Neoadjuvant nivolumab with or without relatlimab in resectable non-small-cell lung cancer: a randomized phase 2 trial
- PMID: 38689060
- PMCID: PMC11186754
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-024-02965-0
Neoadjuvant nivolumab with or without relatlimab in resectable non-small-cell lung cancer: a randomized phase 2 trial
Abstract
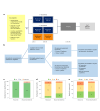
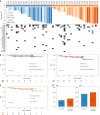
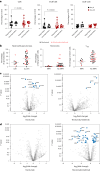
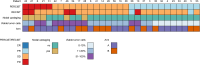
Antibodies targeting the immune checkpoint molecules PD-1, PD-L1 and CTLA-4, administered alone or in combination with chemotherapy, are the standard of care in most patients with metastatic non-small-cell lung cancers. When given before curative surgery, tumor responses and improved event-free survival are achieved. New antibody combinations may be more efficacious and tolerable. In an ongoing, open-label phase 2 study, 60 biomarker-unselected, treatment-naive patients with resectable non-small-cell lung cancer were randomized to receive two preoperative doses of nivolumab (anti-PD-1) with or without relatlimab (anti-LAG-3) antibody therapy. The primary study endpoint was the feasibility of surgery within 43 days, which was met by all patients. Curative resection was achieved in 95% of patients. Secondary endpoints included pathological and radiographic response rates, pathologically complete resection rates, disease-free and overall survival rates, and safety. Major pathological (≤10% viable tumor cells) and objective radiographic responses were achieved in 27% and 10% (nivolumab) and in 30% and 27% (nivolumab and relatlimab) of patients, respectively. In 100% (nivolumab) and 90% (nivolumab and relatlimab) of patients, tumors and lymph nodes were pathologically completely resected. With 12 months median duration of follow-up, disease-free survival and overall survival rates at 12 months were 89% and 93% (nivolumab), and 93% and 100% (nivolumab and relatlimab). Both treatments were safe with grade ≥3 treatment-emergent adverse events reported in 10% and 13% of patients per study arm. Exploratory analyses provided insights into biological processes triggered by preoperative immunotherapy. This study establishes the feasibility and safety of dual targeting of PD-1 and LAG-3 before lung cancer surgery.ClinicalTrials.gov Indentifier: NCT04205552 .
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
M.S., K.C., B.H., J.K., F.M., A.P., B.M., H.R., P.B., A.S. and C.A. received institutional funding, paid to the University Hospital Essen, from Bristol Myers Squibb to support the study NEOpredict-Lung. The following authors declare potential conflicts of interest: M.S. (Fees for consulting from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Blueprint Medicines, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, GSK, Janssen, MSD, Novartis, Roche, Sanofi and Tacalyx; honoraria for CME presentations from Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, GSK, Janssen, MSD, Roche and Sanofi; institutional research funding to University Hospital Essen from AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb and Janssen); K.C. (Fees for consulting from AstraZeneca/Medimmune, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, MSD; institutional research funding from Bristol Myers Squibb; travel support from MSD; other relationship to Bristol Myers Squibb); M.W. (Fees for consulting from Daiichi Sankyo, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer and Roche; honoraria for CME presentations from Amgen, AstraZeneca, GSK, Janssen, Novartis, Roche and Takeda; institutional research funding to University Hospital Essen from Bristol Myers Squibb and Takeda; travel support from Amgen and Bristol Myers Squibb), B.H. (institutional research funding to University Hospital Essen from Bristol Myers Squibb), K.D. (Fees for consulting from bess, Boehringer Ingelheim, Boston Scientific, Broncus Medical, FreeFlow, Fujifilm, Lys Medical, Medtronic, Morair Medtech, Olympus, Pulmonx and Storz; honoraria for CME presentations from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Boston Scientific, Broncus Medical, Erbe Elektromedizin, Olympus and Storz; institutional research funding to University Medicine Essen – Ruhrlandklinik from Ambu, Broncus Medical, Epigenomics, Gala Therapeutics, Novartis, Nuvaira, PneumRx, Pulmonx and Roche); H.H. (Honoraria for CME presentations from Urenco; travel support from Pari; institutional research funding to University Hospital Essen from Pari), H.R. (Honoraria for CME presentations from AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chop GmbH, Diaceutics, GSK, HUeG, Janssen-Cilag, MCI, Merck, Novartis, Roche Pharma, Sanofi and Wolfsburg Klinikum; institutional research funding from Bristol Myers Squibb), P.B. (Fees for consulting from AstraZeneca, Beigene, Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck Sharp & Dohme; honoraria from Bristol Myers Squibb, MSD; research funding to the Netherlands Cancer Institute from Bristol Myers Squibb; travel support from MSD; other relationship to Bristol Myers Squibb), A.S. (Institutional research funding to University Hospital Essen from Bristol Myers Squibb) and C.A. (Fees for consulting from Ewimed; honoraria for CME presentations from AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Roche; institutional research funding to University Hospital Essen Bristol Myers Squibb, and to University Medicine Essen – Ruhrlandklinik from PharmaCept). The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Comment in
-
Neoadjuvant dual immuno-combination therapy with anti-LAG3 and anti-PD-1 antibodies is feasible and safe for resectable non-small cell lung cancer.J Thorac Dis. 2025 Feb 28;17(2):528-530. doi: 10.21037/jtd-24-1789. Epub 2025 Feb 27. J Thorac Dis. 2025. PMID: 40083522 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Sung H, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021;71:209–249. - PubMed
-
- Reck M, Remon J, Hellmann MD. First-line immunotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022;40:586–597. - PubMed
-
- Tan AC, Tan DSW. Targeted therapies for lung cancer patients with oncogenic driver molecular alterations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022;40:611–625. - PubMed
-
- Tsuboi M, et al. Overall survival with osimertinib in resected EGFR-mutated NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023;389:137–147. - PubMed
-
- Solomon BJ, et al. LBA2 ALINA: efficacy and safety of adjuvant alectinib versus chemotherapy in patients with early-stage ALK+ non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) Ann. Oncol. 2023;34:S1295–S1296.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

