YBX1 as a prognostic biomarker and potential therapeutic target in hepatocellular carcinoma: A comprehensive investigation through bioinformatics analysis and in vitro study
- PMID: 38688048
- PMCID: PMC11070759
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tranon.2024.101965
YBX1 as a prognostic biomarker and potential therapeutic target in hepatocellular carcinoma: A comprehensive investigation through bioinformatics analysis and in vitro study
Abstract
Backgrounds: Y-box binding protein 1 (YBX1) is a DNA/RNA binding protein known to contribute to the progression of various malignancies, however, a comprehensive pan-cancer analysis to investigate YBX1 across a broad spectrum of cancer types has not yet been conducted.
Methods: We utilized the TIMER database for a comprehensive pan-cancer analysis and assessed YBX-1 expression via the TCGA and GEO databases. The relationship between YBX-1 expression and tumor-infiltrating cells was examined using TIMER and the R programming language. To evaluate the prognostic value of YBX1, we performed Kaplan-Meier plots and Cox regression analyses. Through LinkedOmics, we identified genes significantly correlated with YBX-1. The WEB-based Gene SeT AnaLysis Toolkit was used for KEGG pathway enrichment analysis. Additionally, using shRNA-mediated knockdown, we explored the potential role of YBX1 in tumor cell biology.
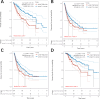
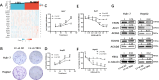
Results: Our study identifies pronounced overexpression of YBX-1 across multiple cancer types, correlating with adverse outcomes, notably in liver hepatocellular carcinoma (LIHC). A distinct association between elevated YBX-1 expression and heightened immune cell infiltration suggests YBX-1's potential role in reshaping the tumor microenvironment. Intriguingly, our KEGG pathway analysis indicated a tight nexus between YBX-1 expression and lipid metabolism. Moreover, the suppression of YBX-1 via shRNA revealed diminished cellular proliferation and marked reductions in crucial molecules steering the fatty acid synthesis pathway, implicating YBX-1's potential regulatory role in lipid metabolism within LIHC.
Conclusions: YBX-1 serves as a favorable prognostic indicator in various cancers, particularly in liver hepatocellular carcinoma. Targeting YBX1 in HCC offers potential therapeutic strategies. This work paves the way for fresh insights into targeted therapeutic approaches for cancers, especially benefiting liver hepatocellular carcinoma patients.
Keywords: Fatty acid metabolism; Liver hepatocellular carcinoma; Pan cancer; YBX1.
Copyright © 2024. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Sung H., Ferlay J., Siegel R.L., Laversanne M., Soerjomataram I., Jemal A., Bray F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021;71(3):209–249. - PubMed
-
- Bedard P.L., Hyman D.M., Davids M.S., Siu L.L. Small molecules, big impact: 20 years of targeted therapy in oncology. Lancet. 2020;395(10229):1078–1088. - PubMed
-
- Ramalingam S.S., Vansteenkiste J., Planchard D., Cho B.C., Gray J.E., Ohe Y., Zhou C., Reungwetwattana T., Cheng Y., Chewaskulyong B., et al. Overall survival with osimertinib in untreated, EGFR-mutated advanced NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020;382(1):41–50. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

