A multi-species, multi-pathogen avian viral disease outbreak event: Investigating potential for virus transmission at the wild bird - poultry interface
- PMID: 38686548
- PMCID: PMC11168234
- DOI: 10.1080/22221751.2024.2348521
A multi-species, multi-pathogen avian viral disease outbreak event: Investigating potential for virus transmission at the wild bird - poultry interface
Abstract
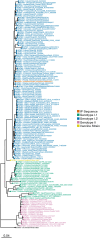
A free-range organic broiler (Gallus gallus domesticus) premises in Staffordshire was infected by high pathogenicity avian influenza virus (HPAIV) H5N8 during the 2020-2021 epizootic in the United Kingdom (UK). Following initial confirmation of the infection in poultry, multiple wild bird species were seen scavenging on chicken carcasses. Detected dead wild birds were subsequently demonstrated to have been infected and succumbed to HPAIV H5N8. Initially, scavenging species, magpie (Pica pica) and raven (Corvus corax) were found dead on the premises but over the following days, buzzards (Buteo buteo) were also found dead within the local area with positive detection of HPAIV in submitted carcasses. The subacute nature of microscopic lesions within a buzzard was consistent with the timeframe of infection. Finally, a considerable number of free-living pheasants (Phasianus colchicus) were also found dead in the surrounding area, with carcasses having higher viral antigen loads compared to infected chickens. Limited virus dissemination was observed in the carcasses of the magpie, raven, and buzzard. Further, an avirulent avian paramyxovirus type 1 (APMV-1) was detected within poultry samples as well as in the viscera of a magpie infected with HPAIV. Immunohistochemistry did not reveal colocalization of avian paramyxovirus antigens with lesions, supporting an avirulent APMV-1 infection. Overall, this case highlights scenarios in which bi-directional transmission of avian viral diseases between commercial and wild bird species may occur. It also underlines the importance of bio separation and reduced access when infection pressure from HPAIV is high.
Keywords: High pathogenicity avian influenza virus (HPAIV); H5N8; clade 2.3.4.4b; multi-species; avian paramyxovirus type 1.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures




Similar articles
-
Pathobiology of Clade 2.3.4.4 H5Nx High-Pathogenicity Avian Influenza Virus Infections in Minor Gallinaceous Poultry Supports Early Backyard Flock Introductions in the Western United States in 2014-2015.J Virol. 2017 Oct 13;91(21):e00960-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00960-17. Print 2017 Nov 1. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28794040 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic relationship between poultry and wild bird viruses during the highly pathogenic avian influenza H5N6 epidemic in the Netherlands, 2017-2018.Transbound Emerg Dis. 2019 May;66(3):1370-1378. doi: 10.1111/tbed.13169. Epub 2019 Apr 5. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2019. PMID: 30874364 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenicity of H5N8 highly pathogenic avian influenza viruses isolated from a wild bird fecal specimen and a chicken in Japan in 2014.Microbiol Immunol. 2016 Apr;60(4):243-52. doi: 10.1111/1348-0421.12369. Microbiol Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26916882
-
The genetics of highly pathogenic avian influenza viruses of subtype H5 in Germany, 2006-2020.Transbound Emerg Dis. 2021 May;68(3):1136-1150. doi: 10.1111/tbed.13843. Epub 2020 Sep 29. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2021. PMID: 32964686 Review.
-
Review of the Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza in Argentina in 2023: Chronicle of Its Emergence and Control in Poultry.Pathogens. 2024 Sep 19;13(9):810. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13090810. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 39339001 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Cyclic Peptide Based on Pheasant Cathelicidin Inhibits Influenza A H1N1 Virus Infection.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Jun 28;13(7):606. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13070606. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39061288 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic Assays for Avian Influenza Virus Surveillance and Monitoring in Poultry.Viruses. 2025 Feb 6;17(2):228. doi: 10.3390/v17020228. Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40006983 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Detection of a Novel Gull-like Clade of Newcastle Disease Virus and H3N8 Avian Influenza Virus in the Arctic Region of Russia (Taimyr Peninsula).Viruses. 2025 Jul 7;17(7):955. doi: 10.3390/v17070955. Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40733572 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Defra . High pathogenicity avian influenza H5N8 and H5N1 outbreaks in Great Britain, United Kingdom, November 2020 to April 2021. 2021. Available from: https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploa....
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
