Insights into Molecular Interactions between a GAPDH-Related Fish Antimicrobial Peptide, Analogs Thereof, and Bacterial Membranes
- PMID: 38683758
- PMCID: PMC11112741
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.biochem.4c00049
Insights into Molecular Interactions between a GAPDH-Related Fish Antimicrobial Peptide, Analogs Thereof, and Bacterial Membranes
Abstract
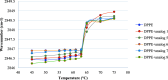
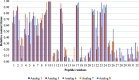
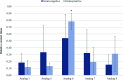
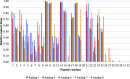
Interactions between SJGAP (skipjack tuna GAPDH-related antimicrobial peptide) and four analogs thereof with model bacterial membranes were studied using Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and molecular dynamics (MD) simulations. MD trajectory analyses showed that the N-terminal segment of the peptide analogs has many contacts with the polar heads of membrane phospholipids, while the central α helix interacts strongly with the hydrophobic core of the membranes. The peptides also had a marked influence on the wave numbers associated with the phase transition of phospholipids organized as liposomes in both the interface and aliphatic chain regions of the infrared spectra, supporting the interactions observed in the MD trajectories. In addition, interesting links were found between peptide interactions with the aliphatic chains of membrane phospholipids, as determined by FTIR and from the MD trajectories, and the membrane permeabilization capacity of these peptide analogs, as previously demonstrated. To summarize, the combined experimental and computational efforts have provided insights into crucial aspects of the interactions between the investigated peptides and bacterial membranes. This work thus makes an original contribution to our understanding of the molecular interactions underlying the antimicrobial activity of these GAPDH-related antimicrobial peptides from Scombridae.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Ergosterol depletion by fish AMP analogs likely enhances fungal membrane permeability.Biophys J. 2025 Apr 1;124(7):1105-1116. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2025.02.015. Epub 2025 Feb 25. Biophys J. 2025. PMID: 40007119
-
Antimicrobial function of the GAPDH-related antimicrobial peptide in the skin of skipjack tuna, Katsuwonus pelamis.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014 Feb;36(2):571-81. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2014.01.003. Epub 2014 Jan 9. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24412436
-
Determination of the Relationships between the Chemical Structure and Antimicrobial Activity of a GAPDH-Related Fish Antimicrobial Peptide and Analogs Thereof.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Feb 23;11(3):297. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11030297. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35326761 Free PMC article.
-
Biological activity and structural aspects of PGLa interaction with membrane mimetic systems.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009 Aug;1788(8):1656-66. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2009.05.012. Epub 2009 May 29. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009. PMID: 19481533 Review.
-
Lipid-induced conformation and lipid-binding properties of cytolytic and antimicrobial peptides: determination and biological specificity.Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999 Dec 15;1462(1-2):89-108. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2736(99)00202-3. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999. PMID: 10590304 Review.
Cited by
-
Ergosterol depletion by fish AMP analogs likely enhances fungal membrane permeability.Biophys J. 2025 Apr 1;124(7):1105-1116. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2025.02.015. Epub 2025 Feb 25. Biophys J. 2025. PMID: 40007119
References
-
- World Health Organization . Antibiotic Resistance, 2024, Available from. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/antibiotic-resistance, Date of access: 2024-01.
-
- Ben said L.; et al.Antimicrobial Peptides: The New Generation of Food Additives. In Encyclopedia of Food Chemistry; Melton L., Shahidi F., Varelis P., Eds.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2019; pp 576–582.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

