Influence of COVID-19 on trust in routine immunization, health information sources and pandemic preparedness in 23 countries in 2023
- PMID: 38684861
- PMCID: PMC11186753
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-024-02939-2
Influence of COVID-19 on trust in routine immunization, health information sources and pandemic preparedness in 23 countries in 2023
Abstract
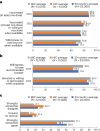
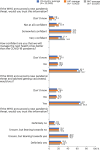
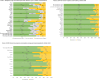
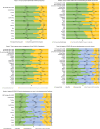
It is unclear how great a challenge pandemic and vaccine fatigue present to public health. We assessed perspectives on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and routine immunization as well as trust in pandemic information sources and future pandemic preparedness in a survey of 23,000 adults in 23 countries in October 2023. The participants reported a lower intent to get a COVID-19 booster vaccine in 2023 (71.6%), compared with 2022 (87.9%). A total of 60.8% expressed being more willing to get vaccinated for diseases other than COVID-19 as a result of their experience during the pandemic, while 23.1% reported being less willing. Trust in 11 selected sources of vaccine information each averaged less than 7 on a 10-point scale with one's own doctor or nurse and the World Health Organization, averaging a 6.9 and 6.5, respectively. Our findings emphasize that vaccine hesitancy and trust challenges remain for public health practitioners, underscoring the need for targeted, culturally sensitive health communication strategies.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Study funding was provided by Moderna, to the City University of New York Research Foundation. The authors retained full autonomy in the design of the study; the development of the survey instrument; the collection, analysis and interpretation of data; the presentation of results; and the decision to submit the article for publication. J.V.L. has received speaker fees from Echosens, Gilead Sciences, Moderna, Novo Nordisk, Novovax, Pfizer and ViiV and grants from Gilead Sciences, GSK, Madrigal Pharmaceuticals and Roche Diagnostics outside the submitted work. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- COVID-19 epidemiological update—19 January 2024. World Health Organizationhttps://www.who.int/publications/m/item/covid-19-epidemiological-update–... (2024).
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

