Medicinal Plants in the Treatment of Myocardial Infarction Disease: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 38685783
- PMCID: PMC11327834
- DOI: 10.2174/011573403X278881240405044328
Medicinal Plants in the Treatment of Myocardial Infarction Disease: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Background: Myocardial infarction (MI), also referred to as a "heart attack," is brought on by a partial or total interruption of blood supply to the myocardium. Myocardial infarction can be "silent," go undiagnosed, or it can be a catastrophic occurrence that results in hemodynamic decline and untimely death. In recent years, herbal remedies for MI have become effective, secure, and readily accessible.
Objective: The purpose of this review was to examine the medicinal plants and phytochemicals that have been used to treat MI in order to assess the potential contribution of natural substances to the development of herbal MI treatments.
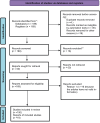
Methodology: A literature search was employed to find information utilizing electronic databases, such as Web of Science, Google Scholar, PubMed, Sci Finder, Reaxys, and Cochrane.
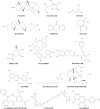
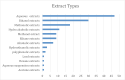
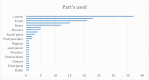
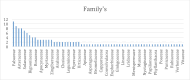
Results: The identification of 140 plants from 12 families led to the abstraction of data on the plant families, parts of the plant employed, chemical contents, extracts, model used, and dose.
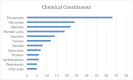
Conclusion: The majority of the MI plants, according to the data, belonged to the Fabaceae (11%) and Asteraceae (9%) families, and the most prevalent natural components in plants with MI were flavonoids (43%), glucosides (25%), alkaloids (23%), phenolic acid (19%), saponins (15%), and tannins (12%).
Keywords: Fabaceae; Myocardial infarction; alkaloids.; coronary artery; glucosides; phytochemicals.
Copyright© Bentham Science Publishers; For any queries, please email at epub@benthamscience.net.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Traditional uses, phytochemistry, and pharmacology of the genus Acer (maple): A review.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Aug 2;189:31-60. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.04.021. Epub 2016 Apr 29. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27132717
-
A critical overview of challenging roles of medicinal plants in improvement of wound healing technology.Daru. 2024 Jun;32(1):379-419. doi: 10.1007/s40199-023-00502-x. Epub 2024 Jan 15. Daru. 2024. PMID: 38225520 Free PMC article.
-
[Volume and health outcomes: evidence from systematic reviews and from evaluation of Italian hospital data].Epidemiol Prev. 2013 Mar-Jun;37(2-3 Suppl 2):1-100. Epidemiol Prev. 2013. PMID: 23851286 Italian.
-
Herbal and dietary therapies for primary and secondary dysmenorrhoea.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001;(3):CD002124. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002124. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Mar 22;3:CD002124. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002124.pub2. PMID: 11687013 Updated.
-
Clopidogrel and modified-release dipyridamole for the prevention of occlusive vascular events (review of Technology Appraisal No. 90): a systematic review and economic analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2011 Sep;15(31):1-178. doi: 10.3310/hta15310. Health Technol Assess. 2011. PMID: 21888837 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
