NIR-responsive magnesium phosphate cement loaded with simvastatin-nanoparticles with biocompatibility and osteogenesis ability
- PMID: 38686291
- PMCID: PMC11056825
- DOI: 10.1039/d4ra01079e
NIR-responsive magnesium phosphate cement loaded with simvastatin-nanoparticles with biocompatibility and osteogenesis ability
Abstract
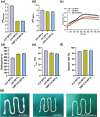
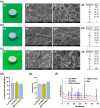
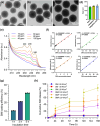
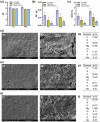
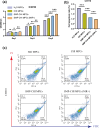
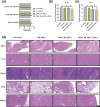
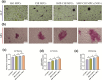
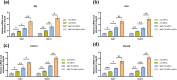
The insufficient osteogenesis of magnesium phosphate cement (MPC) limits its biomedical application. It is of great significance to develop a bioactive MPC with osteogenic performance. In this study, an injectable MPC was reinforced by the incorporation of a near infrared (NIR)-responsive nanocontainer, which was based on simvastatin (SIM)-loaded mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs) modified with a polydopamine (PDA) bilayer, named SMP. In addition, chitosan (CHI) was introduced into MPC (K-struvite) to enhance its mechanical properties and cytocompatibility. The results showed that nanocontainer-incorporated MPC possessed a prolonged setting time, almost neutral pH, excellent injectability, and enhanced compressive strength. Immersion tests indicated that SMP-CHI MPC could suppress rapid degradation. Based on its physicochemical features, the SMP-CHI MPC had good biocompatibility and osteogenesis properties, as shown via in vitro and in vivo experiments. These findings can provide a simple way to produce a multifunctional MPC with improved osteogenesis for further orthopedic applications.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
NIR-responsive injectable magnesium phosphate bone cement loaded with icariin promotes osteogenesis.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2024 Feb;150:106256. doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2023.106256. Epub 2023 Dec 2. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2024. PMID: 38048713
-
An Injectable Magnesium-Based Cement Stimulated with NIR for Drug-Controlled Release and Osteogenic Potential.Adv Healthc Mater. 2024 Jul;13(19):e2400207. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202400207. Epub 2024 Apr 2. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024. PMID: 38529833
-
Effect of ZnO-doped magnesium phosphate cements on osteogenic differentiation of mBMSCs in vitro.J Appl Biomater Funct Mater. 2022 Jan-Dec;20:22808000221136369. doi: 10.1177/22808000221136369. J Appl Biomater Funct Mater. 2022. PMID: 36416210
-
Enhancing the mechanical properties and cytocompatibility of magnesium potassium phosphate cement by incorporating oxygen-carboxymethyl chitosan.Regen Biomater. 2020 Dec 3;8(1):rbaa048. doi: 10.1093/rb/rbaa048. eCollection 2021 Feb 1. Regen Biomater. 2020. PMID: 33732494 Free PMC article.
-
Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for drug and gene delivery.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2018 Mar;8(2):165-177. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2018.01.007. Epub 2018 Feb 12. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2018. PMID: 29719777 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ginebra M. P. Canal C. Espanol M. Pastorino D. Montufar E. B. Calcium phosphate cements as drug delivery materials. Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 2012;64(12):1090–1110. - PubMed
-
- Tamimi F. Le Nihouannen D. Bassett D. C. Ibasco S. Gbureck U. Knowles J. Wright A. Flynn A. Komarova S. V. Barralet J. E. Biocompatibility of magnesium phosphate minerals and their stability under physiological conditions. Acta Biomater. 2011;7(6):2678–2685. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

