Endovascular Thrombectomy for Large Ischemic Strokes with ASPECTS 0-2: a Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
- PMID: 38687364
- PMCID: PMC11339095
- DOI: 10.1007/s00062-024-01414-2
Endovascular Thrombectomy for Large Ischemic Strokes with ASPECTS 0-2: a Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
Purpose: Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) demonstrated a treatment effect of endovascular thrombectomy in acute ischemic stroke with large infarct, commonly defined as an Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score (ASPECTS) of 3-5. However, data on endovascular thrombectomy in patients with very low ASPECTS of 0-2 remain scarce.
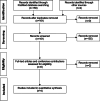
Methods: We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of RCTs comparing endovascular thrombectomy versus medical treatment alone in acute ischemic anterior circulation stroke with very large infarct, defined as ASPECTS of 0-2. The primary outcome was the shift toward better functional outcomes on the 90-day modified Rankin Scale (mRS). Random effects meta-analysis was performed using the generic inverse variance method.
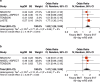
Results: Literature research identified four RCTs which evaluated the treatment effect of endovascular thrombectomy for large infarcts and provided a subgroup analysis of the mRS shift in patients with ASPECTS of 0-2. The pooled analysis showed a significant shift toward better 90-day mRS scores in favor of endovascular thrombectomy (pooled odds ratio, 1.62, 95% confidence interval, 1.29-2.04, P < 0.001).
Conclusion: This meta-analysis suggests a treatment effect of endovascular thrombectomy in specific patients with very low ASPECTS of 0-2, challenging the use of ASPECTS for treatment selection in acute ischemic stroke due to large vessel occlusion. An individual patient meta-analysis of RCTs would strengthen evidence in the treatment of patients with ASPECTS of 0-2.
Keywords: Cerebral infarction; Infarction; Ischemic stroke; Stroke; Thrombectomy.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
L. Winkelmeier, C. Heitkamp, G. Schön declare that they have no competing interests. M. Maros, F. Flottmann: Personal fees from Eppdata. G. Thomalla: Personal fees from Acandis, Alexion, Amarin, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb/Pfizer, Daiichi Sankyo, Portola, and Stryker. J. Fiehler: Personal fees from Acandis, Cerenovus, Medtronic, MicroVention, Medtronic, Penumbra, Phenox, Stryker, Tonbride, and Roche; stocks or stock options from Tegus Medical, Eppdata, and Vastrax. U. Hanning: Personal fees from Eppdata and Stryker.
Figures
References
-
- Bendszus M, Fiehler J, Subtil F, Bonekamp S, Aamodt AH, Fuentes B, Gizewski ER, Hill MD, Krajina A, Pierot L, et al. Endovascular thrombectomy for acute ischaemic stroke with established large infarct: multicentre, open-label, randomised trial. Lancet. 2023; 10.1016/S0140-6736(23)02032-9. 10.1016/S0140-6736(23)02032-9 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jovin T, Costalat V, Lapergue B, Labreuche J, Arquizan C, LASTE-Investigators. IN EXTREMIS LASTE: evaluation of mechanical thrombectomy in large stroke (ASPECTS 0–5) with T or M1 occlusion 〈 7 hours LSW [conference presentation. SVIN Anual Meeting. 2023.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

