Overexpressed KCNK1 regulates potassium channels affecting molecular mechanisms and biological pathways in bladder cancer
- PMID: 38689322
- PMCID: PMC11059691
- DOI: 10.1186/s40001-024-01844-1
Overexpressed KCNK1 regulates potassium channels affecting molecular mechanisms and biological pathways in bladder cancer
Erratum in
-
Correction: Overexpressed KCNK1 regulates potassium channels affecting molecular mechanisms and biological pathways in bladder cancer.Eur J Med Res. 2024 Jun 20;29(1):342. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-01905-5. Eur J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 38902786 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to explore the expression, molecular mechanism and its biological function of potassium two pore domain channel subfamily K member 1 (KCNK1) in bladder cancer (BC).
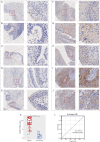
Methods: We integrated large numbers of external samples (n = 1486) to assess KCNK1 mRNA expression levels and collected in-house samples (n = 245) for immunohistochemistry (IHC) experiments to validate at the KCNK1 protein level. Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) analysis was performed to further assess KCNK1 expression and cellular communication. The transcriptional regulatory mechanisms of KCNK1 expression were explored by ChIP-seq, ATAC-seq and ChIA-PET data. Highly expressed co-expressed genes (HECEGs) of KCNK1 were used to explore potential signalling pathways. Furthermore, the immunoassay, clinical significance and molecular docking of KCNK1 were calculated.
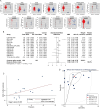
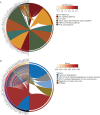
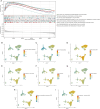
Results: KCNK1 mRNA was significantly overexpressed in BC (SMD = 0.58, 95% CI [0.05; 1.11]), validated at the protein level (p < 0.0001). Upregulated KCNK1 mRNA exhibited highly distinguishing ability between BC and control samples (AUC = 0.82 [0.78-0.85]). Further, scRNA-seq analysis revealed that KCNK1 expression was predominantly clustered in BC epithelial cells and tended to increase with cellular differentiation. BC epithelial cells were involved in cellular communication mainly through the MK signalling pathway. Secondly, the KCNK1 transcription start site (TSS) showed promoter-enhancer interactions in three-dimensional space, while being transcriptionally regulated by GRHL2 and FOXA1. Most of the KCNK1 HECEGs were enriched in cell cycle-related signalling pathways. KCNK1 was mainly involved in cellular metabolism-related pathways and regulated cell membrane potassium channel activity. KCNK1 expression was associated with the level of infiltration of various immune cells. Immunotherapy and chemotherapy (docetaxel, paclitaxel and vinblastine) were more effective in BC patients in the high KCNK1 expression group. KCNK1 expression correlated with age, pathology grade and pathologic_M in BC patients.
Conclusions: KCNK1 was significantly overexpressed in BC. A complex and sophisticated three-dimensional spatial transcriptional regulatory network existed in the KCNK1 TSS and promoted the upregulated of KCNK1 expression. The high expression of KCNK1 might be involved in the cell cycle, cellular metabolism, and tumour microenvironment through the regulation of potassium channels, and ultimately contributed to the deterioration of BC.
Keywords: Biological functions; Gene expression; KCNK1; Molecular mechanism; Potassium channel.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The upregulation and transcriptional regulatory mechanisms of Extra spindle pole bodies like 1 in bladder cancer: An immunohistochemistry and high-throughput screening Evaluation.Heliyon. 2024 May 15;10(10):e31192. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31192. eCollection 2024 May 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38813236 Free PMC article.
-
The two-pore domain potassium channel, TWIK-1, has a role in the regulation of heart rate and atrial size.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2016 Aug;97:24-35. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2016.04.006. Epub 2016 Apr 19. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2016. PMID: 27103460
-
KCNK1 promotes proliferation and metastasis of breast cancer cells by activating lactate dehydrogenase A (LDHA) and up-regulating H3K18 lactylation.PLoS Biol. 2024 Jun 21;22(6):e3002666. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002666. eCollection 2024 Jun. PLoS Biol. 2024. PMID: 38905316 Free PMC article.
-
Complexity, retinoid-responsive gene networks, and bladder carcinogenesis.Adv Exp Med Biol. 1999;462:449-67. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-4737-2_35. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1999. PMID: 10599447 Review.
-
Involvement of potassium channels in the progression of cancer to a more malignant phenotype.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Oct;1848(10 Pt B):2477-92. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2014.12.008. Epub 2014 Dec 14. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25517985 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the potential function of high expression of ANAPC1 in regulating ubiquitination in hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2025 May 15;17(5):103594. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i5.103594. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40487972 Free PMC article.
-
Lactate-associated gene MCU promotes the proliferation, migration, and invasion of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2025 May 21;25(1):913. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-14319-1. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40399795 Free PMC article.
-
Correction: Overexpressed KCNK1 regulates potassium channels affecting molecular mechanisms and biological pathways in bladder cancer.Eur J Med Res. 2024 Jun 20;29(1):342. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-01905-5. Eur J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 38902786 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Homeobox C6 plays an oncogenic role in bladder cancer.World J Clin Oncol. 2025 May 24;16(5):103830. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v16.i5.103830. World J Clin Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40503400 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2022JGA146/Guangxi Higher Education Undergraduate Teaching Reform Project
- 2022ZJY2791/Guangxi Educational Science Planning Key Project
- 2023Z10/Guangxi Medical University Undergraduate Education and Teaching Reform Project
- Z-A20230519/Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region Health Commission Scientific Research Project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

