Application of artificial intelligence in hypertension
- PMID: 38689376
- PMCID: PMC11061896
- DOI: 10.1186/s40885-024-00266-9
Application of artificial intelligence in hypertension
Abstract
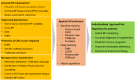
Hypertension is an important modifiable risk factor for morbidity and mortality associated with cardiovascular disease. The incidence of hypertension is increasing not only in Korea but also in many Western countries due to the aging of the population and the increase in unhealthy lifestyles. However, hypertension control rates remain low due to poor adherence to antihypertensive medications, low awareness of hypertension, and numerous factors that contribute to hypertension, including diet, environment, lifestyle, obesity, and genetics. Because artificial intelligence (AI) involves data-driven algorithms, AI is an asset to understanding chronic diseases that are influenced by multiple factors, such as hypertension. Although several hypertension studies using AI have been published recently, most are exploratory descriptive studies that are often difficult for clinicians to understand and have little clinical relevance. This review aims to provide a clinician-centered perspective on AI by showing recent studies on the relevance of AI for patients with hypertension. The review is organized into sections on blood pressure measurement and hypertension diagnosis, prognosis, and management.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Disease management; Hypertension; Machine learning.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Jae-Hyeong Park serves on the editorial boards as a deputy editor in the Clinical Hypertension. Jung Sun Cho has no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Whelton PK, Carey RM, Aronow WS, Casey DE Jr., Collins KJ, Dennison Himmelfarb C, DePalma SM, Gidding S, Jamerson KA, Jones DW, MacLaughlin EJ, Muntner P, Ovbiagele B, Smith SC Jr., Spencer CC, Stafford RS, Taler SJ, Thomas RJ, Williams KA, Sr., Williamson JD, Wright JT Jr, 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA Guideline for the prevention, detection, evaluation, and management of high blood pressure in adults: executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice guidelines. Hypertension. 2018;71:1269–324. - PubMed
-
- Williams B, Mancia G, Spiering W, Agabiti Rosei E, Azizi M, Burnier M, Clement DL, Coca A, de Simone G, Dominiczak A, Kahan T, Mahfoud F, Redon J, Ruilope L, Zanchetti A, Kerins M, Kjeldsen SE, Kreutz R, Laurent S, Lip GYH, McManus R, Narkiewicz K, Ruschitzka F, Schmieder RE, Shlyakhto E, Tsioufis C, Aboyans V, Desormais I. 2018 ESC/ESH guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: the Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology and the European Society of Hypertension: the Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology and the European Society of Hypertension. J Hypertens. 2018;36:1953–2041. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000001940. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
