Mycophenolate-induced colitis in a patient with lupus nephritis: a case report and review of the literature
- PMID: 38689344
- PMCID: PMC11061913
- DOI: 10.1186/s13256-024-04539-7
Mycophenolate-induced colitis in a patient with lupus nephritis: a case report and review of the literature
Abstract
Background: Mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) is an immunosuppressive drug that is frequently prescribed to patients with rheumatological diseases. MMF's side effects include abdominal discomfort, nausea, vomiting, and other gastro-intestinal side effects, which typically appear in the first few months of treatment. However, late-onset diarrhea does not rule out the presence of MMF-induced colitis, which can be misdiagnosed since it is linked to a broad range of histopathological characteristics, including alterations that resemble inflammatory bowel disease, graft-versus-host disease, and ischemia. The differences in treatment response may be explained by the complexity of the histopathologic characteristics.
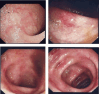
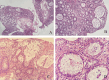
Case presentation: Here we present a case of a 29-year-old Arabian female with lupus nephritis who started on MMF as induction therapy. In two months, the patient was presented to the Emergency Department with diarrhea and manifestations of severe dehydration. Infectious diseases and adverse drug events were suspected, so the patient was admitted for further workup, and MMF was stopped. The patient was diagnosed with MMF-induced colitis based on colonoscopy and histological findings. Fourteen days after stopping MMF, she was within her baseline.
Conclusion: The purpose of this paper is to report a case of early-onset MMF-induced colitis in a patient with lupus nephritis who had started MMF as induction therapy. A review of the available literature on this uncommon immunosuppressive effect is also presented.
Keywords: Case report; Colitis; MMF; Mycophenolate mofetil.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Allison AC, Eugui EM. Purine metabolism and immunosuppressive effects of mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) Clin Transplant. 1996;10(1 Pt 2):77–84. - PubMed
-
- Tierce JC, Porterfield-Baxa J, Petrilla AA, Kilburg A, Ferguson RM. Impact of mycophenolate mofetil (MMF)-related gastrointestinal complications and MMF dose alterations on transplant outcomes and healthcare costs in renal transplant recipients. Clin Transplant. 2005;19(6):779–784. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0012.2005.00421.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

