Evolving Evidence-Based Value Assessment of One-Time Therapies: Tisagenlecleucel as a Case Study
- PMID: 38683438
- PMCID: PMC11339080
- DOI: 10.1007/s40258-024-00882-4
Evolving Evidence-Based Value Assessment of One-Time Therapies: Tisagenlecleucel as a Case Study
Abstract
Background: Economic evaluation of one-time therapies during reimbursement decision-making is challenging due to uncertain long-term outcomes. The availability of 5-year outcome data from the ELIANA trial and real-world evidence of tisagenlecleucel, the first chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR-T) therapy, presents an opportunity to re-evaluate the predictions of prior cost-effectiveness analyses (CEAs).
Objective: To conduct a systematic literature review (SLR) of prior CEAs of tisagenlecleucel for pediatric/young adult relapsed or refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia (r/r ALL) and evaluate the impact of recently available 5-year efficacy data from ELIANA and advances in CAR-T manufacturing in an updated CEA model.
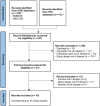
Methods: OVID MEDLINE/Embase and health technology assessment (HTA) databases were searched for full-text economic evaluations in English reporting cost-effectiveness results for tisagenlecleucel for r/r ALL. Evaluations with publicly reported incremental cost-effectiveness ratios (ICERs) were included in the SLR. Study screening and data abstraction were conducted following PRISMA guidelines. Data extracted included the country/currency, perspective, clinical trial evidence, model structures, long-term efficacy extrapolation approaches (i.e., overall survival [OS]), time horizon, discount rates, and outcomes (i.e., life years [LY], quality-adjusted LY [QALY], and ICERs). The CEA model reported in Wakase et al. was updated using 5-year OS data from ELIANA and the CAR-T infusion rate informed by real-world practice.
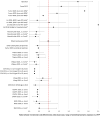
Results: Sixteen records corresponding to 15 unique studies were included in the SLR (11 publications and 5 HTA reports); all were conducted from the health care system perspective of the respective countries. Most studies found tisagenlecleucel to be cost effective, but all studies' projected 3- and 5-year OS rates for tisagenlecleucel were lower than the observed 3- and 5-year rates, respectively, derived from 5-year ELIANA data. When applying updated OS projections from the most recent ELIANA data cut and higher infusion rates of 92.5% (per the real-world infusion rate)-96.0% (per the manufacturer success rate) to the CEA of Wakase et al., the associated QALYs for tisagenlecleucel increased from 11.6 to 14.6-15.0, and LYs increased from 13.3 to 17.0-17.5. Accordingly, the ICERs for tisagenlecleucel decreased from ¥2,035,071 to ¥1,787,988-¥1,789,048 versus blinatumomab and from ¥2,644,702 to ¥2,257,837-¥2,275,181 versus clofarabine combination therapy in the updated CEA model.
Conclusions and relevance: Projections at launch of the likely cost effectiveness of tisagenlecleucel appear to have underestimated its ultimate economic value given more recent trial and real-world data. To balance uncertainty in initial valuation with the need to provide access to novel oncology therapies, payers can consider flexible reimbursement policies alongside ongoing assessments as new data emerge.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Theodore Laetsch holds stock in Advanced Microbubbles; has consulting or advisory roles with Novartis, Aptitude Health, Jumo Health, Massive Bio, Medscape, AI Therapeutics, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, GentBio, Menarini, Pyramid Biosciences, Targeted Oncology, and Treeline Biosciences; and research funding from Lilly, Roche/Genentech, Taiho Oncology, Advanced Accelerator Applications/Novartis, Bristol-Myers Squibb, BioAtla, Hoffman-LaRoche, Pfizer, Bayer, and Turning Point Therapeutics. Louis Garrison reports having received consulting fees in the last 2 years for other research activities with a number of biopharmaceutical companies, including Novartis Gene Therapy, Pfizer, Astra-Zeneca, GSK, MSD, Eli Lilly, Genentech, Roche Molecular Systems, BioMarin, and UniQure. Jie Zhang is an employee of Novartis and owns stock/options. Hongbo Yang, Yanwen Xie, and Dudan Zhang are employees of Analysis Group, Inc., which has received consulting fees from Novartis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of topotecan for ovarian cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(28):1-110. doi: 10.3310/hta5280. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11701100
-
Topotecan, pegylated liposomal doxorubicin hydrochloride and paclitaxel for second-line or subsequent treatment of advanced ovarian cancer: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Mar;10(9):1-132. iii-iv. doi: 10.3310/hta10090. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16545208
-
Adefovir dipivoxil and pegylated interferon alfa-2a for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Aug;10(28):iii-iv, xi-xiv, 1-183. doi: 10.3310/hta10280. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16904047
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
The clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of cardiac resynchronisation (biventricular pacing) for heart failure: systematic review and economic model.Health Technol Assess. 2007 Nov;11(47):iii-iv, ix-248. doi: 10.3310/hta11470. Health Technol Assess. 2007. PMID: 17999842
Cited by
-
ARM's Perspective on the First Joint Clinical Assessments for ATMPs: Challenges and Opportunities on the Path Ahead.J Mark Access Health Policy. 2025 Apr 3;13(2):14. doi: 10.3390/jmahp13020014. eCollection 2025 Jun. J Mark Access Health Policy. 2025. PMID: 40276090 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rodrigues M, Kuzan D, Yallouridis A, Saffar J-M, Eschgfaeller B. Commercial manufacturing experience of tisagenlecleucel in Europe: > 3 years journey. 48th annual meeting of the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT); March 19-23, 2022; Prague, Czech Republic.
-
- Mullard A. FDA approves first CAR T therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2017;16(10):669. - PubMed
-
- United States Food and Drug Administration. Highlights of prescribing information: KYMRIAH (tisagenlecleucel) 2017. https://www.fda.gov/media/107296/download. Accessed 1 June 2023.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

