High Intraepithelial Mast Cell Density in Warthin's Tumor
- PMID: 38688595
- PMCID: PMC11059896
- DOI: 10.21873/invivo.13544
High Intraepithelial Mast Cell Density in Warthin's Tumor
Abstract
Background/aim: Warthin's tumor, the second most frequent neoplasia of the parotid gland, is characterized by a proliferation of both epithelial and lymphoid components. In addition to epithelial and lymphoid cells, various other cell types are implicated to varying degrees in the immune response. Notably, mast cells have long been recognized as a consistent cell population within this tumor. Despite the historical acknowledgment of mast cell presence, their true distribution and significance within Warthin's tumor remain unclear. In this study, we aimed to elucidate the distribution and significance of mast cells in Warthin's tumor.
Materials and methods: Histochemical and immunohistochemical methods were employed for the evaluation of mast cells within tumor specimens.
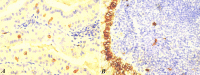
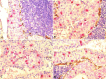
Results: Our study revealed a notable concentration of mast cells in the epithelial component of Warthin's tumor. Microscopic examination showed predominant lymphoid and epithelial elements with occasional cystic formations. Immunohistochemical analysis identified mast cells in both components, emphasizing their role in the tumor microenvironment. Double immunostaining (mast cell tryptase and CD34) revealed no significant correlation between mast cells and blood vessels. Intraepithelial mast cells (IEMCs) had a significantly higher density in the epithelial component, suggesting a potential association with the tumor's benign nature. The relationship between IEMCs and epithelial cells, especially in the presence of cystic structures, offers valuable insights into the unique features of Warthin's tumor.
Conclusion: Our study contributes to the understanding of mast cells in Warthin's tumor, highlighting a substantial concentration within the epithelial component. This knowledge may pave the way for further investigations into the roles of mast cells in the pathogenesis and treatment of Warthin's tumor.
Keywords: Warthin tumor; immunohistochemistry; mast cell; tryptase.
Copyright © 2024, International Institute of Anticancer Research (Dr. George J. Delinasios), All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors declare no conflicts of interest in relation to this study.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Warthin's tumor of parotid gland on Tc-99m pertechnetate scintigraphy with lemon juice stimulation: Tc-99m uptake, size, and pathologic correlation.Eur Radiol. 2001;11(12):2472-8. doi: 10.1007/s003300100839. Epub 2001 Mar 17. Eur Radiol. 2001. PMID: 11734943
-
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma arising in Warthin's tumor of the parotid gland.Pathol Int. 2002 Oct;52(10):653-6. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1827.2002.01408.x. Pathol Int. 2002. PMID: 12445138
-
Association of mast cells with Warthin's tumor in fine needle aspirates of the salivary gland.Acta Cytol. 1999 Nov-Dec;43(6):1052-8. doi: 10.1159/000331353. Acta Cytol. 1999. PMID: 10578978
-
Pathogenesis of Warthin's tumors.Interv Med Appl Sci. 2016 Jun 1;8(2):41-48. doi: 10.1556/1646.8.2016.2.2. Interv Med Appl Sci. 2016. PMID: 28386459 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Warthin's tumor-associated neoplasms: report of two cases and review of the literature.Ear Nose Throat J. 1993 Apr;72(4):264-9, 272-3. Ear Nose Throat J. 1993. PMID: 8486105 Review.
References
-
- Goldblum JR, Lamps LW, Myers J. Elsevier. 2017. Head and Neck Pathology. In: Rosai and Ackerman’s surgical pathology, 11th Edition. , -884, 2017. pp. pp. 883–884.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
