RNA-binding proteins and exoribonucleases modulating miRNA in cancer: the enemy within
- PMID: 38689093
- PMCID: PMC11148060
- DOI: 10.1038/s12276-024-01224-z
RNA-binding proteins and exoribonucleases modulating miRNA in cancer: the enemy within
Abstract
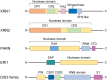
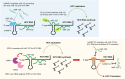
Recent progress in the investigation of microRNA (miRNA) biogenesis and the miRNA processing machinery has revealed previously unknown roles of posttranscriptional regulation in gene expression. The molecular mechanistic interplay between miRNAs and their regulatory factors, RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) and exoribonucleases, has been revealed to play a critical role in tumorigenesis. Moreover, recent studies have shown that the proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)-causing hepatitis C virus (HCV) is also characterized by close crosstalk of a multitude of host RBPs and exoribonucleases with miR-122 and its RNA genome, suggesting the importance of the mechanistic interplay among these factors during the proliferation of HCV. This review primarily aims to comprehensively describe the well-established roles and discuss the recently discovered understanding of miRNA regulators, RBPs and exoribonucleases, in relation to various cancers and the proliferation of a representative cancer-causing RNA virus, HCV. These have also opened the door to the emerging potential for treating cancers as well as HCV infection by targeting miRNAs or their respective cellular modulators.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Complex interactions between microRNAs and hepatitis B/C viruses.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Oct 7;20(37):13477-92. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i37.13477. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25309078 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interaction of host cell microRNAs with the HCV RNA genome during infection of liver cells.Semin Liver Dis. 2015 Feb;35(1):75-80. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1397351. Epub 2015 Jan 29. Semin Liver Dis. 2015. PMID: 25632937 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-mediated interactions between host and hepatitis C virus.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Jan 28;22(4):1487-96. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i4.1487. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 26819516 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting miRNAs to treat Hepatitis C Virus infections and liver pathology: Inhibiting the virus and altering the host.Pharmacol Res. 2013 Sep;75:48-59. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2013.03.004. Epub 2013 Mar 27. Pharmacol Res. 2013. PMID: 23541631 Review.
-
Hepatitis C Virus-Induced Exosomal MicroRNAs and Toll-Like Receptor 7 Polymorphism Regulate B-Cell Activating Factor.mBio. 2021 Dec 21;12(6):e0276421. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02764-21. Epub 2021 Nov 2. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34724826 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Identification of a novel survival and immune microenvironment related ceRNA regulatory network for hepatocellular carcinoma based on circHECTD1.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 27;10(13):e33763. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33763. eCollection 2024 Jul 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39040406 Free PMC article.
-
Regulating the expression of exercise-induced micro-RNAs and long non-coding RNAs: implications for controlling cardiovascular diseases and heart failure.Front Mol Biosci. 2025 May 20;12:1587124. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2025.1587124. eCollection 2025. Front Mol Biosci. 2025. PMID: 40463932 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unraveling the Role of the microRNA-Mediated Regulation of Actin-Binding Proteins in Ovarian Cancer: A Narrative Review.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Jul 11;17(14):2315. doi: 10.3390/cancers17142315. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40723199 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deciphering the roles of non-coding RNAs in liposarcoma development: Challenges and opportunities for translational therapeutic advances.Noncoding RNA Res. 2024 Nov 15;11:73-90. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2024.11.005. eCollection 2025 Apr. Noncoding RNA Res. 2024. PMID: 39736850 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Three Siblings With an Attenuated Presentation of Perlman Syndrome: A Case Report and Literature Review.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2025 Jul;13(7):e70124. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.70124. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2025. PMID: 40704758 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

