The clinical efficacy of single-hole punch excision combined with intralesional steroid injection for nodular keloid treatment: a self-controlled trial
- PMID: 38684804
- PMCID: PMC11058828
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-60670-x
The clinical efficacy of single-hole punch excision combined with intralesional steroid injection for nodular keloid treatment: a self-controlled trial
Abstract
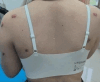
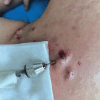
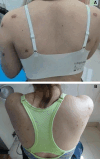
There are many methods to treat keloid, including various excision operations, laser, injection and radiotherapy. However, few studies have explored the effectiveness of single-hole punch excision in keloid treatment. This study aimed to investigate the efficacy and safety of lateral punch excision combined with intralesional steroid injection for keloid treatment through self-control trial. In this self-controlled trial, 50 patients meet the diagnosis of nodular keloid, and try to choose left-right symmetrical control, one skin lesion in the control group (50 skin lesionsin total) and the other in the observation group (50 skin lesions in total).The keloids in the treatment group were initially treated with punch excision combined with intralesional steroid injection, followed by injection treatment alone. Keloids in the control group received intralesional steroid injection alone. The Vancouver Scar Scale (VSS) of the keloid before and after the punch excision was evaluated; the keloid scores at different time points and the number of injection treatments required in both groups were compared, and adverse reactions were observed. The effective rate of the observation group was 86.0%, which was significantly higher than that of the control group (66.0%), and the recurrence rate of 22% was lower than that of the control group (χ2 = 4.141,63417), all of which were statistically significant (all P < 0.05). At the end of treatment, the VSS and total injection times in the observation group were significantly lower than those in the control group (t = 5.900,3.361), with statistical significance (P < 0.01). The combination of single-hole punch excision and intralesional steroid injection is an effective method to treat multiple nodular keloids, shortening the treatment course of tralesional steroid injection without obvious adverse reactions.
Keywords: Intralesional injection; Nodular keloid; Punch excision; Recurrence; Single-hole; Steroid; Symmetry.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Clinical Efficacy of Punch Excision Combined With Intralesional Steroid Injection for Keloid Treatment.Dermatol Surg. 2023 May 1;49(5S):S70-S74. doi: 10.1097/DSS.0000000000003776. Dermatol Surg. 2023. PMID: 37116004 Clinical Trial.
-
Intralesional cryotherapy versus excision with corticosteroid injections or brachytherapy for keloid treatment: Randomised controlled trials.J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2018 Jun;71(6):847-856. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2018.01.033. Epub 2018 Feb 6. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2018. PMID: 29426811 Clinical Trial.
-
Intralesional cryosurgery and intralesional steroid injection: a good combination therapy for treatment of keloids and hypertrophic scars.Dermatol Ther. 2012 May-Jun;25(3):273-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1529-8019.2012.01456.x. Dermatol Ther. 2012. PMID: 22913446
-
Comparison of surgical excision followed by adjuvant radiotherapy and laser combined with steroids for the treatment of keloids: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Int Wound J. 2024 Mar;21(3):e14449. doi: 10.1111/iwj.14449. Epub 2023 Nov 15. Int Wound J. 2024. PMID: 37967571 Free PMC article.
-
Remarkable efficiency of surgical shave excision of keloids followed by intralesional injection of Bleomycin. A retrospective study of 314 cases.Dermatol Ther. 2022 May;35(5):e15425. doi: 10.1111/dth.15425. Epub 2022 Mar 13. Dermatol Ther. 2022. PMID: 35261136 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

