality outcomes in people with Type 2 diabetes and proteinuria. Diabetic Medicine 2019;37(1):44-52. [PMID: ] - PubMed
CREDENCE 2019
-
- Perkovic V, Jardine MJ, Neal B, Bompoint S, Heerspink HJL, Charytan DM, et al. Canagliflozin and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. New England Journal of Medicine 2019;380(24):2295-306. [PMID: ] - PubMed
DAPA‐CKD 2021
-
- Wheeler DC, Stefánsson BV, Jongs N, Chertow GM, Greene T, Hou FF, et al. Effects of dapagliflozin on major adverse kidney and cardiovascular events in patients with diabetic and non-diabetic chronic kidney disease: a prespecified analysis from the DAPA-CKD trial. Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology 2021;9(1):22-31. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Georgianos 2018
Go 2004
-
- Go AS, Chertow GM, Fan D, McCulloch CE, Hsu CY. Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. New England Journal of Medicine 2004;351(13):1296-305. [PMID: ] - PubMed
GRADE 2008
GRADE 2011
-
- Guyatt G, Oxman AD, Akl EA, Kunz R, Vist G, Brozek J, et al. GRADE guidelines: 1. Introduction-GRADE evidence profiles and summary of findings tables. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011;64(4):383-94. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2022
-
- Higgins JP, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, et al. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviewsof Interventions version 6.3 (updated February 2022), Cochrane, 2022. Available from www.training.cochrane.org/handbook.
JNC 8 2014
-
- James PA, Oparil S, Carter BL, Cushman WC, Dennison-Himmelfarb C, Handler J, et al. 2014 evidence-based guideline for the management of high blood pressure in adults: Report from the panel members appointed to the Eighth Joint National Committee (JNC 8) [Erratum in: JAMA. 2014 May 7;311(17):1809]. JAMA 2014;311(5):507-20. [DOI: 10.1001/jama.2013.284427] [PMID: ] - DOI - PubMed
Joshi 2021
KDIGO Blood Pressure Guidelines 2021
-
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Blood Pressure Work Group. KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Blood Pressure in Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney International Supplement 2021;99(1):S1-87. [DOI: 10.1016/j.kint.2020.11.003] - DOI
Lv 2012
Lv 2012a
Messerli 2018
-
- Messerli FH, Bangalore S, Bavishi C, Rimoldi SF. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors in hypertension: to use or not to use? Journal of the American College of Cardiology 2018;71(13):1474-82. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Mogensen 1995
-
- Mogensen CE. Microalbuminuria in prediction and prevention of diabetic nephropathy in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus patients. Journal of Diabetes & its Complications 1995;9(4):337-49. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Mogensen 1999
-
- Mogensen CE. Drug treatment for hypertensive patients in special situations: diabetes and hypertension. Clinical & Experimental Hypertension (New York) 1999;21(5-6):895-906. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
NKF KDOQI Guidelines 2004
-
- K/DOQI Clinical Practice Guidelines on Hypertension and Antihypertensive Agents in Chronic Kidney Disease. Guideline 11: use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers in CKD. https://kidneyfoundation.cachefly.net/professionals/KDOQI/guidelines_bp/... (date accessed: 4 March 2024).
Ritter 2011
-
- Ritter JM. Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers in hypertension. BMJ 2011;342:d1673. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Ritz 1999
-
- Ritz E, Ortho SR. Nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. New England Journal of Medicine 1999;341(15):1127-33. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Schünemann 2022a
-
- Schünemann HJ, Higgins JP, Vist GE, Glasziou P, Akl EA, Skoetz N, et al. Chapter 14: Completing ‘Summary of findings’ tables and grading the certainty of the evidence. In: Higgins JP, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Welch VA (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 6.3 (updated February 2022). Cochrane, 2022. www.training.cochrane.org/handbook.
Schünemann 2022b
-
- Schünemann HJ, Vist GE, Higgins JP, Santesso N, Deeks JJ, Glasziou P, et al. Chapter 15: Interpreting results and drawing conclusions. In: Higgins JP, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Welch VA (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 6.3 (updated February 2022). Cochrane, 2022. Available fromwww.training.cochrane.org/handbook.
SONG
-
- Standardised Outcomes in Nephrology. https://songinitiative.org/ (accessed: 4 March 2024).
Stringer 2013
Tabriziani 2018
Vaidya 2022
-
- Vaidya SR, Aeddula NR. Chronic kidney disease. StatPearls 2022. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK535404/] - PubMed
Wang 2018
-
- Wang K, Hu J, Luo T, Wang Y, Yang S, Qing H, et al. Effects of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin ii receptor blockers on all-cause mortality and renal outcomes in patients with diabetes and albuminuria: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Kidney & Blood Pressure Research 2018;43(3):768-79. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Yuan 2017
References to other published versions of this review
Strippoli 2004
Strippoli 2006
-
- Strippoli GFM, Bonifati C, Craig M, Navaneethan SD, Craig JC. Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor antagonists for preventing the progression of diabetic kidney disease. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2006, Issue 4. Art. No: CD006257. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD006257] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

