Cheminformatics approach to identify andrographolide derivatives as dual inhibitors of methyltransferases (nsp14 and nsp16) of SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 38684706
- PMCID: PMC11058777
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-58532-7
Cheminformatics approach to identify andrographolide derivatives as dual inhibitors of methyltransferases (nsp14 and nsp16) of SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
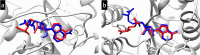
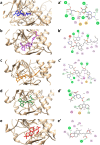
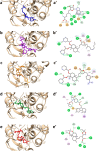
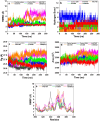
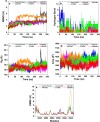
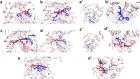
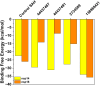
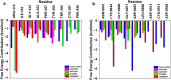
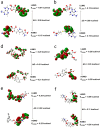
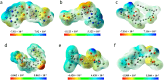
The Covid-19 pandemic outbreak has accelerated tremendous efforts to discover a therapeutic strategy that targets severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) to control viral infection. Various viral proteins have been identified as potential drug targets, however, to date, no specific therapeutic cure is available against the SARS-CoV-2. To address this issue, the present work reports a systematic cheminformatic approach to identify the potent andrographolide derivatives that can target methyltransferases of SARS-CoV-2, i.e. nsp14 and nsp16 which are crucial for the replication of the virus and host immune evasion. A consensus of cheminformatics methodologies including virtual screening, molecular docking, ADMET profiling, molecular dynamics simulations, free-energy landscape analysis, molecular mechanics generalized born surface area (MM-GBSA), and density functional theory (DFT) was utilized. Our study reveals two new andrographolide derivatives (PubChem CID: 2734589 and 138968421) as natural bioactive molecules that can form stable complexes with both proteins via hydrophobic interactions, hydrogen bonds and electrostatic interactions. The toxicity analysis predicts class four toxicity for both compounds with LD50 value in the range of 500-700 mg/kg. MD simulation reveals the stable formation of the complex for both the compounds and their average trajectory values were found to be lower than the control inhibitor and protein alone. MMGBSA analysis corroborates the MD simulation result and showed the lowest energy for the compounds 2734589 and 138968421. The DFT and MEP analysis also predicts the better reactivity and stability of both the hit compounds. Overall, both andrographolide derivatives exhibit good potential as potent inhibitors for both nsp14 and nsp16 proteins, however, in-vitro and in vivo assessment would be required to prove their efficacy and safety in clinical settings. Moreover, the drug discovery strategy aiming at the dual target approach might serve as a useful model for inventing novel drug molecules for various other diseases.
Keywords: Andrographolide; Covid-19; Drug discovery; Natural compounds; nsp14; nsp16.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Structure-Based Virtual Screening for Methyltransferase Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 nsp14 and nsp16.Molecules. 2024 May 15;29(10):2312. doi: 10.3390/molecules29102312. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38792173 Free PMC article.
-
In silico evaluation of S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine analogs as inhibitors of nsp14-viral cap N7 methyltranferase and PLpro of SARS-CoV-2: synthesis, molecular docking, physicochemical data, ADMET and molecular dynamics simulations studies.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2025 Apr;43(7):3258-3275. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2023.2297005. Epub 2023 Dec 26. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2025. PMID: 38147408
-
Integrated molecular and quantum mechanical approach to identify novel potent natural bioactive compound against 2'-O-methyltransferase (nsp16) of SARS-CoV-2.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2024 Feb-Mar;42(4):1999-2012. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2023.2206287. Epub 2023 May 2. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2024. PMID: 37129206
-
Perspective for Drug Discovery Targeting SARS Coronavirus Methyltransferases: Function, Structure and Inhibition.J Med Chem. 2024 Nov 14;67(21):18642-18655. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.4c01749. Epub 2024 Oct 31. J Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39478665 Review.
-
Coronavirus 2'-O-methyltransferase: A promising therapeutic target.Virus Res. 2023 Oct 15;336:199211. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2023.199211. Epub 2023 Sep 4. Virus Res. 2023. PMID: 37634741 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Design and Evaluation of Andrographolide Analogues as SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Inhibitors: Molecular Modeling and in vitro Studies.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025 May 15;19:3907-3924. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S514193. eCollection 2025. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025. PMID: 40391180 Free PMC article.
-
Computational screening combined with well-tempered metadynamics simulations identifies potential TMPRSS2 inhibitors.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 13;14(1):16197. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-65296-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39003338 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

