Ghrelin Induces the Production of Hypothalamic NPY Through the AMPK-mTOR Pathway to Alleviate Cancer-induced Bone Pain
- PMID: 38688635
- PMCID: PMC11059913
- DOI: 10.21873/invivo.13548
Ghrelin Induces the Production of Hypothalamic NPY Through the AMPK-mTOR Pathway to Alleviate Cancer-induced Bone Pain
Abstract
Background/aim: Cancer-induced bone pain (CIBP) is one of the most common symptoms of bone metastasis of tumor cells. The hypothalamus may play a pivotal role in the regulation of CIBP. However, little is known about the exact mechanisms.
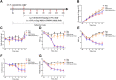
Materials and methods: First, we established a CIBP model to explore the relationship among hypothalamic ghrelin, NPY and CIBP. Then, we exogenously administered NPY and NPY receptor antagonists to investigate whether hypothalamic NPY exerted an antinociceptive effect through binding to NPY receptors. Finally, we exogenously administered ghrelin to investigate whether ghrelin alleviated CIBP by inducing the production of hypothalamic NPY through the AMPK-mTOR pathway. Body weight, food intake and behavioral indicators of CIBP were measured every 3 days. Hypothalamic ghrelin, NPY and the AMPK-mTOR pathway were also measured.
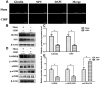
Results: The expression of hypothalamic ghrelin and NPY was simultaneously decreased in cancer-bearing rats, which was accompanied by CIBP. Intracerebroventricular (i.c.v.) administration of NPY significantly alleviated CIBP in the short term. The antinociceptive effect of NPY was reversed with the i.c.v. administration of the Y1R and Y2R antagonists. The administration of ghrelin activated the AMPK-mTOR pathway and induced hypothalamic NPY production to alleviate CIBP. This effect of ghrelin on NPY and antinociception was reversed with the administration of a GHS-R1α antagonist.
Conclusion: Ghrelin could induce the production of hypothalamic NPY through the AMPK-mTOR pathway to alleviate CIBP, which can provide a novel therapeutic mechanism for CIBP.
Keywords: AMPK-mTOR pathway; Cancer-induced bone pain; Ghrelin; NPY; SHZ-88.
Copyright © 2024, International Institute of Anticancer Research (Dr. George J. Delinasios), All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors report no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Octanoic acid-rich diet alleviates breast cancer-induced bone pain via the acyl-ghrelin/NPY pathway.Korean J Pain. 2025 Apr 1;38(2):138-151. doi: 10.3344/kjp.24388. Epub 2025 Mar 20. Korean J Pain. 2025. PMID: 40108771 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) signaling pathway in the orexigenic effects of endogenous ghrelin.Regul Pept. 2012 Jan 10;173(1-3):27-35. doi: 10.1016/j.regpep.2011.09.001. Epub 2011 Oct 1. Regul Pept. 2012. PMID: 21963822
-
Hypothalamic AMPK-induced autophagy increases food intake by regulating NPY and POMC expression.Autophagy. 2016 Nov;12(11):2009-2025. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2016.1215382. Epub 2016 Aug 17. Autophagy. 2016. PMID: 27533078 Free PMC article.
-
Central mechanisms involved in the orexigenic actions of ghrelin.Peptides. 2011 Nov;32(11):2248-55. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2011.05.014. Epub 2011 May 17. Peptides. 2011. PMID: 21619904 Review.
-
Hypothalamic mTOR: the rookie energy sensor.Curr Mol Med. 2014 Jan;14(1):3-21. doi: 10.2174/1566524013666131118103706. Curr Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 24236459 Review.
Cited by
-
Neuropeptide Y and Pain: Insights from Brain Research.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2024 Nov 2;7(12):3718-3728. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.4c00333. eCollection 2024 Dec 13. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2024. PMID: 39698268 Review.
-
Octanoic acid-rich diet alleviates breast cancer-induced bone pain via the acyl-ghrelin/NPY pathway.Korean J Pain. 2025 Apr 1;38(2):138-151. doi: 10.3344/kjp.24388. Epub 2025 Mar 20. Korean J Pain. 2025. PMID: 40108771 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
