Discovery of an Aldo-Keto reductase 1C3 (AKR1C3) degrader
- PMID: 38684887
- PMCID: PMC11059152
- DOI: 10.1038/s42004-024-01177-4
Discovery of an Aldo-Keto reductase 1C3 (AKR1C3) degrader
Abstract
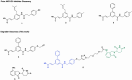
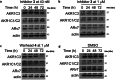
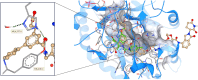
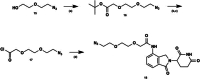
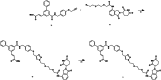
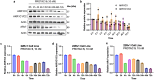
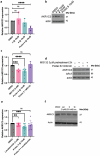
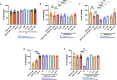
Aldo-keto reductase 1C3 (AKR1C3) is a protein upregulated in prostate cancer, hematological malignancies, and other cancers where it contributes to proliferation and chemotherapeutic resistance. Androgen receptor splice variant 7 (ARv7) is the most common mutation of the AR receptor that confers resistance to clinical androgen receptor signalling inhibitors in castration-resistant prostate cancer. AKR1C3 interacts with ARv7 promoting stabilization. Herein we report the discovery of the first-in-class AKR1C3 Proteolysis-Targeting Chimera (PROTAC) degrader. This first-generation degrader potently reduced AKR1C3 expression in 22Rv1 prostate cancer cells with a half-maximal degradation concentration (DC50) of 52 nM. Gratifyingly, concomitant degradation of ARv7 was observed with a DC50 = 70 nM, along with degradation of the AKR1C3 isoforms AKR1C1 and AKR1C2 to a lesser extent. This compound represents a highly useful chemical tool and a promising strategy for prostate cancer intervention.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
P.C.T. and A.V.C. are inventors on a patent application describing the PROTAC compound.
Figures

References
-
- Birtwistle L, et al. The aldo-keto reductase AKR1C3 contributes to 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene-3,4-dihydrodiol mediated oxidative DNA damage in myeloid cells: Implications for leukemogenesis. Mutat. Res.-Fund. Mol. Mech. Mutagenesis. 2009;662:67–74. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2008.12.010. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

