Tocilizumab demonstrates superiority in decreasing C-reactive protein levels in hospitalized COVID-19 patients, compared to standard care treatment alone
- PMID: 38687065
- PMCID: PMC11237561
- DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.02498-23
Tocilizumab demonstrates superiority in decreasing C-reactive protein levels in hospitalized COVID-19 patients, compared to standard care treatment alone
Abstract
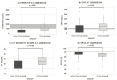
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 has caused a global pandemic, leading to health, economic, and political crisis. The virus triggers the activation of inflammatory reactants including interleukin-6 (IL-6), ferritin, and C-reactive protein (CRP), causing multiorgan damage, particularly affecting the lungs. Tocilizumab, an IL-6 receptor blocker, has the potential to diminish the progression of the disease and reduce organ damage and long-term complications. The aim of this observational retrospective cohort study was to evaluate the efficacy of tocilizumab in decreasing CRP levels in hospitalized coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients compared to standard care without the drug. The study included 141 patients during their Hospital Stay (HS), with 100 in the Tocilizumab group and 41 in the non-Tocilizumab group. Clinical information was collected from the electronic clinical record, analyzed using statistical software, and homogenized the CRP levels from the severe group to the levels of the less complicated group at 48 h of hospitalization. The results showed a statistically significant greater decrease in CRP levels in the Tocilizumab group at 48 h after the use of the treatment, with no differences in mortality or length of stay between the groups. In conclusion, tocilizumab accelerates the diminishing of CRP levels compared to standard treatment alone, and its use may have potential benefits in the management of severe COVID-19 patients when used alongside with follow-up quantification of CRP levels reduction.IMPORTANCESevere acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 has caused a global pandemic, leading to health, economic, and political crises. International guidelines for managing coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) give recommendations according to the severity of the disease and the level of oxygen therapy needed. Tocilizumab is an option for the therapeutic management of hospitalized patients with any level of oxygen therapy; IL-6 serum level is the parameter for the follow-up on the efficacy, but it is not available at many hospitals. In this study, we demonstrate that C-reactive protein determination can predict the response to tocilizumab in severe COVID-19, the target patients for treatment with this drug. The use of this affordable and extensively available biomarker supports clinical decisions for the early escalation of the therapy and for the rational use of this drug on those prone to improve with the use of it.
Keywords: C reactive protein; COVID-19; interleukin 6; tocilizumab.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Trajectories and predictive significance of inflammatory parameters for clinical outcome in COVID-19 patients treated with tocilizumab.Infection. 2025 Feb;53(1):339-348. doi: 10.1007/s15010-024-02375-x. Epub 2024 Aug 29. Infection. 2025. PMID: 39210228 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Tocilizumab vs Standard Care on Clinical Worsening in Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Randomized Clinical Trial.JAMA Intern Med. 2021 Jan 1;181(1):24-31. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.6615. JAMA Intern Med. 2021. PMID: 33080005 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of tocilizumab on mortality in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a multicentre cohort study.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2021 Feb;27(2):238-243. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2020.09.021. Epub 2020 Sep 23. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2021. PMID: 32979572 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical outcomes in COVID-19 patients treated with tocilizumab: An individual patient data systematic review.J Med Virol. 2020 Nov;92(11):2516-2522. doi: 10.1002/jmv.26038. Epub 2020 Jun 9. J Med Virol. 2020. PMID: 32436994 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of tocilizumab in COVID-19 patients: a living systematic review and meta-analysis, first update.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2021 Aug;27(8):1076-1082. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2021.04.019. Epub 2021 Apr 27. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2021. PMID: 33915284 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Serial biomarker measurements may be helpful to predict the successful application of high flow nasal cannula in COVID-19 pneumonia patients.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 4;15(1):756. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-85210-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39755869 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the efficacy of different doses of tocilizumab in treating critically ill COVID-19 patients: a single-center retrospective cohort study.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jul 24;16:1571372. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1571372. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40777985 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Organización Mundial de la Salud . 2021. Manejo clínico de la COVID-19. Available from: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/340629/WHO-2019-nCoV- c...
-
- COVID-19 Map. Johns Hopkins coronavirus resource center. Citado el 13 de febrero de 2023. Available from: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html
-
- Canovi S, Besutti G, Bonelli E, Iotti V, Ottone M, Albertazzi L, Zerbini A, Pattacini P, Giorgi Rossi P, Colla R, Fasano T, Reggio Emilia COVID-19 Working Group . 2021. The association between clinical laboratory data and chest CT findings explains disease severity in a large Italian cohort of COVID-19 patients. BMC Infect Dis 21:157. doi: 10.1186/s12879-021-05855-9 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Angus DC, Berry S, Lewis RJ, Al-Beidh F, Arabi Y, van Bentum-Puijk W, Bhimani Z, Bonten M, Broglio K, Brunkhorst F, et al. 2020. The REMAP-CAP (randomized embedded multifactorial adaptive platform for community-acquired pneumonia) study. Rationale and design. Ann Am Thorac Soc 17:879–891. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.202003-192SD - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

