Fangchinoline inhibits growth and biofilm of Candida albicans by inducing ROS overproduction
- PMID: 38686557
- PMCID: PMC11058694
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.18354
Fangchinoline inhibits growth and biofilm of Candida albicans by inducing ROS overproduction
Abstract
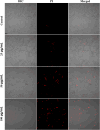
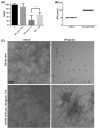
Infections caused by Candida species, especially Candida albicans, threaten the public health and create economic burden. Shortage of antifungals and emergence of drug resistance call for new antifungal therapies while natural products were attractive sources for developing new drugs. In our study, fangchinoline, a bis-benzylisoquinoline alkaloid from Chinese herb Stephania tetrandra S. Moore, exerted antifungal effects on planktonic growth of several Candida species including C. albicans, with MIC no more than 50 μg/mL. In addition, results from microscopic, MTT and XTT reduction assays showed that fangchinoline had inhibitory activities against the multiple virulence factors of C. albicans, such as adhesion, hyphal growth and biofilm formation. Furthermore, this compound could also suppress the metabolic activity of preformed C. albicans biofilms. PI staining, followed by confocal laser scanning microscope (CLSM) analysis showed that fangchinoline can elevate permeability of cell membrane. DCFH-DA staining suggested its anti-Candida mechanism also involved overproduction of intracellular ROS, which was further confirmed by N-acetyl-cysteine rescue tests. Moreover, fangchinoline showed synergy with three antifungal drugs (amphotericin B, fluconazole and caspofungin), further indicating its potential use in treating C. albicans infections. Therefore, these results indicated that fangchinoline could be a potential candidate for developing anti-Candida therapies.
Keywords: Candida albicans; ROS; antifungal; biofilm; fangchinoline; virulence factor.
© 2024 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

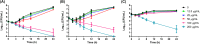




Similar articles
-
Inhibitory effects and mode of antifungal action of isobavachalcone on Candida albicans growth and virulence factors.Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Oct;179:117352. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.117352. Epub 2024 Aug 28. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 39208670
-
Antifungal effects of Metformin against Candida albicans by autophagy regulation.J Microbiol. 2025 Apr;63(4):e2411008. doi: 10.71150/jm.2411008. Epub 2025 Apr 29. J Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40313147
-
Inhibitory Effect of Sophorolipid on Candida albicans Biofilm Formation and Hyphal Growth.Sci Rep. 2016 Mar 31;6:23575. doi: 10.1038/srep23575. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27030404 Free PMC article.
-
Dracorhodin perchlorate inhibits biofilm formation and virulence factors of Candida albicans.J Mycol Med. 2018 Mar;28(1):36-44. doi: 10.1016/j.mycmed.2017.12.011. Epub 2018 Feb 22. J Mycol Med. 2018. PMID: 29477784
-
Thymus vulgaris essential oil and thymol inhibit biofilms and interact synergistically with antifungal drugs against drug resistant strains of Candida albicans and Candida tropicalis.J Mycol Med. 2020 Apr;30(1):100911. doi: 10.1016/j.mycmed.2019.100911. Epub 2019 Nov 7. J Mycol Med. 2020. PMID: 32008964
Cited by
-
Effect of the Sho1 gene on the pathogenicity of Candida albicans and immune function in vivo.Heliyon. 2024 Sep 25;10(19):e38219. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38219. eCollection 2024 Oct 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39397919 Free PMC article.
-
Chitosan nanoparticles encapsulating farnesol show potent antifungal activity against Candida albicans biofilms.Braz J Microbiol. 2025 Jun;56(2):905-912. doi: 10.1007/s42770-025-01624-x. Epub 2025 Feb 12. Braz J Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39937379
-
Pinosylvin and Sanguinarine Combination to Enhance Antifungal Activity against Candida albicans.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025 May 15;35:e2412055. doi: 10.4014/jmb.2412.12055. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40374536 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

