Impact of the diagnosis of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in patients undergoing liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 38686208
- PMCID: PMC11056585
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1306091
Impact of the diagnosis of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in patients undergoing liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Purpose: Whether the diagnosis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease or metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty disease has a different impact on liver transplant recipients with hepatocellular carcinoma is not yet clear.
Methods: Data from a two-center retrospective cohort study were collected to compare and investigate the differences between non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease in clinicopathologic parameters and prognosis among liver transplant recipients with hepatocellular carcinoma.
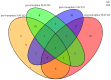
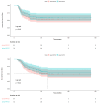
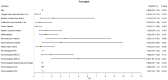
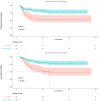
Results: A total of 268 liver transplant recipients with hepatocellular carcinoma were included. The prevalence among pre- and post-transplant metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease was 10.82% and 30.22%, while for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, it was 7.09% and 26.87%, respectively. The clinicopathological parameters were similar between the two pre-transplant groups. In contrast, the post-transplant group with metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease exhibited a higher prevalence of diabetes mellitus and a greater body mass index. However, the other parameters were similar between the two post-transplant groups (p > 0.05). Factors such as the largest tumor size > 4 cm, microvascular invasion, lack of tumor capsule, post-transplant metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease, and decreased post-transplant lymphocyte percentage were related to an increased risk of recurrence.
Conclusion: In patients undergone liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma, the diagnosis of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty disease is more strongly associated with metabolic abnormalities than the diagnosis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and is an independent predictor of hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma; liver transplantation; metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease; non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; prognosis.
Copyright © 2024 Zhu, Liu, Yang, Ren, Ye, Liu, Li, Han and He.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease on liver transplant recipients with hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma.Eur J Clin Nutr. 2024 Feb;78(2):107-113. doi: 10.1038/s41430-023-01363-y. Epub 2023 Nov 7. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2024. PMID: 37935889
-
Metabolic factors affecting hepatocellular carcinoma in steatohepatitis.Liver Int. 2019 Mar;39(3):531-539. doi: 10.1111/liv.14002. Epub 2018 Dec 2. Liver Int. 2019. PMID: 30427105 Free PMC article.
-
Liver transplantation recipients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis have lower risk hepatocellular carcinoma.Liver Transpl. 2017 Aug;23(8):1015-1022. doi: 10.1002/lt.24764. Epub 2017 Jun 26. Liver Transpl. 2017. PMID: 28340509
-
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Metabolic Syndrome after Liver Transplant.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Apr 2;17(4):490. doi: 10.3390/ijms17040490. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27049380 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Trends in hepatocellular carcinoma due to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Feb;13(2):179-187. doi: 10.1080/17474124.2019.1549989. Epub 2018 Dec 29. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 30791782 Review.
Cited by
-
Correlation between gynecomastia and endocrine regulation in patients with metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: A cross-sectional study.World J Hepatol. 2025 Jun 27;17(6):108096. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i6.108096. World J Hepatol. 2025. PMID: 40606934 Free PMC article.
-
Overweight Impacts Histological Disease Activity of De Novo Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease After Liver Transplantation.Clin Transplant. 2024 Nov;38(11):e70039. doi: 10.1111/ctr.70039. Clin Transplant. 2024. PMID: 39575514 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

