Insomnia and risk of mortality in older adults
- PMID: 38685752
- PMCID: PMC12229267
- DOI: 10.1111/jsr.14229
Insomnia and risk of mortality in older adults
Abstract
Existing evidence linking insomnia to all-cause mortality in older individuals remains inconclusive. We conducted a retrospective study of a large cohort of veterans aged 65-80 years old identified from the Corporate Data Warehouse, a large data repository derived from the Veterans Health Administration integrated medical records. Veterans' enrollees with and without International Classification of Diseases, Ninth and Tenth Revision, codes corresponding to insomnia diagnosis between 1 January 2010 and 30 March 2019 were assessed for eligibility. The primary outcome was all-cause mortality. A total of 36,269 veterans, 9584 with insomnia and 26,685 without insomnia, were included in the analysis. Baseline mean (SD) age was 72.6 (4.2) years. During a mean follow-up of 6.0 (2.9) years of the propensity score matched sample, the mortality rate was 34.8 [95% confidence interval: 33.2-36.6] deaths per 1000 person-years among patients with insomnia compared with 27.8 [95% confidence interval: 26.6-29.1] among patients without insomnia. In a Cox proportional hazards model, insomnia was significantly associated with higher mortality (hazard ratio: 1.39; [95% confidence interval: 1.27-1.52]). Patients with insomnia also had a higher risk of non-fatal cardiovascular events (hazard ratio: 1.21; [95% confidence interval: 1.06-1.37]). Secondary stratified analyses by sex, race, ethnicity and hypertension showed no evidence of effect modification. A higher risk of mortality (hazard ratio: 1.51; [95% confidence interval: 1.33-1.71]) was observed when depression was present compared with absent (hazard ratio: 1.26; [95% confidence interval: 1.12-1.44]; p = 0.02). In this cohort study, insomnia was associated with increased risk-adjusted mortality and non-fatal cardiovascular events in older individuals.
Keywords: depression; elderly; insomnia; major cardiovascular events; mortality.
© 2024 European Sleep Research Society.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
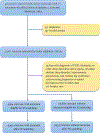
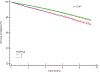
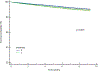

References
-
- Anothaisintawee T, Reutrakul S, Van Cauter E, & Thakkinstian A. (2016). Sleep disturbances compared to traditional risk factors for diabetes development: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Medicine Reviews, 30, 11–24. - PubMed
-
- Association AP. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th ed.). American Psychiatric Pub.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

