[Automatic detection method of intracranial aneurysms on maximum intensity projection images based on SE-CaraNet]
- PMID: 38686402
- PMCID: PMC11058495
- DOI: 10.7507/1001-5515.202301008
[Automatic detection method of intracranial aneurysms on maximum intensity projection images based on SE-CaraNet]
Abstract
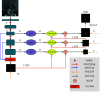
Conventional maximum intensity projection (MIP) images tend to ignore some morphological features in the detection of intracranial aneurysms, resulting in missed detection and misdetection. To solve this problem, a new method for intracranial aneurysm detection based on omni-directional MIP image is proposed in this paper. Firstly, the three-dimensional magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) images were projected with the maximum density in all directions to obtain the MIP images. Then, the region of intracranial aneurysm was prepositioned by matching filter. Finally, the Squeeze and Excitation (SE) module was used to improve the CaraNet model. Excitation and the improved model were used to detect the predetermined location in the omni-directional MIP image to determine whether there was intracranial aneurysm. In this paper, 245 cases of images were collected to test the proposed method. The results showed that the accuracy and specificity of the proposed method could reach 93.75% and 93.86%, respectively, significantly improved the detection performance of intracranial aneurysms in MIP images.
传统的单一方位最大密度投影(MIP)图像在检测颅内动脉瘤时容易忽略部分形态特征,造成漏检和误检。针对该问题,本文提出一种新的基于全方位MIP图像的颅内动脉瘤检测方法。首先,对三维磁共振血管造影(MRA)图像进行全方位最大密度投影,获得MIP图像;然后,利用匹配滤波对颅内动脉瘤区域进行预定位;最后,使用Squeeze and Excitation(SE)模块对CaraNet模型进行了改进,并用改进后的模型对全方位MIP图像中的预定位区域进行检测,确定是否患有颅内动脉瘤。本文收集了245例图像对所提方法进行了测试实验。实验结果表明本文所提方法的精确率和特异性分别可以达到93.75%和93.86%,显著提高了对MIP图像中颅内动脉瘤的检测性能。.
Keywords: CaraNet; Intracranial aneurysm detection; Maximum intensity projection; Squeeze-and-Excitation module.
Conflict of interest statement
利益冲突声明:本文全体作者均声明不存在利益冲突。
Figures








References
-
- Alwalid O, Long X, Xie M, et al Artificial intelligence applications in intracranial aneurysm: Achievements, challenges and opportunities. Acad Radiol. 2022;29(Suppl 3):S201–S214. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
