Sex disparities in the association between serum cotinine and chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 38686043
- PMCID: PMC11056949
- DOI: 10.18332/tid/185965
Sex disparities in the association between serum cotinine and chronic kidney disease
Abstract
Introduction: Despite the existence of numerous studies highlighting the adverse effects of smoking on kidney function, the investigation of the correlation between serum cotinine and chronic kidney disease (CKD) remains inconclusive due to insufficient evidence. Consequently, the primary objective of this study was to ascertain the association between serum cotinine levels and CKD.
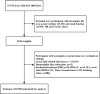
Methods: This study analyzed data from 10900 Americans participating in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey between 2005 and 2016. The independent variable under investigation was log serum cotinine, while the dependent variable was the presence of CKD. To investigate the potential linear and non-linear correlations between serum cotinine and CKD, logistic regression models and generalized additive models (GAM) were employed. Furthermore, stratified analyses and interaction tests were conducted to evaluate potential disparities in the relationship between serum cotinine and CKD, based on sex.
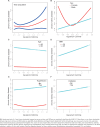
Results: The median age in the study participants was 49.28 ± 17.96 years, and the median log serum cotinine (ng/mL) was -0.54 ± 1.68. The prevalence of CKD was found to be 17.04%. Multifactorial regression analysis did not show a statistically significant association between log serum cotinine and CKD (OR=1.02; 95% CI: 0.98-1.06, p=0.4387). A statistically significant non-linear association between log serum cotinine and CKD was also not observed in the GAM analysis (p non-linear value=0.091). Subgroup analyses revealed sex differences in the association between log serum cotinine and CKD. Briefly, males had a positive association between log serum cotinine and incident CKD (OR=1.08; 95% CI: 1.02-1.15, p=0.0049). In females, there was a U-shaped association between log serum cotinine and CKD, with an optimal inflection point for log serum cotinine of -0.30 (serum cotinine=0.5 ng/mL).
Conclusions: Cross-sectional analyses of NHANES data showed gender differences in the association between serum cotinine and the development of CKD.
Keywords: chronic kidney disease; cotinine; sex disparities; smoking.
© 2024 Song J. et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have completed and submitted the ICMJE Form for Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest and none was reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hydroxycotinine exhibits a stronger association with chronic kidney disease in smokers when compared to cotinine: Evidence from NHANES 2013-2018.Tob Induc Dis. 2025 Mar 18;23. doi: 10.18332/tid/201969. eCollection 2025. Tob Induc Dis. 2025. PMID: 40104399 Free PMC article.
-
The Association Between Smoking and Renal Function in People Over 20 Years Old.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Jun 3;9:870278. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.870278. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35721101 Free PMC article.
-
Exposure to low levels of heavy metals and chronic kidney disease in the US population: A cross sectional study.PLoS One. 2024 Apr 16;19(4):e0288190. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0288190. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38625896 Free PMC article.
-
Association between serum cotinine and total testosterone in adult males based on NHANES 2011-2016.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 4;14(1):23042. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-74482-6. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39362996 Free PMC article.
-
Association between serum cotinine and α-Klotho levels among adults: Findings from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007-2016.Tob Induc Dis. 2022 Jun 14;20:57. doi: 10.18332/tid/144622. eCollection 2022. Tob Induc Dis. 2022. PMID: 35799621 Free PMC article.
References
-
- GBD 2015 DALYs and HALE Collaborators . Global, regional, and national disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs) for 315 diseases and injuries and healthy life expectancy (HALE), 1990-2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet. 2016;388(10053):1603-1658. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31460-X - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- GBD 2015 Mortality and Causes of Death Collaborators . Global, regional, and national life expectancy, all-cause mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of death, 1980-2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet. 2016;388(10053):1459-1544. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31012-1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
