Oncogenic Kras induces spatiotemporally specific tissue deformation through converting pulsatile into sustained ERK activation
- PMID: 38689013
- PMCID: PMC11519783
- DOI: 10.1038/s41556-024-01413-y
Oncogenic Kras induces spatiotemporally specific tissue deformation through converting pulsatile into sustained ERK activation
Abstract
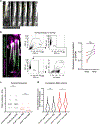
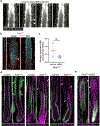
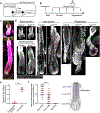
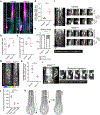
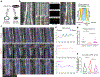
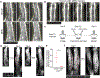
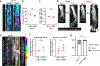
Tissue regeneration and maintenance rely on coordinated stem cell behaviours. This orchestration can be impaired by oncogenic mutations leading to cancer. However, it is largely unclear how oncogenes perturb stem cells' orchestration to disrupt tissue. Here we used intravital imaging to investigate the mechanisms by which oncogenic Kras mutation causes tissue disruption in the hair follicle. Through longitudinally tracking hair follicles in live mice, we found that KrasG12D, a mutation that can lead to squamous cell carcinoma, induces epithelial tissue deformation in a spatiotemporally specific manner, linked with abnormal cell division and migration. Using a reporter mouse capture real-time ERK signal dynamics at the single-cell level, we discovered that KrasG12D, but not a closely related mutation HrasG12V, converts ERK signal in stem cells from pulsatile to sustained. Finally, we demonstrated that interrupting sustained ERK signal reverts KrasG12D-induced tissue deformation through modulating specific features of cell migration and division.
© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing financial or non-financial interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA279546/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DP1 AG066590/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR072668/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R35GM133499/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- R01AR067755/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (NIAMS)
- UL1 TR001863/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA279546/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- DP1AG066590/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute on Aging (U.S. National Institute on Aging)
- R35 GM133499/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR063663/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR067755/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01AR063663/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (NIAMS)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

