The Effects of a Healthy Lifestyle on Depressive Symptoms in Older Chinese Adults: The Mediating Role of Psychological Resilience
- PMID: 38686246
- PMCID: PMC11057559
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.57258
The Effects of a Healthy Lifestyle on Depressive Symptoms in Older Chinese Adults: The Mediating Role of Psychological Resilience
Abstract
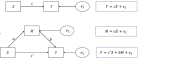
Objectives This study aimed to validate the interrelationships and potential pathways of influence between healthy lifestyles, psychological resilience, and depressive symptoms in the Chinese elderly population. Methods We utilized data from the Chinese Elderly Health Influential Factors Tracking Survey 2018 and included 9448 samples for the study after screening according to the qualifying conditions. The interrelationships among healthy lifestyles, psychological resilience and depressive symptoms were analyzed using stepwise regression, and the robustness of mediation effects was assessed using Sobel and Bootstrap test. Results Among Chinese older adults, healthy lifestyles were negatively associated with depressive symptoms (β = -0.310, 95% CI: -0.405, -0.215), positively associated with psychological resilience (β = 0.137, 95% CI:0.071, 0.023), and psychological resilience was negatively associated with depressive symptoms (β = -1.014, 95% CI: -1.037, -0.990). Conclusions Psychological resilience partially mediated the association between healthy lifestyles and depressive symptoms, with the mediating effect accounting for 44.8% of the total effect. Our study contributes to the understanding of the relationship between healthy lifestyles and depressive symptoms in the elderly population and emphasizes the important role of psychological resilience. It is recommended that the government and policymakers improve depressive symptoms among older adults through comprehensive measures such as promoting healthy lifestyles and education, providing psychological support services, and creating a favorable environment.
Keywords: depression symptoms; healthy lifestyles; mediating effect; older adults; psychological resilience.
Copyright © 2024, Duan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Similar articles
-
The mediating and moderating effect of health-promoting lifestyle on frailty and depressive symptoms for Chinese community-dwelling older adults: A cross-sectional study.J Affect Disord. 2024 Sep 15;361:91-96. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2024.06.011. Epub 2024 Jun 8. J Affect Disord. 2024. PMID: 38857627
-
The relationship between healthy lifestyles and cognitive function in Chinese older adults: the mediating effect of depressive symptoms.BMC Geriatr. 2024 Mar 28;24(1):299. doi: 10.1186/s12877-024-04922-5. BMC Geriatr. 2024. PMID: 38549104 Free PMC article.
-
The mediating and moderating effects of resilience between childhood trauma and geriatric depressive symptoms among Chinese community-dwelling older adults.Front Public Health. 2023 Apr 14;11:1137600. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1137600. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37124808 Free PMC article.
-
Chinese elderly migrants' loneliness, anxiety and depressive symptoms: The mediation effect of perceived stress and resilience.Front Public Health. 2022 Aug 25;10:998532. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.998532. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36091520 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of healthy eating index on cognitive function in older adults: chain mediation by psychological balance and depressive symptoms.BMC Geriatr. 2024 Nov 1;24(1):904. doi: 10.1186/s12877-024-05497-x. BMC Geriatr. 2024. PMID: 39487392 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Psychological Distress and Quality of Life in Patients with Colon Cancer: Predictors, Moderating Effects, and Longitudinal Impact.Healthcare (Basel). 2025 Mar 27;13(7):753. doi: 10.3390/healthcare13070753. Healthcare (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40218051 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Population ageing is a global phenomenon, which affects both Taiwan and China. Preface. Chen LK. Ageing Res Rev. 2010;9:0. - PubMed
-
- Interpretation of the Seventh National Census Bulletin (Website in Chinese) [ Jan; 2024 ];https://www.stats.gov.cn/sj/sjjd/202302/t20230202_1896484.html 2024 12:2024.
-
- Depression as a major component of public health for older adults. Chapman DP, Perry GS. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18082011/ Prev Chronic Dis. 2008;5:0. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Global prevalence of depression in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis of epidemiological surveys. Cai H, Jin Y, Liu R, et al. Asian J Psychiatr. 2023;80:103417. - PubMed
-
- A meta-analysis of the prevalence of depressive symptoms in Chinese older adults. Li D, Zhang DJ, Shao JJ, Qi XD, Tian L. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2014;58:1–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources