Gene regulatory network analysis identifies MYL1, MDH2, GLS, and TRIM28 as the principal proteins in the response of mesenchymal stem cells to Mg2+ ions
- PMID: 38689715
- PMCID: PMC11058716
- DOI: 10.1016/j.csbj.2024.04.033
Gene regulatory network analysis identifies MYL1, MDH2, GLS, and TRIM28 as the principal proteins in the response of mesenchymal stem cells to Mg2+ ions
Abstract
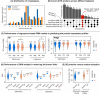
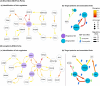
Magnesium (Mg)-based implants have emerged as a promising alternative for orthopedic applications, owing to their bioactive properties and biodegradability. As the implants degrade, Mg2+ ions are released, influencing all surrounding cell types, especially mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). MSCs are vital for bone tissue regeneration, therefore, it is essential to understand their molecular response to Mg2+ ions in order to maximize the potential of Mg-based biomaterials. In this study, we conducted a gene regulatory network (GRN) analysis to examine the molecular responses of MSCs to Mg2+ ions. We used time-series proteomics data collected at 11 time points across a 21-day period for the GRN construction. We studied the impact of Mg2+ ions on the resulting networks and identified the key proteins and protein interactions affected by the application of Mg2+ ions. Our analysis highlights MYL1, MDH2, GLS, and TRIM28 as the primary targets of Mg2+ ions in the response of MSCs during 1-21 days phase. Our results also identify MDH2-MYL1, MDH2-RPS26, TRIM28-AK1, TRIM28-SOD2, and GLS-AK1 as the critical protein relationships affected by Mg2+ ions. By offering a comprehensive understanding of the regulatory role of Mg2+ ions on MSCs, our study contributes valuable insights into the molecular response of MSCs to Mg-based materials, thereby facilitating the development of innovative therapeutic strategies for orthopedic applications.
Keywords: Gene regulatory network analysis; Magnesium ions; Mesenchymal stem cells; Proteomics.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Insights into the Role of Magnesium Ions in Affecting Osteogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2021 Feb;199(2):559-567. doi: 10.1007/s12011-020-02183-y. Epub 2020 May 24. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2021. PMID: 32449009 Review.
-
Different Sources of Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Tissue Regeneration: A Guide to Identifying the Most Favorable One in Orthopedics and Dentistry Applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 6;23(11):6356. doi: 10.3390/ijms23116356. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35683035 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The relative effects of Ca and Mg ions on MSC osteogenesis in the surface modification of microrough Ti implants.Int J Nanomedicine. 2019 Jul 23;14:5697-5711. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S214363. eCollection 2019. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019. PMID: 31413570 Free PMC article.
-
A Comparative In Vitro and In Vivo Study of Osteogenicity by Using Two Biomaterials and Two Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell Subtypes.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 May 30;10:913539. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.913539. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35712655 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping of equine mesenchymal stromal cell surface proteomes for identification of specific markers using proteomics and gene expression analysis: an in vitro cross-sectional study.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018 Oct 25;9(1):288. doi: 10.1186/s13287-018-1041-8. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018. PMID: 30359315 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A first-in-human, prospective pilot trial of umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell eye drops therapy for patients with refractory non-Sjögren's and Sjögren's syndrome dry eye disease.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025 Apr 23;16(1):202. doi: 10.1186/s13287-025-04292-8. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 40269970 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Willumeit-Römer R. The interface between degradable mg and tissue. Jom. 2019;vol. 71(4):1447–1455. doi: 10.1007/s11837-019-03368-0. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
