Molecular farming for sustainable production of clinical-grade antimicrobial peptides
- PMID: 38685599
- PMCID: PMC11258990
- DOI: 10.1111/pbi.14344
Molecular farming for sustainable production of clinical-grade antimicrobial peptides
Abstract
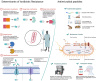
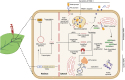
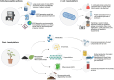
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) are emerging as next-generation therapeutics due to their broad-spectrum activity against drug-resistant bacterial strains and their ability to eradicate biofilms, modulate immune responses, exert anti-inflammatory effects and improve disease management. They are produced through solid-phase peptide synthesis or in bacterial or yeast cells. Molecular farming, i.e. the production of biologics in plants, offers a low-cost, non-toxic, scalable and simple alternative platform to produce AMPs at a sustainable cost. In this review, we discuss the advantages of molecular farming for producing clinical-grade AMPs, advances in expression and purification systems and the cost advantage for industrial-scale production. We further review how 'green' production is filling the sustainability gap, streamlining patent and regulatory approvals and enabling successful clinical translations that demonstrate the future potential of AMPs produced by molecular farming. Finally, we discuss the regulatory challenges that need to be addressed to fully realize the potential of molecular farming-based AMP production for therapeutics.
Keywords: antimicrobial peptides; clinical‐grade AMP production; green synthesis; molecular farming.
© 2024 The Authors. Plant Biotechnology Journal published by Society for Experimental Biology and The Association of Applied Biologists and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


References
-
- Adebomi, V. , Cohen, R.D. , Wills, R. , Chavers, H.A.H. , Martin, G.E. and Raj, M. (2019) CyClick chemistry for the synthesis of cyclic peptides. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 58, 19073–19080. - PubMed
-
- Ajikumar, P.K. and Devaky, K.S. (2001) Solid phase synthesis of hydrophobic difficult sequence peptides on BDDMA‐PS support. J. Pept. Sci. 7, 641–649. - PubMed
-
- Akishiba, M. , Takeuchi, T. , Kawaguchi, Y. , Sakamoto, K. , Yu, H.H. , Nakase, I. , Takatani‐Nakase, T. et al. (2017) Cytosolic antibody delivery by lipid‐sensitive endosomolytic peptide. Nat. Chem. 9, 751–761. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

