A Targetable N-Terminal Motif Orchestrates α-Synuclein Oligomer-to-Fibril Conversion
- PMID: 38683963
- PMCID: PMC11082882
- DOI: 10.1021/jacs.4c02262
A Targetable N-Terminal Motif Orchestrates α-Synuclein Oligomer-to-Fibril Conversion
Abstract
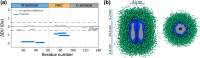
Oligomeric species populated during α-synuclein aggregation are considered key drivers of neurodegeneration in Parkinson's disease. However, the development of oligomer-targeting therapeutics is constrained by our limited knowledge of their structure and the molecular determinants driving their conversion to fibrils. Phenol-soluble modulin α3 (PSMα3) is a nanomolar peptide binder of α-synuclein oligomers that inhibits aggregation by blocking oligomer-to-fibril conversion. Here, we investigate the binding of PSMα3 to α-synuclein oligomers to discover the mechanistic basis of this protective activity. We find that PSMα3 selectively targets an α-synuclein N-terminal motif (residues 36-61) that populates a distinct conformation in the mono- and oligomeric states. This α-synuclein region plays a pivotal role in oligomer-to-fibril conversion as its absence renders the central NAC domain insufficient to prompt this structural transition. The hereditary mutation G51D, associated with early onset Parkinson's disease, causes a conformational fluctuation in this region, leading to delayed oligomer-to-fibril conversion and an accumulation of oligomers that are resistant to remodeling by molecular chaperones. Overall, our findings unveil a new targetable region in α-synuclein oligomers, advance our comprehension of oligomer-to-amyloid fibril conversion, and reveal a new facet of α-synuclein pathogenic mutations.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): SV, IP and JS have submitted a patent protecting the use of PSM3 for therapy and diagnosis. Request number: EP20382658. Priority date: 22-07-2020.
Figures


References
-
- Polymeropoulos M. H.; Lavedan C.; Leroy E.; Ide S. E.; Dehejia A.; Dutra A.; Pike B.; Root H.; Rubenstein J.; Boyer R.; Stenroos E. S.; Chandrasekharappa S.; Athanassiadou A.; Papapetropoulos T.; Johnson W. G.; Lazzarini A. M.; Duvoisin R. C.; Di Iorio G.; Golbe L. I.; Nussbaum R. L. Mutation in the α-Synuclein Gene Identified in Families with Parkinson’s Disease. Science 1997, 276 (5321), 2045–2047. 10.1126/science.276.5321.2045. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cremades N.; Cohen S. I. A.; Deas E.; Abramov A. Y.; Chen A. Y.; Orte A.; Sandal M.; Clarke R. W.; Dunne P.; Aprile F. A.; Bertoncini C. W.; Wood N. W.; Knowles T. P. J.; Dobson C. M.; Klenerman D. Direct Observation of the Interconversion of Normal and Toxic Forms of α-Synuclein. Cell 2012, 149 (5), 1048–1059. 10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.037. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

