Genome-wide analysis in over 1 million individuals of European ancestry yields improved polygenic risk scores for blood pressure traits
- PMID: 38689001
- PMCID: PMC11096100
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-024-01714-w
Genome-wide analysis in over 1 million individuals of European ancestry yields improved polygenic risk scores for blood pressure traits
Abstract
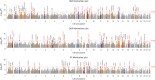
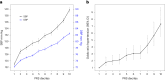
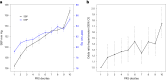
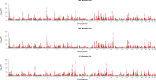
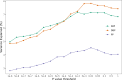
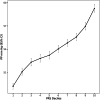
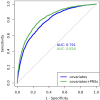
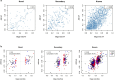
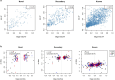
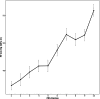
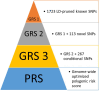
Hypertension affects more than one billion people worldwide. Here we identify 113 novel loci, reporting a total of 2,103 independent genetic signals (P < 5 × 10-8) from the largest single-stage blood pressure (BP) genome-wide association study to date (n = 1,028,980 European individuals). These associations explain more than 60% of single nucleotide polymorphism-based BP heritability. Comparing top versus bottom deciles of polygenic risk scores (PRSs) reveals clinically meaningful differences in BP (16.9 mmHg systolic BP, 95% CI, 15.5-18.2 mmHg, P = 2.22 × 10-126) and more than a sevenfold higher odds of hypertension risk (odds ratio, 7.33; 95% CI, 5.54-9.70; P = 4.13 × 10-44) in an independent dataset. Adding PRS into hypertension-prediction models increased the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) from 0.791 (95% CI, 0.781-0.801) to 0.826 (95% CI, 0.817-0.836, ∆AUROC, 0.035, P = 1.98 × 10-34). We compare the 2,103 loci results in non-European ancestries and show significant PRS associations in a large African-American sample. Secondary analyses implicate 500 genes previously unreported for BP. Our study highlights the role of increasingly large genomic studies for precision health research.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The participation of M.A.N. in this project was part of a competitive contract awarded to Data Tecnica International by the National Institutes of Health to support open science research. He also currently serves on the scientific advisory board for Clover Therapeutics and is an advisor to Neuron23 as a data science fellow. B.M.P. serves on the steering committee of the Yale Open Data Access Project funded by Johnson & Johnson. P.V. received an unrestricted grant from GlaxoSmithKline to build the CoLaus study (2003). V.S. has received honoraria for consulting from Novo Nordisk and Sanofi and has ongoing research collaboration with Bayer (all unrelated to this project). R.L. is a part-time consultant of Metabolon. M.J.C. is Chief Scientist for Genomics England, a UK Government company. M. Traylor and J.M.M.H. are employees and stockholders of Novo Nordisk. C.J.O. is currently employed by Novartis Institutes for Biomedical Research (unrelated to this project) and remains credentialed as a ‘without compensation’ researcher with the Veterans Administration. T.S. is co-founder of Zoe Ltd. A.S.B. reports institutional grants from AstraZeneca, Bayer, Biogen, BioMarin, Bioverativ, Novartis, Regeneron and Sanofi. J.N.D. reports grants, personal fees and non-financial support from Merck Sharp & Dohme (MSD), grants, personal fees and non-financial support from Novartis, grants from Pfizer and grants from AstraZeneca outside the submitted work. J.N.D. sits on the International Cardiovascular and Metabolic Advisory Board for Novartis (since 2010); the Steering Committee of UK Biobank (since 2011); the MRC International Advisory Group (ING) member, London (since 2013); the MRC High Throughput Science Omics Panel Member, London (since 2013); the Scientific Advisory Committee for Sanofi (since 2013); the International Cardiovascular and Metabolism Research and Development Portfolio Committee for Novartis; and the AstraZeneca Genomics Advisory Board (2018). E.E was co-founder and has received consultation fees from Open DNA (unrelated to this project). The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- GBD 2017 Causes of Death Collaborators. Global, regional, and national age-sex-specific mortality for 282 causes of death in 195 countries and territories, 1980–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392:1736–1788. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32203-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- GBD 2017 Risk Factor Collaborators. Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 84 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392:1923–1994. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32225-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed

