Sulfasalazine-induced drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) coinfected with COVID-19 complicated by hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: a case report
- PMID: 38686382
- PMCID: PMC11056499
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1371490
Sulfasalazine-induced drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) coinfected with COVID-19 complicated by hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: a case report
Abstract
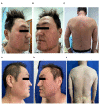
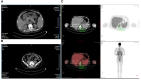
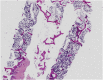
Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS) is characterized by a widespread maculopapular rash, lymphadenopathy, fever, and multisystem involvement. Conversely, hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) is an infrequent yet critical condition presenting with fever, hepatosplenomegaly, cytopenias, coagulation abnormalities, and elevated inflammatory markers. The overlapping clinical and laboratory features between DRESS and HLH poses a significant diagnostic challenge. Secondary HLH (sHLH) typically occurs in adults triggered by viral infections, malignancies, rheumatologic diseases, or immune deficiencies. Recently, COVID-19 has also been identified as one of the triggers for sHLH. Herein, we present a case of Sulfasalazine-induced DRESS coinfected with COVID-19 that subsequently progressed into HLH. Our patient exhibited common hepatorenal and splenic involvement along with rare cholecystitis and appendicitis. However, a significant improvement was observed upon the addition of etoposide and azathioprine. We hypothesize that excessive activation of the immune system and cytokine storm due to DRESS combined with COVID-19 infection led to more extensive systemic damage resulting in HLH development. This highlights the potential for severe consequences when DRESS coincides with HLH during a COVID-19 infection.
Keywords: CMV; COVID-19; drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms; ebv; hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis.
Copyright © 2024 Li, li, Dai, Zeng and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

