Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for the treatment of hypoxic/ischemic injury upon perinatal asphyxia-are we there yet?
- PMID: 38685945
- PMCID: PMC11057380
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1386695
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for the treatment of hypoxic/ischemic injury upon perinatal asphyxia-are we there yet?
Abstract
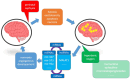
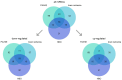
Birth asphyxia and its main sequel, hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy, are one of the leading causes of children's deaths worldwide and can potentially worsen the quality of life in subsequent years. Despite extensive research efforts, efficient therapy against the consequences of hypoxia-ischemia occurring in the perinatal period of life is still lacking. The use of hyperbaric oxygen, improving such vital consequences of birth asphyxia as lowered partial oxygen pressure in tissue, apoptosis of neuronal cells, and impaired angiogenesis, is a promising approach. This review focused on the selected aspects of mainly experimental hyperbaric oxygen therapy. The therapeutic window for the treatment of perinatal asphyxia is very narrow, but administering hyperbaric oxygen within those days improves outcomes. Several miRNAs (e.g., mir-107) mediate the therapeutic effect of hyperbaric oxygen by modulating the Wnt pathway, inhibiting apoptosis, increasing angiogenesis, or inducing neural stem cells. Combining hyperbaric oxygen therapy with drugs, such as memantine or ephedrine, produced promising results. A separate aspect is the use of preconditioning with hyperbaric oxygen. Overall, preliminary clinical trials with hyperbaric oxygen therapy used in perinatal asphyxia give auspicious results.
Keywords: apoptosis; brain; hyperbaric oxygen therapy; microRNA; oxidative stress; perinatal hypoxia-ischemia.
Copyright © 2024 Mielecki, Godlewski and Salinska.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization . Perinatal asphyxia. Available at: https://www.who.int/teams/maternal-newborn-child-adolescent-health-and-a... (Accessed February, 2024).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

